Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
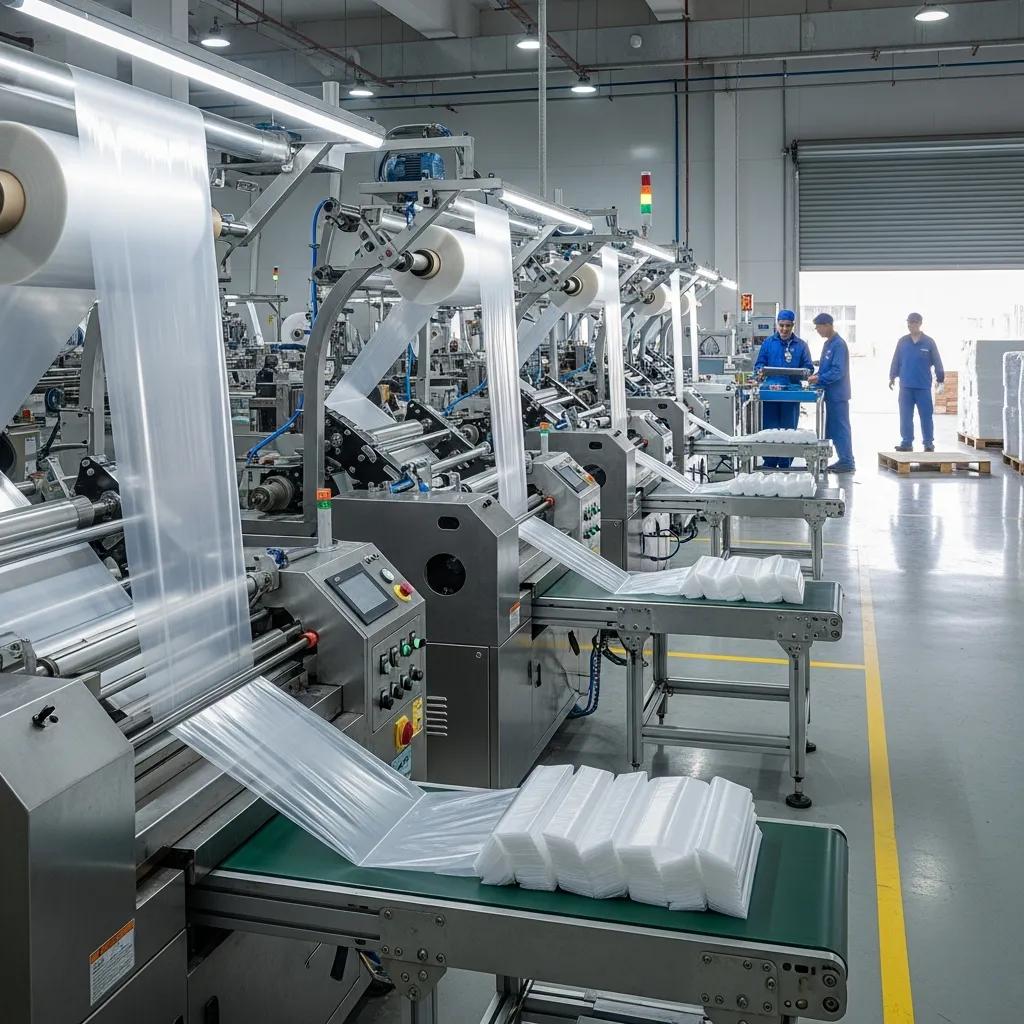

Selecting the right bag-making machine—whether a side sealing machine or a bottom sealing machine—directly affects product strength, production cost, and design flexibility. This guide explains how each machine type forms seals, which bag formats they produce, and the trade-offs in speed, material use, and downstream finishing such as printing and gusseting. Readers will learn how sealing geometry, film compatibility (LDPE, LLDPE, HDPE), and production volumes inform the optimal choice for retail, courier, waste management, or industrial packaging. The article maps core differences, practical decision criteria for choosing side or bottom sealing equipment, complementary technologies that improve throughput and branding, and when to consult an experienced manufacturer. By the end you will understand operational mechanisms, performance benchmarks, material recommendations, and how to align machine selection with product goals and cost targets.
Side sealing and bottom sealing machines are two families of plastic bag making machinery that differ by where the heat seals are formed on the film web, and each yields distinct bag geometries and performance characteristics. A side sealing machine applies longitudinal seals along the film edges to create side seams while cutting forms the bag bottom, producing items like retail or courier bags. In contrast, a bottom sealing machine creates a continuous transverse bottom seal that becomes the base of the bag, producing stronger single-seam bags suited for heavy or filled loads. These mechanical differences affect seal integrity, material handling, and suitability for gussets or handles. Understanding the basic mechanics clarifies which industries and bag formats are best matched to each machine family.
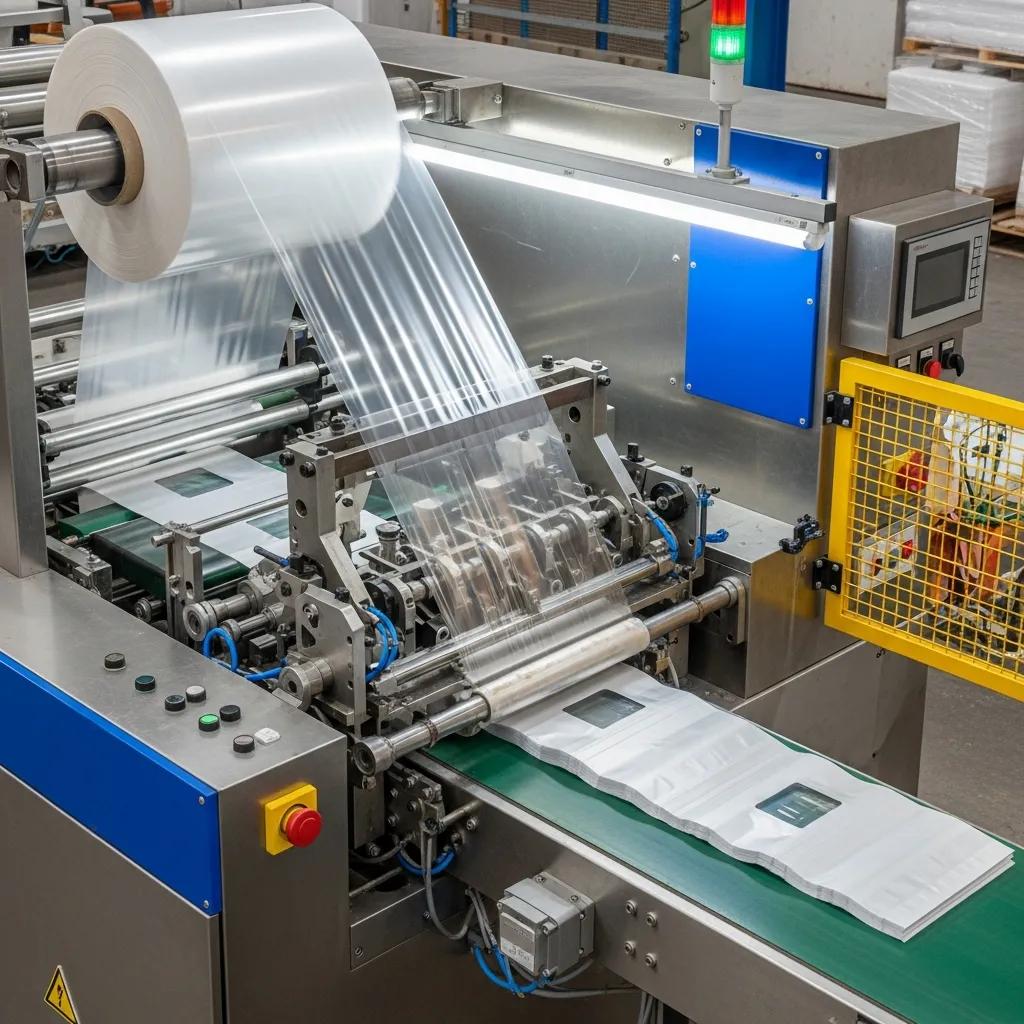

Side sealing machines feed tubular or flat film through a film feeding system where sealing heads create longitudinal seams at the sides while a cutting knife separates individual bags. The process typically involves film tension control, synchronized sealing and cutting motions, and a film winding unit or bag take-off. Common outputs include retail shopping bags, t-shirt bags with handles (when combined with punch or handle modules), courier bags, and printed retail bags where registration is important. Side seal equipment is usually compatible with LDPE and LLDPE films and supports thinner gauges that favor high-speed, high-variation production. This mechanism makes side sealing ideal for manufacturers prioritizing varied designs and printing registration.
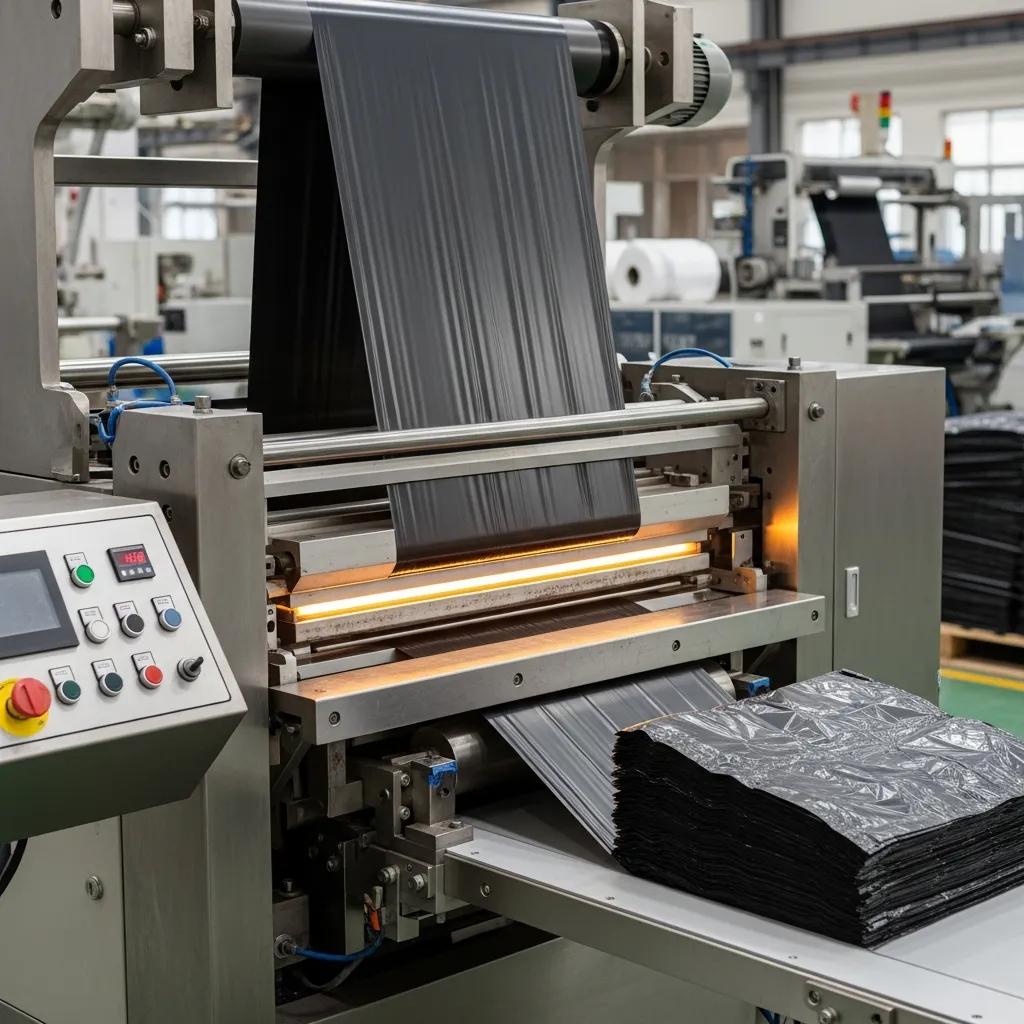

Bottom sealing machines form a transverse seal across a film tube or layflat film to create a single, robust base seam and then cut to separate bags, often with continuous feeding and sealed bottom formation. Tension control, a heated bottom plate or roller, and precise temperature regulation are core to creating leak-resistant seals suitable for heavy-duty films.
Typical outputs are garbage bags, industrial liners, agricultural sacks, and heavy-duty packaging that require reinforced bottoms and high load-bearing capacity. Bottom sealing machines handle thicker films and are compatible with gusseting options and reinforced bottom designs for granular or liquid products. The continuous bottom seal approach favors bulk production where durability and leakage prevention are primary objectives.
Bottom sealing distributes load across a single, continuous base seam, which often results in higher resistance to tearing and leakage under heavy loads. This mechanism produces a single robust weld that reduces the number of seam failure points and is therefore preferred for waste management and industrial liners where puncture and load-bearing are critical. Side sealing creates two longitudinal seams that can be points of weakness when carrying heavy or irregular loads, so material thickness and seal quality must be optimized to avoid seam failure. Film selection—gauge, polymer type, and additives—directly influences seal integrity; thicker LDPE or HDPE blends improve strength for either machine type. Understanding these dynamics helps match seal geometry to product weight and leak-resistance requirements.
These differences indicate that bottom sealing is generally superior for heavy-duty applications, while side sealing is preferred for varied bag formats and printed retail use.
Intro to comparison table: The table below compactly compares sealing characteristics, common failure modes, and typical suitability for each machine family.
| Attribute | Side Seal Machine | Bottom Seal Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing type | Two longitudinal side seams | Single transverse bottom seam |
| Typical failure points | Seam separation at sides under heavy load | Bottom seam stress if improperly welded |
| Suitability | Retail, printed bags, light-to-medium loads | Garbage bags, industrial liners, heavy loads |
Intro to speed/cost table: Production speed and material usage determine cost-per-bag; the table below estimates typical throughput and cost drivers to guide machine choice.
| Performance Metric | Side Seal Machine | Bottom Seal Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Typical throughput (bags/min) | Higher for thin-film, high-variation runs | Optimized for moderate speed, heavy films |
| Material usage | Efficient for narrow-width printed film | Economies of scale with wider layflat film |
| Cost drivers | Printing registration, frequent changeovers | Film thickness and weld robustness |
These performance comparisons show that side seal machines generally support higher variety and faster cycles for lightweight bags, while bottom seal machines achieve cost-effectiveness in large-volume heavy-duty production.
Side sealing machines are the right choice when flexibility, printing registration, and varied bag shapes are primary objectives, and when the intended bags carry light-to-moderate loads. Side-seal equipment supports rapid format changes, accurate flexo printing alignment, and the production of specialized retail items such as promotional or branded shopping bags. When production requires frequent design updates or multiple SKUs, side sealing minimizes downtime for tooling changes and supports on-demand runs. If seals will not be load-bearing structural elements—such as lightweight retail, courier, or produce bags—side sealing balances finish quality with throughput.
Side sealing is particularly effective where bag shape and surface graphics matter more than extreme load-bearing capacity. Retail and promotional bags benefit from clean side seams that present branding effectively, while courier and lightweight packaging prioritize cost-per-bag and fast changeovers. Side seal machines also integrate well with flexo printing equipment for one- or multi-color branding, and they are compatible with thinner LDPE and LLDPE films that keep material costs down. When production runs are shorter and frequent format changes are required, side sealing enables agile manufacturing without sacrificing print quality. These factors make side sealing the preferred option for consumer-facing bag lines.
Side sealing machines deliver versatility, high-quality finishes, and strong printing registration, but they have limitations when it comes to heavy loads and extreme leak-resistance requirements. Advantages include simplified tooling for varied bag sizes, compatibility with flexo printing, and efficient material usage for narrow-width films. Limitations include potential seam weakness under heavy loads and a greater need for strict quality control to prevent seam defects. Operational considerations include operator training for temperature and pressure settings, routine maintenance of sealing heads and cutting knives, and careful specification of film gauge and polymer blends to match end-use demands.
Bottom sealing machines are the better choice when durability, leak resistance, and cost-per-bag at scale are top priorities—especially for garbage bags, industrial liners, and agricultural sacks. The bottom seal design creates a single, reinforced seam that spreads stress across the base rather than concentrating it at side welds, making it ideal for filled or heavy materials. For manufacturers focusing on long production runs with consistent formats and thicker film usage, bottom sealing yields better economies of scale and simplified quality assurance for base weld strength. If the application involves liquids, granular materials, or heavy loads, bottom sealing typically delivers superior performance.
Bottom sealing excels in waste management, industrial packaging, and agricultural contexts where robustness matters. Common examples include garbage bags designed to resist tearing when handling sharp or heavy refuse, liners for drums and containers that must prevent leakage, and agricultural sacks for seeds or fertilizer that require reinforced bottoms. Recommended film thickness ranges for these uses tend toward higher microns and may include HDPE or reinforced LDPE blends to increase puncture resistance. Reinforcement options like thicker weld widths or folded bottoms further enhance durability for extreme applications.
Strengths of bottom sealing machines include a single, strong base seam that improves load handling and leak prevention, and cost advantages on large, consistent runs due to efficient material layouts. Constraints include less flexibility for complex bag shapes, potentially higher tooling costs for specialty forms, and the need for precise temperature and pressure control to ensure weld quality with thick films. Operational notes include robust film handling systems, attention to sealing head wear, and planning for minimal format variation to exploit cost efficiencies. For buyers prioritizing durability and scale, bottom sealing machines often deliver the best lifecycle cost.
Blown film extrusion, flexo printing, and recycling equipment form an upstream and downstream ecosystem that amplifies the capabilities of side and bottom sealing machines. Blown film control over width, layflat, and gauge determines what bag formats are possible and how efficient material usage will be. Flexo printing integrates with bag machines to add branding and regulatory information, and on-site recycling reduces material costs and enables recycled-content bags. Efficient workflows synchronize extrusion output, printing registration, and bag-making throughput to minimize waste and maximize uptime across the production line.
Blown film extrusion produces the base film used by bag machines and directly affects film thickness (microns), layflat width, and material properties, which in turn determine sealability and bag strength. Matching film output—width and gauge—to the bag machine reduces waste and improves cost-per-bag; for example, wider layflat film suits bottom sealing where full-width base seams are efficient, while narrower layflat film can be ideal for side-seal retail bags. Co-extrusion options allow multilayer films for enhanced mechanical properties or biodegradable blends, and precise gauge control helps ensure consistent weld quality on both side and bottom sealing equipment. Synchronizing film production with bag-making schedules reduces changeovers and scrap.
Intro to EAV table on film vs compatibility: The table below connects blown film outputs to downstream bag machine compatibility.
| Film Feature | Attribute | Value / Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | Micron range | Thin (15–30 µm) for retail; Thick (50–150+ µm) for heavy-duty |
| Layflat width | Compatibility | Narrow widths for side-seal; wide layflat for bottom-seal economies |
| Layering | Function | Co-extrusion adds strength, barrier, or recyclability |
Flexo printing integrates branding, regulatory text, and design features directly onto film before or after bag formation, increasing perceived value and meeting compliance needs. Registration accuracy and machine synchronization are crucial, especially for side sealing where print alignment with cut and seal positions affects final appearance. Ink selection and drying/curing methods must suit the polymer substrate to prevent smudging or print defects during subsequent sealing operations. Effective pre-press preparation and collaboration between printing and bag-making teams reduce misprints and material waste while enabling multi-color branding that differentiates products in retail channels.
Intro to recycling table: Integrating recycling machinery on-site supports circular production and reduces raw-material expenses; the table below outlines typical recycling outputs and their application.
| Recycling Function | Attribute | Value / Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Granulation | Output | Regrind from trimmings for reprocessing |
| Pelletizing | Use | Recycled pellets blended into extrusion feed |
| On-site reprocessing | Impact | Lowers material cost; enables recycled-content bags |
After explaining these technologies, manufacturers can evaluate combined investments in extrusion, printing, and recycling to optimize cost-per-bag and product differentiation. Plastic Bag Machine South Africa offers complementary equipment such as blown film extrusion, flexo printing, and recycling machines and can advise on integrated workflows and service support.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa operates as a manufacturer and supplier focused on lead generation and offers a comprehensive range of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment relevant to both side seal and bottom seal production lines. The company’s stated strengths include quality assurance procedures—100% final inspection with a reported defective rate of 1%–3%—and a two-year warranty on timer switches for certain controls, which can reduce risk for buyers. Their capabilities span blown film machines, plastic bag making machines, flexo and gravure printing machines, stretch film systems, and recycling units that support end-to-end production strategies.
Quality assurance practices emphasize final inspection of finished equipment and functionality, and the company reports a defective product rate between 1% and 3%, which buyers should account for when validating acceptance criteria. The two-year warranty on timer switches is an explicit coverage detail that can reduce maintenance exposure for electronic timing components. Prospective purchasers should request documentation of inspection protocols and warranty terms during procurement to ensure alignment with their quality-control standards. These manufacturer commitments can be especially valuable when integrating multiple technologies into a single production line.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa promotes one-stop and customized solutions, backed by a strong R&D team that supports design adaptations and bespoke configurations across blown film, bag-making, and printing lines. This end-to-end approach enables coordinated design choices—such as matching extrusion layflat width to bag machine format or calibrating printing registration for side seal output—that reduce integration friction. The company also notes 24-hour online customer support to assist with technical queries and commissioning, and buyers should discuss installation, operator training, and spare parts strategies as part of the procurement process to secure long-term uptime.
Competitive pricing is attributed to manufacturing scale—16 production lines and more than 30 testing pieces of equipment—along with efficient labour deployment that the company cites as contributing factors, which may translate into lower capital costs for buyers. Delivery timelines stated include sample delivery within three days and bulk orders in 15–20 days, providing predictable lead times for project planning. Global installation experience—more than 1700 machines installed across 102 countries—supports claims of cross-market deployment and practical commissioning knowledge. When evaluating suppliers, request validation of stated lead times and installation references that match the intended machine configuration.
This supplier information helps manufacturers balance technical requirements with procurement risk and delivery planning.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on being a leading manufacturer of plastic bag making machines. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that our customers receive the best machinery tailored to their specific production needs. By choosing us, you are partnering with a company that has established itself as a trusted name in the industry.
Our extensive range of plastic bag machinery includes options for various applications, from shopping bags to biodegradable solutions. We understand the importance of efficiency and reliability in production, which is why our machines are designed for optimal performance, ensuring your business can meet market demands effectively.
Our plastic bag machines are engineered to provide numerous advantages, including ease of operation, low maintenance costs, and high productivity rates. These features make them ideal for businesses looking to enhance their manufacturing processes while keeping operational costs low.
Additionally, our machines are equipped with advanced technology that ensures consistent quality in production. With energy-efficient designs and robust construction, our equipment not only meets but exceeds industry standards, providing you with a competitive edge in the market.
We have had the pleasure of serving over 1000 satisfied customers across various regions, each with unique needs and challenges. Our commitment to customer satisfaction is reflected in the positive feedback we receive, showcasing the effectiveness of our machines in real-world applications.
From small start-ups to large manufacturing plants, our clients have successfully integrated our machinery into their operations, leading to increased productivity and profitability. These success stories underscore our dedication to providing tailored solutions that foster growth and innovation.
As a forward-thinking manufacturer, we continuously invest in research and development to bring the latest innovations to our plastic bag machines. This commitment allows us to offer cutting-edge technology that enhances production efficiency and reduces waste.
Our innovations include features such as automated controls, real-time monitoring systems, and environmentally friendly production processes. By adopting these advancements, our clients can not only improve their operational efficiency but also align with global sustainability goals.