Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
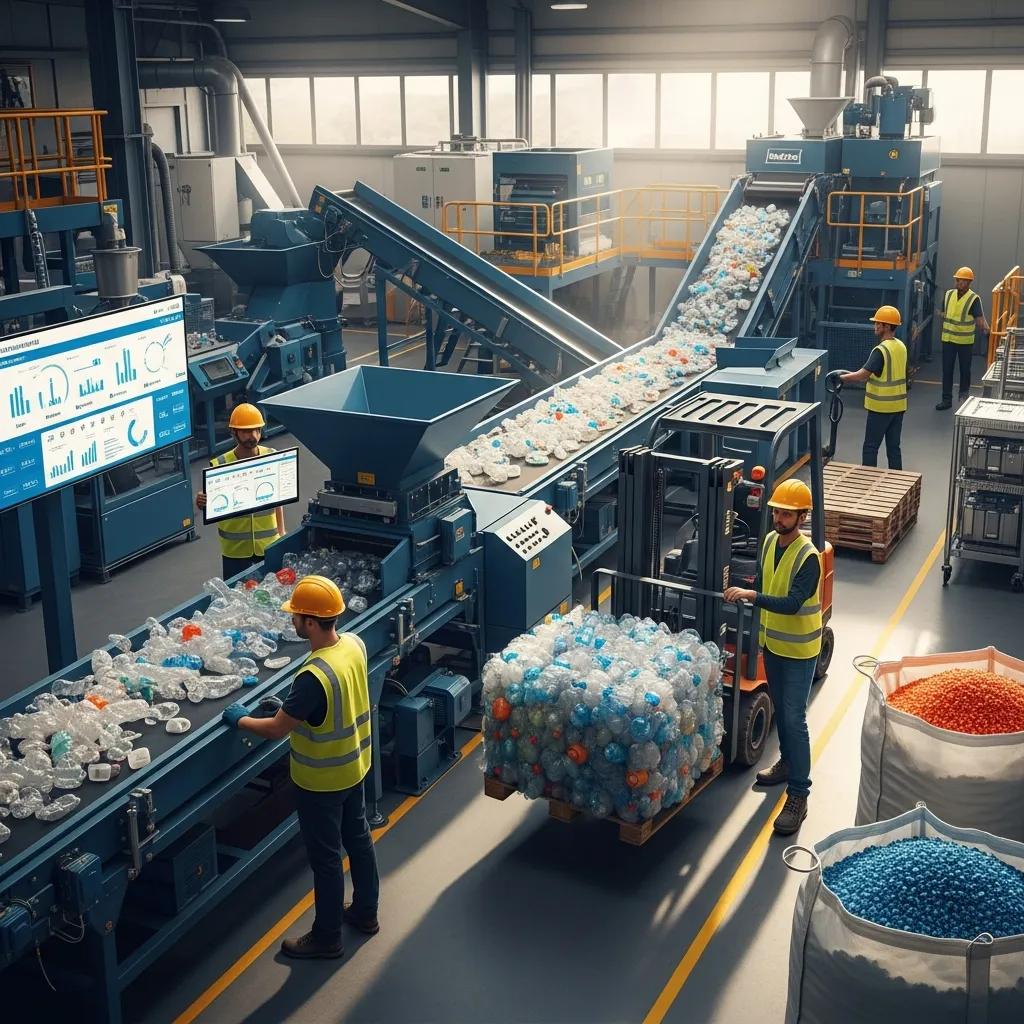

Plastic waste presents a growing operational and regulatory challenge for Midrand businesses, and on-site or local recycling machines convert that liability into a resource through material recovery and cost reduction. This article explains which industrial recycling machines suit Midrand operations, how different plastics are processed, and the step-by-step workflow from shredding to pelletizing so that managers can evaluate CAPEX, throughput, and product-quality outcomes. You will learn how pelletizers, commercial shredders, and water-cooling recycling systems function, which plastics (PP, PE, HDPE, PET) they handle best, and the economic and environmental gains achievable by integrating recycling into production or waste management. The guide maps machine categories to common Midrand use cases, compares capacity and power considerations, and provides practical process controls and maintenance tips to maximize yield and pellet quality. Finally, the article outlines why Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.)’s manufacturing and service capabilities are relevant when sourcing turnkey lines, and includes actionable next steps for requesting machine details or quotations.
Plastic recycling machinery suitable for Midrand ranges from compact film reprocessing lines to industrial bottle-to-pellet systems; the right choice depends on feedstock type, throughput need, and target pellet quality. At the core, a recycling line typically combines pre-shredding, washing/separation, drying, and pelletizing stages; selecting machines that balance capacity (kg/h) with energy efficiency is essential for predictable operating costs.
Small to medium enterprises processing film or offcuts often use single-shaft shredders and water-ring pelletizers to produce rPE/rPP for internal reuse, while larger converters handling bottles and rigid containers require granulators, hot-wash systems, and strand or strand-and-water-cooled pelletizers to reach higher purity and flake specifications.
Below is a quick comparison table to help Midrand businesses match machine families to typical applications and expected capacity ranges.
Intro table explaining machine comparison and purpose.
| Machine Model / Type | Key Attributes (capacity kg/h, power kW, suitable plastics) | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Single-shaft Shredder | 100–800 kg/h, 2–15 kW, film & rigid plastics | Pre-processing film, sacks, offcuts for small/medium plants |
| Twin-shaft Shredder | 500–2500 kg/h, 15–75 kW, mixed rigid & bulky | High-throughput municipal or industrial bulky waste |
| Washing Line (Hot/Float) | Flow-through wash, separations, 5–50 m³/h water recirc | Bottle flake cleaning and contamination removal |
| Strand Pelletizer (Water-cooled) | 100–1500 kg/h, 10–120 kW, PE/PP film & regrind | High-quality pellets for blown film or extrusion |
This table helps decision-makers narrow machine families by matching capacity and material fit; the next section explains pelletizers and shredders in greater detail and links those machine choices to pellet quality and downstream uses.
Plastic pelletizer machines convert cleaned, dried plastic feed into uniform pellets that are easier to store, transport, and reuse; pelletizing improves bulk density and creates a consistent feedstock for blown film extrusion or injection molding.
Two common pelletizer types are water-ring (or underwater) pelletizers and strand pelletizers; water-ring designs cut pellets in a water jacket delivering rapid cooling and typically produce rounder pellets with less dust, while strand pelletizers extrude strands that are cooled in air or water and granulated, offering lower maintenance and simpler integration for some PP/PE lines.
For Midrand businesses, water-ring pelletizers are especially beneficial when processing LDPE/LLDPE film where pellet shape and low dust improve extruder feed reliability, whereas strand pelletizers suit operations prioritizing lower water use and easier upstream integration.
Regular maintenance on cutters and filters, plus optimizing melt temperature and throughput balance, enhances energy efficiency and pellet quality for local recyclers.
These pelletizer choices lead naturally to selecting the right shredder upstream to ensure consistent feed size and throughput.

Commercial shredders provide the essential pre-processing step that determines downstream washing and pelletizing efficiency by reducing feedstock to consistent particle sizes and removing oversized contaminants.
Single-shaft shredders are common for film and soft plastics because they deliver controlled granulate sizes with lower noise and energy consumption, while twin-shaft or heavy-duty industrial shredders handle rigid containers, crates, and bulky mixed waste with higher torque and throughput; matching shredder throughput to pelletizer capacity prevents bottlenecks.
Proper rotor design, screen selection, and fragmentation strategy reduce fines and contamination, improving wash-line performance and final pellet yield for Midrand processors.
Optimizing shredder selection reduces wear on downstream systems and improves overall line uptime, which is critical for predictable production planning.
Midrand recycling lines can process a broad set of commodity plastics including PP, PE (LDPE/LLDPE), HDPE, and PET, with machine selection and pre-processing steps tailored to each polymer’s morphology and contamination profile. Film feedstock such as LDPE and LLDPE benefits from gentle shredding, efficient washing to remove adhesives and labels, and water-cooled pelletizing to retain pellet roundness for extrusion. Rigid PP and HDPE containers require more robust shredding, possible hot-wash and float-sink separation for density sorting, and higher-temperature drying prior to pelletizing to avoid steam-induced defects. PET beverage bottles typically follow a route toward flake production then decontamination for rPET markets; achieving food-contact grades requires extra purification steps beyond standard washing.
Intro to mapping plastics to machines and outputs.
| Plastic Type | Common Forms | Recommended Machine(s) | Expected Pellet Quality / Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE / LLDPE | Films, sacks, agricultural film | Single-shaft shredder, washing line, water-ring pelletizer | Round pellets, good for blown film and pipes |
| PP | Film & rigid parts | Shredder, washing line, strand/water-cooled pelletizer | Consistent rPP for injection/extrusion |
| HDPE | Bottles, containers | Granulator, hot-wash/float-sink, strand pelletizer | High-density rHDPE for containers and pipes |
| PET | Bottles, trays | Bottle flaker, hot-wash, decontamination & drying | Flakes or rPET for fiber, bottles (with decontamination) |
This mapping clarifies how feeds translate into machine choices and commercial outputs, and prepares Midrand teams to estimate quality outcomes before equipment selection.
Processing PP and PE begins with source sorting and shredding to a controlled particle size, which enhances wash penetration and reduces downstream melt contamination; these polymers require attention to moisture and temperature during pelletizing.
After shredding, a staged washing approach—cold pre-wash to remove debris and hot washing or friction washing for oily contaminants—improves surface cleanliness; subsequent drying targets moisture below 0.2–0.3% for most pelletizing lines to prevent hydrolytic defects.
Pelletizer settings differ: PP typically runs at slightly higher melt temperatures than PE and benefits from specific die and cutter clearances to maintain pellet integrity.
Common contamination issues include PVC traces and labels; pre-sorting and density separation are critical mitigation measures to preserve pellet market value.
These operational controls directly influence pellet yield and determine whether recycled pellets are suitable for internal reuse or commercial sale.
HDPE and PET recycling require more robust separation and cleaning because of their common use in containers and beverage bottles; processing aims either for high-density pellets (rHDPE) or cleaned flakes for rPET markets.
For HDPE, heavy-duty shredders or granulators reduce bottle streams to consistent flake sizes, followed by hot-wash, friction washing, and float-sink separation to remove labels and contaminants; strand pelletizing produces dense rHDPE suitable for injection molding or extrusion.
PET lines often prioritize flake production with rigorous decontamination and drying steps—thermal or vacuum drying systems lower residual moisture before crystallization or extrusion to avoid hydrolytic degradation.
Typical end-markets for rHDPE include piping and molding, while rPET flakes feed fiber and container recycling streams when decontamination standards are met.
Choosing the correct sequence of machines and wash technologies is essential to meet downstream quality and compliance expectations in Gauteng markets.
Recycling plastic on-site or through local recycling lines reduces disposal costs, recovers material value, and lowers reliance on virgin resin, producing measurable economic benefits while reducing landfill volume and embodied carbon from raw polymer production.
Intro to benefits table and metrics for decision-makers.
| Benefit Category | Metric / Attribute | Example Value / Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Disposal avoided per ton | Reduced municipal waste fees and transport costs |
| Revenue | Sale of recycled pellets per ton | Additional income stream if quality meets buyer specs |
| Environmental | Landfill diversion (tons/year) | Lowered waste footprint and CO₂-equivalent savings |
| Compliance | Support for EPR reporting | Demonstrable recycled content and diversion metrics |
This metric-oriented view helps quantify business cases and informs ROI conversations when selecting recycling machinery for Midrand operations.
Cost savings stem largely from reduced landfill and transport fees, plus substitution of virgin resin with recycled pellets for in-house production, while revenue opportunities arise from selling surplus rPE/rPP/rHDPE or supplying local converters.
The economic outcome depends on throughput, yield (percentage of clean pellet from input), contamination levels, and local demand for recycled material; higher yield and consistent pellet quality shorten payback timelines.
Example drivers include reduced procurement spend for raw resin when recycled pellets replace a portion of virgin material, and potential revenue from selling off-spec or excess pellets to local recyclers.
Operational factors—labour, energy costs, water treatment, and maintenance—should be modelled alongside market prices for recycled material when calculating projected ROI.
A careful assessment of these variables enables Midrand businesses to prioritize investments that yield the fastest operational and financial benefits.
Adopting industrial recycling contributes to a circular economy by converting disposed polymer back into feedstock, lowering demand for virgin polymers and decreasing life-cycle emissions associated with production and disposal.
Recycling aligns with Extended Producer Responsibility frameworks by providing traceable diversion, recycled-content evidence, and documented process controls necessary for compliance and sustainability reporting. Local recycling also reduces transport-related emissions by shortening supply chains between waste source and processing, while creating opportunities for local downstream manufacturing that uses rPP/rPE/rHDPE. Recent industry focus on recycled content targets increases demand for verified recycled pellets, making robust quality control and traceability essential for businesses pursuing sustainability commitments.
This systems-level impact supports corporate ESG goals and strengthens resilience against material-price volatility in 2024 and beyond.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers a one-stop approach to plastic recycling equipment and production lines, combining machine families such as blown film extrusion, bag making, flexo printing, and plastic recycling machines including water cooling recycling units that are relevant for film and pellet production.
The company’s highlighted commitments include 100% final inspection during production, a two-year warranty on timer switches, an experienced R&D and engineering team, and a one-stop/customized service that supports innovation to mass production, logos/labels, and packaging. Their operational claims note 16 production lines, over 30 testing equipment items, competitive pricing driven by large-scale production and trained workers, and fast delivery times with samples within 3 days and bulk deliveries in 15–20 days. For Midrand businesses evaluating suppliers, these factors speak to quality control, customization capability, and procurement predictability.
Below are concrete service attributes and how they translate to procurement assurance for buyers.
| Service / Assurance | Characteristic | Buyer Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Final inspection | 100% final inspection during production | Reduced likelihood of defects arriving on-site |
| Warranty | Two-year warranty on timer switches | Targeted assurance for critical control components |
| Capacity & Testing | 16 production lines, 30+ testing equipment | Scalability and validated product performance |
| Delivery | Samples in 3 days, bulk 15–20 days | Faster test and production ramp-up for projects |
These service elements reduce procurement risk and support faster commissioning for Midrand recycling projects.
Quality assurance includes systematic final inspection during production and targeted component warranties, while after-sales support is provided through an experienced R&D and engineering team capable of customization and troubleshooting. The explicit commitments—100% final inspection and a two-year warranty on timer switches—indicate attention to production QA and certain control components, and the presence of engineering and R&D resources suggests capacity for tailored configurations and problem resolution.
After-sales pathways typically involve installation guidance, spare-parts provisioning, and technical support for commissioning and process tuning to reach desired pellet quality and throughput.
Reliability in QA and accessible technical support minimize downtime and protect production targets when integrating new recycling lines.
Competitive pricing stems from large-scale production capabilities and an experienced workforce, allowing suppliers to offer value while maintaining quality; fast delivery timelines accelerate pilot testing and full-line deployment for businesses with tight turnaround requirements. The declared lead times—sample shipments within 3 days and bulk deliveries within 15–20 days—enable rapid prototyping and quicker transition from procurement to production, which is valuable for projects seeking fast ROI or seasonal processing windows.
By leveraging these advantages, Midrand companies can shorten commissioning schedules, begin recovering material value sooner, and adapt production to evolving sustainability targets without protracted lead times. For precise machine pricing and configuration-specific lead times, prospective buyers should request a tailored quotation.
This procurement speed and pricing advantage supports faster operational returns and easier scaling of recycling capacity in Midrand operations.
Implementing a recycling process requires a staged approach—shredding, washing, drying, and pelletizing—with machine selection and process parameters tuned to material type, contamination, and throughput goals. Integrating these stages with water management, filtration, and throughput balancing ensures efficient resource use and consistent pellet properties.
Each key step has a distinct purpose: shredding creates uniform feed particle size for cleaning, washing removes surface contaminants, drying prevents moisture-related defects, and pelletizing produces a usable feedstock for extrusion or sale. Typical machine parameters include shred sizes tailored to wash-line penetration, wash temperatures and residence times for effective decontamination, drying temperatures and residence to achieve residual moisture targets, and pelletizer melt-temperature and cutter-speed combinations to control pellet density and shape. Common issues include fines generation at shredding, inadequate wash-line separation of contaminants, incomplete drying, and pellet agglomeration; addressing these requires appropriate screen selection, water filtration, and melt-temperature monitoring. Balancing throughput across stages prevents bottlenecks and stabilizes production yields for Midrand recycling lines.
Understanding machine objectives at each stage enables better procurement and operational planning for reliable line performance.
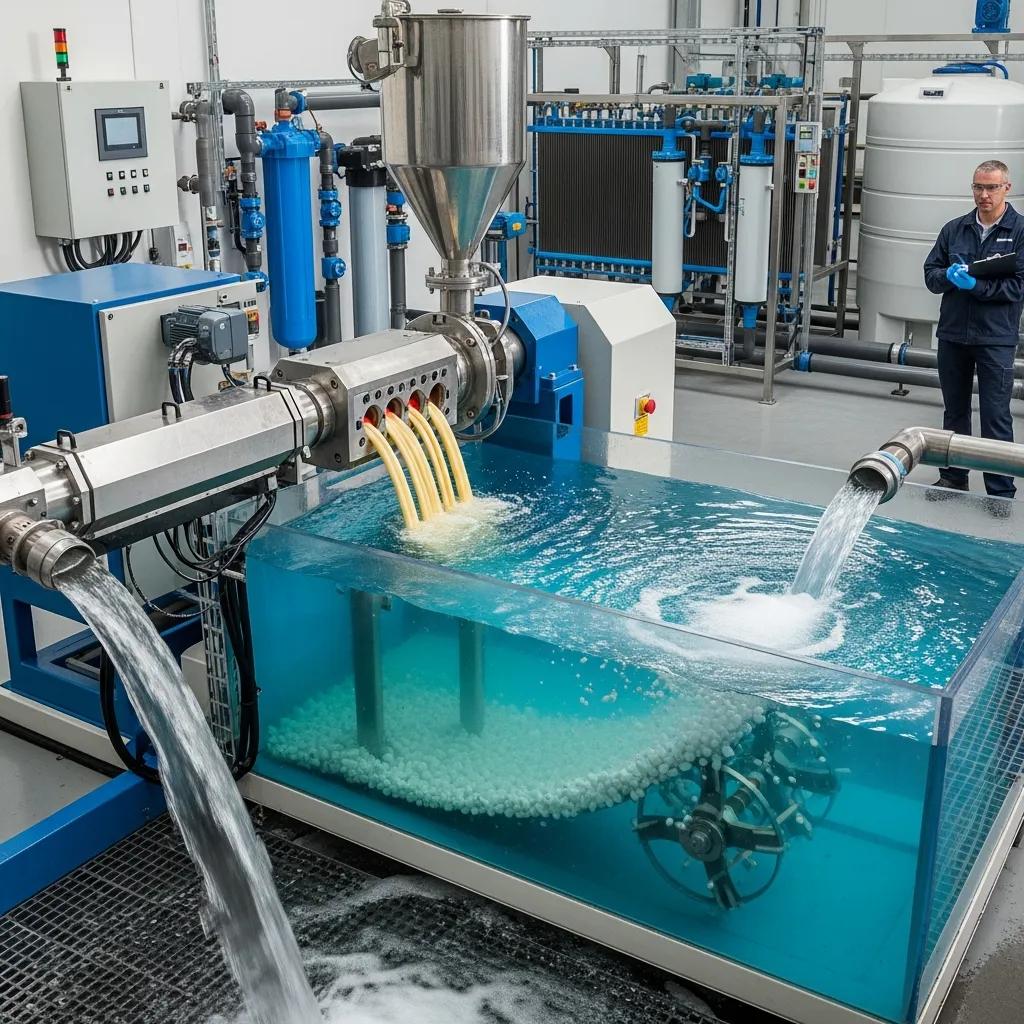

Water-cooling pelletizers improve pellet shape, surface finish, and bulk density by quenching molten strands immediately after cutting, which reduces dust and improves downstream handling for film extrusion applications. These machines are particularly effective for LDPE/LLDPE film recycling where round, dense pellets feed blown film extruders more consistently, reducing clogging and improving melt homogeneity.
Operational considerations include water circulation, filtration to remove fines, and temperature control to avoid thermal shock or excessive crystallization for certain polymers. Proper water treatment and recirculation systems also reduce freshwater use and maintain pellet quality over sustained runs, offering both performance and resource-efficiency advantages for Midrand processors.
Selecting water-cooling pelletizers where material and market demands require high pellet quality can improve product acceptance and internal reuse rates.
Midrand buyers commonly ask about pricing drivers, lead times, and processing throughput; these questions hinge on capacity, customization, and material-specific requirements rather than fixed machine rates. Pricing depends on machine capacity, customization needs, inclusion of washing/dewatering systems, and whether turnkey integration or modular supply is desired; the supplier’s competitive pricing claim suggests value from scale, but precise figures require a tailored specification. Lead times influence project schedules; sample delivery in 3 days and bulk shipment in 15–20 days speeds initial testing and procurement. For specific specifications, pricing, and lead-time confirmations, businesses should request detailed quotes with feedstock and throughput parameters to obtain accurate proposals.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.