Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
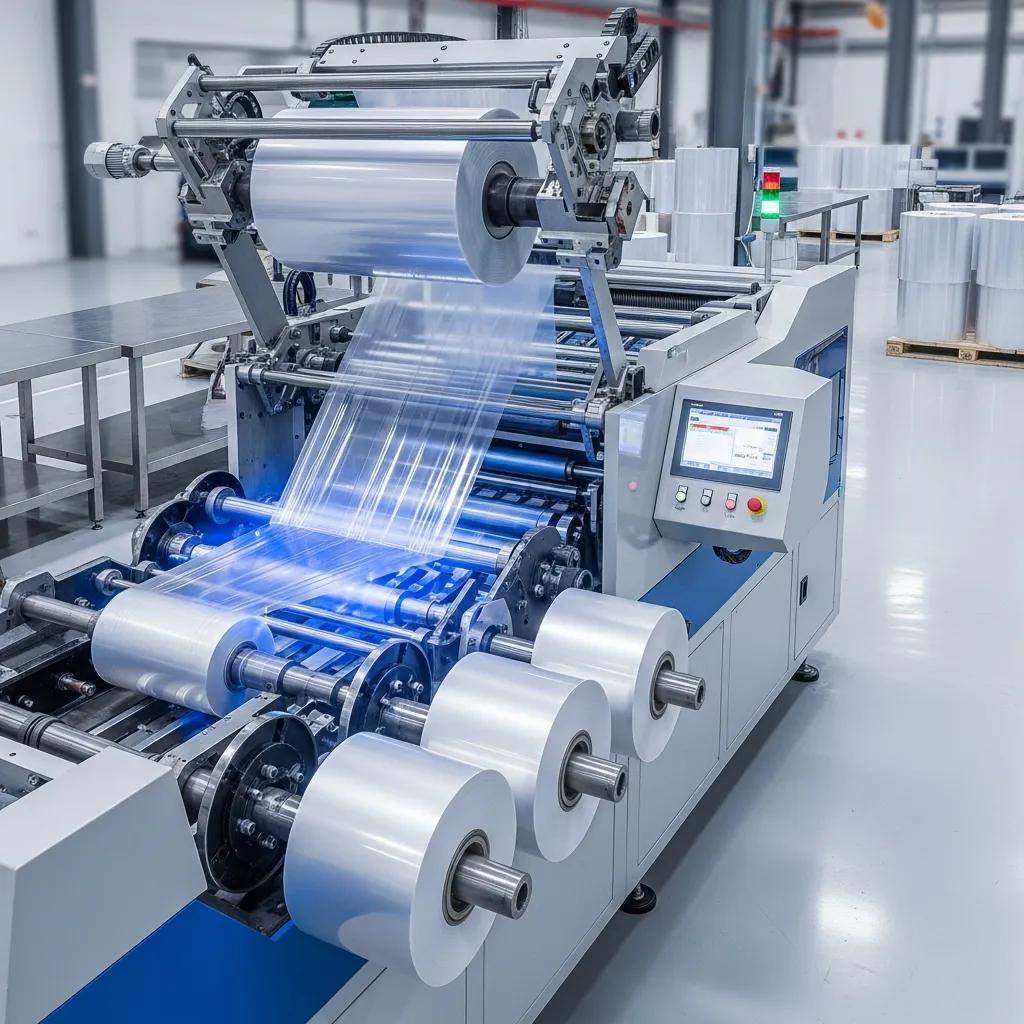

Film slitting machines convert wide parent rolls of plastic film into precise narrower rolls for downstream converting and packaging, enabling manufacturers to meet exact width, edge quality, and rewind specifications. This article explains how film slitting machines — often called slitter rewinders or slitting lines — deliver precision plastic film cutting, reduce waste, and raise throughput for Rustenburg producers of flexible packaging and plastic bags. Readers will learn how slitting machines work (unwind → slit → rewind), which machine types suit BOPP, PET, LDPE and laminated films, key features to prioritise, and practical integration with extrusion and bag-making workflows. The guidance emphasises local industrial use-cases in Rustenburg, comparisons of machine classes, expected automation capabilities, and how suppliers support buyers with inspection, warranty and after-sales service. Throughout we weave actionable buying criteria, technical terms such as tension control system and touchscreen PLC control, and clear steps for matching a slitter rewinder to production goals.
Film slitting machines are industrial converting systems that cut a wide roll of plastic film into multiple narrower rolls with controlled edges, consistent diameter and repeatable tension. They work by unwinding the parent roll, guiding the web through a slit station using rotary knives or razor modules, then rewinding slit webs onto cores with automatic tension control; this process increases yield and delivers customer-ready roll widths. For Rustenburg manufacturers, slitting reduces scrap, improves sealing and printing quality downstream, and enables multiple SKUs from a single extrusion run. The following list summarises core business benefits manufacturers can expect when they adopt modern slitting technology.
These benefits lead directly into how slitting machines operate in a converting workflow and why blade choice and tension matter to final product quality.
Film slitting equipment follows a defined workflow: unwind the parent roll, stabilise the web with web guides and tension control, perform slitting with blades or rotary cutters, then rewind slit rolls with controlled winding force. The mechanism relies on components such as a razor blade holder or rotary knife module, a tension control system, and a rewind station driven by servo motors and monitored by a touchscreen PLC control. Choice of slitting method depends on film type: razor slitting often suits thin, delicate films while rotary knives handle thicker laminates and PET. Efficient slitting also requires correct core handling and corona or anti-static measures to prevent edge defects and ensure printing registration for downstream flexo printers.
Careful selection of blade geometry and adjustment of web tension reduces edge fray and roll telescoping, which preserves material and lowers rejects. This mechanical overview leads into which local industries in Rustenburg rely most on slitting technology.
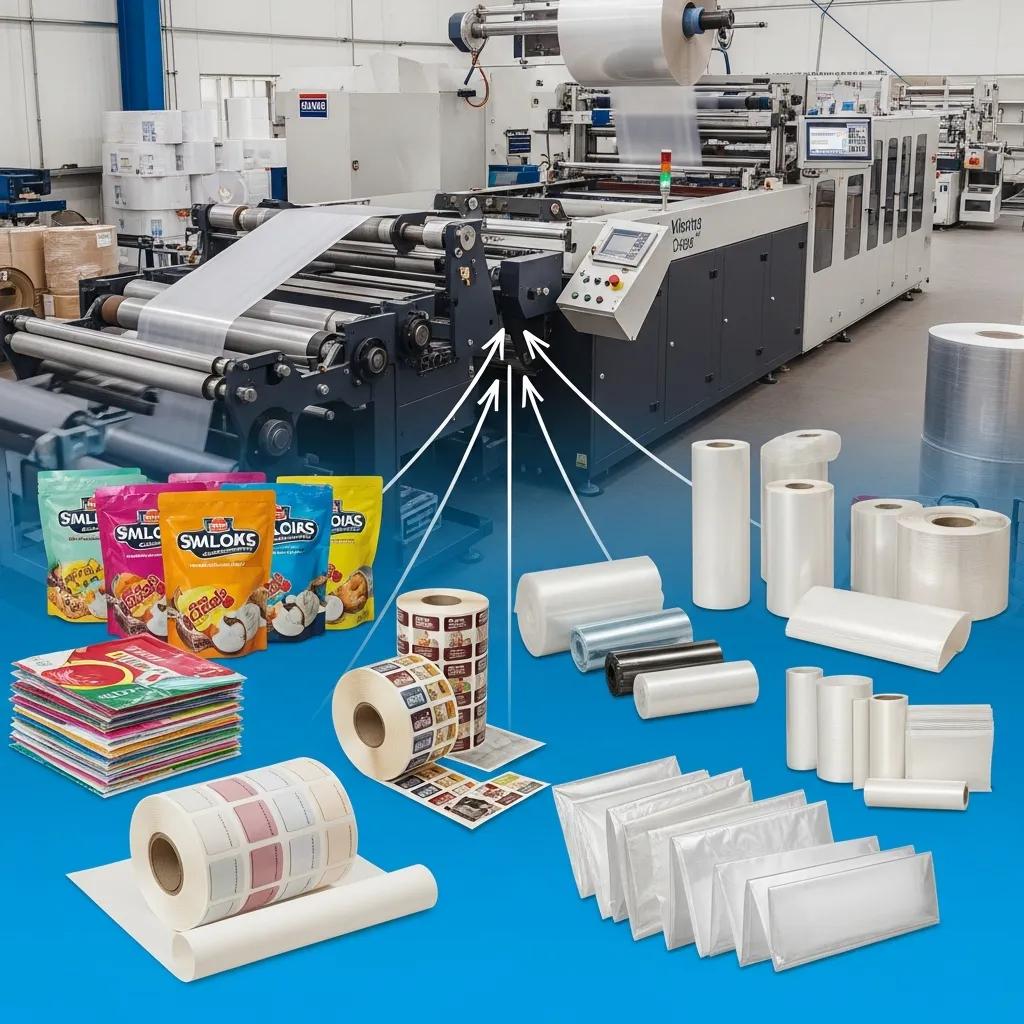

Multiple Rustenburg sectors depend on slitting to convert extrusion outputs into saleable rolls and substrates, with each industry requiring particular tolerances and materials. Flexible packaging converters use slitting to supply printed and laminated films for snack, retail and industrial packaging; plastic bag makers rely on slit LDPE or HDPE rolls to feed bag-making machines; labels and narrow-web converters use BOPP and PET slit to precise widths for high-speed applicators. Agricultural film producers and construction-sheet processors also slit wide rolls into transportable lengths and specific widths.
Typical production outputs vary by application — labels often need tight tolerances within ±0.5 mm, while commodity bag producers accept wider tolerances but higher throughput. Understanding these differences helps buyers select the correct slitter rewinder configuration for their Rustenburg operation.
Film slitting machines come in classes defined by automation level, material compatibility and intended application, from manual slitters to fully automatic slitter rewinders with center winding and servo controls. Buyers should prioritise the automation level that matches production targets: manual machines suit small runs, semi-automatic models balance flexibility and efficiency, and fully automatic lines deliver the highest uptime and repeatability. Below is a concise enumerated list of common machine types and short descriptors to help Rustenburg businesses identify which class fits their needs.
When comparing classes, an EAV table clarifies typical width, speed, automation and material compatibility to support selection.
Different machine tiers support a range of materials and speeds; many suppliers also pair slitting with upstream equipment like blown film extrusion and downstream bag making to create an end-to-end converting line. This practical linkage helps Rustenburg plants convert parent rolls into finished bags or printed webs efficiently.
Intro to comparison table: The table below helps compare representative machine classes by key purchasing attributes so converters can match capabilities to production goals.
| Machine Type | Max Web Width | Typical Max Speed | Automation Level | Compatible Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| manual Slitter | 1600 mm | 200 m/min | manual/semi | LDPE, CPP |
| Semi-Automatic Slitter Rewinder | 1600–2000 mm | 300–400 m/min | Semi-automatic | BOPP, LDPE, CPP |
| Automatic Slitter Rewinder | 2000 mm+ | 400–500 m/min | Fully automatic | BOPP, PET, laminated films |
| Center Winding Slitter | 1600–2200 mm | 300–450 m/min | Automatic | Thin films, metalized films |
This comparison highlights how automation and width affect throughput and material range, guiding buyers toward the machine class most aligned with their Rustenburg facility needs.
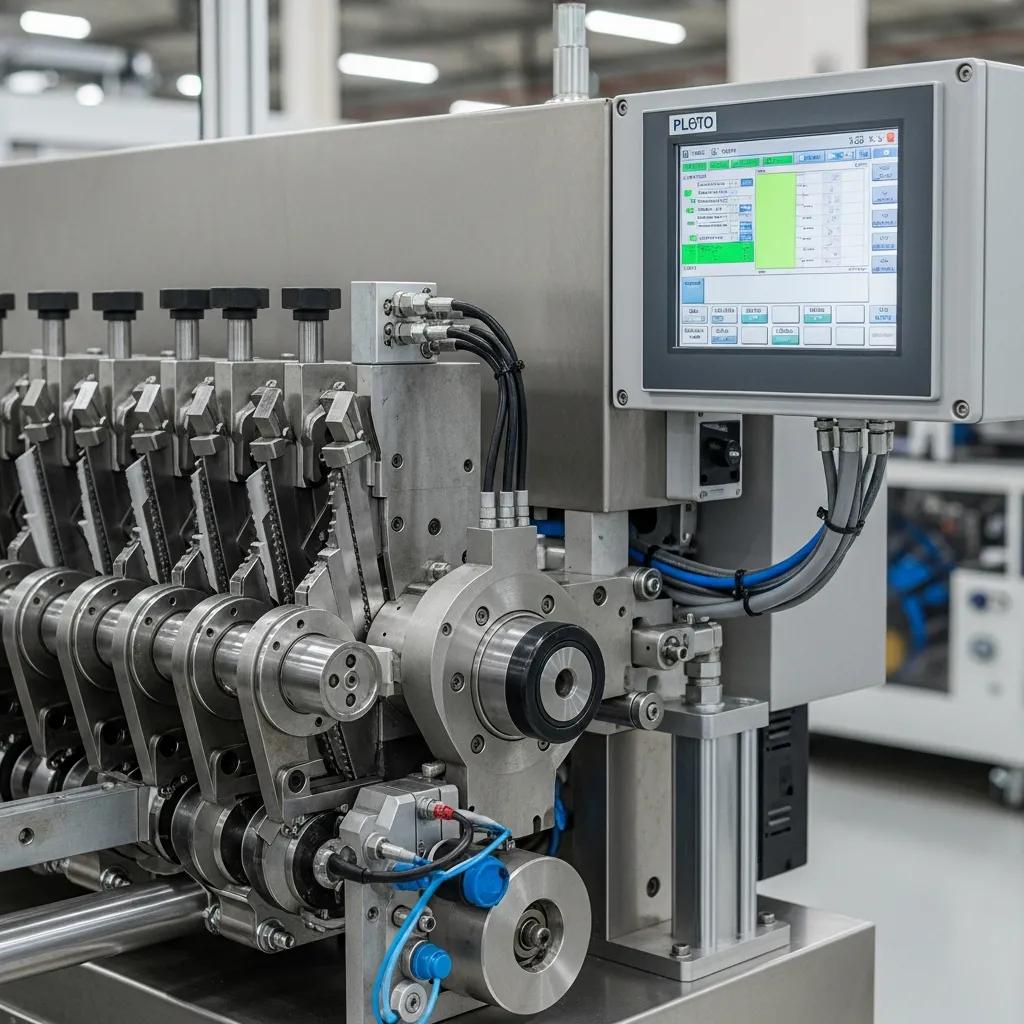

BOPP slitting requires blade systems and web handling measures that deliver clean edges, minimal burr and stable web tension to protect print and lamination integrity. Key features include precise rotary knife modules or razor holders, air shafts for quick roll changes, anti-static devices, and corona treatment compatibility for downstream printing. Control systems commonly use a touchscreen PLC control that stores slitting recipes, enabling repeatable setups for different film grades and widths.
Operators should prioritise systems that mitigate static and neck-in, and select blade geometries that reduce fibre pull on BOPP. Recommended spec ranges for high-quality BOPP slitting typically favour stable speeds with automatic tension control to maintain ±0.5–1 mm edge tolerances and ensure consistent lamination and printing compatibility. These equipment features transition into how automatic slitter rewinders boost industrial slitting performance.
Automatic slitter rewinders reduce manual intervention and standardise production by combining automatic tension control, recipe recall and rapid job changeovers into one system. Automatic core handling, servo-driven process control, and electronic dancer or load-cell based tension systems cut changeover times and lessen operator error, improving overall equipment effectiveness. Quantifiable benefits include reduced downtime during bobbin changes, lower scrap rates through repeatable tension settings, and higher effective line speed due to fewer manual adjustments.
Automatic features such as auto knife positioning and roll diameter compensation increase throughput and free skilled operators for higher-value tasks. These operational improvements lead into the technical features and technologies buyers should prioritise when specifying a slitter rewinder.
Industrial slitter rewinders combine precision mechanical components and modern control electronics — precision tension control, advanced knife technology, and efficient winding methods are core elements that drive performance. Precision tension control reduces scrap and ensures consistent roll build; knife systems (rotary and razor) determine edge quality while winding strategies like center or surface winding influence roll stability. PLC/HMI controls and touchscreen PLC control enable recipe management and remote diagnostics, while safety features protect operators and preserve uptime.
Intro to features table: The table maps core slitter rewinder features to their operational impact to help quantify potential savings and performance gains.
| Feature | Benefit | Operational Impact / ROI |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic Tension Control | Reduced stretch and scrap | Lower material waste, faster setup → improved yield |
| Rotary Knife Module | Clean cuts on thicker films | Fewer rejects on PET/laminates → lower rework costs |
| Touchscreen PLC Control | Recipe recall and diagnostics | Shorter changeovers and remote troubleshooting |
| Automatic Core Handling | Faster roll changes | Reduced downtime and labour cost savings |
Summary paragraph: Prioritising these features produces measurable improvements in yield and uptime for converters, guiding the selection of equipment that balances speed, precision and total cost of ownership.
Precision film cutting improves package integrity by producing consistent film widths and edge conditions that enable accurate sealing, registration for printing, and reliable lamination. When slitting tolerances are tight, downstream sealing jaws and printers maintain alignment, reducing rejects and improving aesthetic and functional quality of flexible packages. Reduced variance in roll diameter and consistent web tension also improve winding stability, lowering defects that appear during converting.
Measurable outcomes include fewer sealing failures, better print registration percentages and a decline in scrap rates — all of which affect cost per metre and customer satisfaction. These improvements are closely tied to machine automation and control features, which we explore in the next subsection.
Modern slitter rewinders offer automation features such as recipe storage, auto knife positioning, automatic core loading, and servo-driven tension control; these capabilities support higher nominal speeds but require matching of speed to material handling tolerances. Typical speed benchmarks range from 200–500 m/min depending on film type and machine class, with higher speeds common on BOPP and thinner films when equipped with advanced winding and dancer control systems. Trade-offs exist: pushing for maximum speed without adequate tension or winding control can increase scrap, so buyers should match automation to production targets.
Selecting the right balance ensures that throughput gains do not compromise edge quality or roll stability, and that energy efficiency and control systems support long-term OEE improvements.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa supports slitting needs through a one-stop service model and a product range that includes Slitting Machine as a product category alongside blown film extrusion, plastic bag making machines, flexo printing and plastic recycling machines. The supplier emphasises simple operation, perfect performance, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service, 100 percent final inspection, control defective products to 1-3 percent, two-year warranty on certain components, strong R&D, one-stop service model, robust production capacity, competitive pricing, and fast delivery. This combination positions the company to supply both individual slitter rewinders and integrated lines that link extrusion to bag-making or printing for Rustenburg converters.
Intro to service table: The table outlines services, their scope and typical values to make expectations explicit for procurement teams.
| Service | Scope | Value / Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Final Inspection | 100 percent final inspection | Defect control 1–3% |
| Warranty | Component-level warranty | Two-year warranty on certain components |
| After-Sales Service | Installation, commissioning, training | Timely after-sales service and spare parts support |
Summary paragraph: These service commitments reduce buyer risk by clarifying inspection standards, warranty terms and local support expectations, helping Rustenburg companies make informed procurement decisions that prioritise uptime and long-term value.
Quality assurance typically includes factory testing, 100 percent final inspection of machines and documented acceptance checks to control defective products to 1-3 percent, measures that lower the risk of initial failures. Warranty coverage often extends to critical components — the supplier notes a two-year warranty on certain components — and is combined with installation verification and operator training to ensure performance targets are met. Buyers should request inspection records and clarify which components are covered under the two-year warranty to align expectations and reduce lifecycle costs.
This quality framework sets the stage for robust after-sales support that maintains machine performance over time.
After-sales support for slitting systems includes preventive maintenance guidance, spare parts provisioning, remote troubleshooting and on-site service visits to preserve OEE. Regular maintenance schedules, timely replacement of wear parts such as blades and bearings, and operator training reduce unplanned downtime and maintain winding quality. Concrete SLAs vary, but an effective program emphasises fast spare parts delivery, clear escalation paths, and documentation for routine checks that operators can perform between service visits.
Good after-sales support transforms a capital purchase into a sustained production asset, ensuring the slitter rewinder continues to deliver the expected reductions in scrap and improvements in throughput.
Film slitting machines enable a range of applications across Rustenburg’s flexible packaging supply chain, from narrow-web label stocks to wide rolls for bag making and laminated packaging films. Slitting supports printed web preparation for flexo printing, creation of bag rolls for automatic bag making machines, and conversion of laminated films into finished pouches. Each application imposes specific requirements on slitting tolerances, blade type and winding method, so converters must match equipment characteristics to end-product demands.
These applications illustrate how slitting integrates into broader converting workflows and the downstream benefits for quality, speed and product diversity.
BOPP film slitting is essential for producing label stock, printable packaging facestocks and laminated structures that require clean edges and stable web properties. Typical setups include razor or fine rotary blade systems, static control, and precise tension loops to maintain print registration and lamination integrity. For label and flexible packaging, slitting tolerances often target ±0.5–1 mm and surface finish is crucial to ensure adhesion in lamination and consistent ink laydown during flexo printing.
Recommended setups include air shafts for fast roll changes and recipe-driven PLC controls that store knife and tension parameters for each BOPP grade. These setup considerations directly impact how slitting supports plastic bag and pouch production in Rustenburg.
In plastic bag production, slitting machines create the rolls that feed bag-making machines, enabling multiple bag widths from a single extrusion run and optimising material usage. The typical workflow is extrusion → slit → rewind → bag maker, where slitting converts a wide extrusion layflat into narrower rolls that meet the bag maker’s core and width requirements. Proper slitting reduces off-spec widths, improves bag sealing consistency, and shortens changeover time on the bag-making line.
Efficient roll changeover, consistent core running and correct edge conditions reduce stoppages on bag makers and allow converters to produce multiple SKUs without excessive downtime, directly impacting output and margin.
Prospective buyers often ask whether a given machine can handle specific film types, how maintenance is managed locally, and how to choose between manual, semi-automatic and fully automatic equipment for production targets. Clear answers focus on material compatibility, maintenance cadence and the supplier’s service model, which together determine total cost of ownership and uptime. The short FAQs below address these recurring queries and invite buyers to request tailored quotations and technical comparisons.
These concise answers segue into more detailed material compatibility guidance and local support practices.
Industrial slitters handle a broad set of films including BOPP, PET, CPP, LDPE, HDPE, metalized laminates and multi-layer films, with each material demanding specific blade choices and web handling. BOPP and PET often require fine rotary knives and static mitigation; LDPE and HDPE tolerate higher knife aggressiveness but may need different tension profiles; metalized films demand controlled winding to avoid surface damage. Blade selection, anti-static systems and the tension control system are all adjusted based on film thickness and neck-in behaviour.
Understanding these material-specific handling tips helps buyers specify the correct modular components and reduces start-up trial-and-error during commissioning.
Local maintenance and support strategies center on preventive maintenance schedules, spare parts stocking and access to remote diagnostics or on-site service visits for critical issues. A recommended checklist includes daily web path inspections, weekly blade checks, monthly bearing and servo evaluations, and scheduled preventive maintenance every 3–6 months depending on usage. Effective programs pair operator-level daily checks with supplier-backed spare parts availability and timely technical support to minimise downtime.
Clear maintenance practices combined with supplier SLAs for parts and service ensure Rustenburg operations sustain consistent production quality and uptime.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.