Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
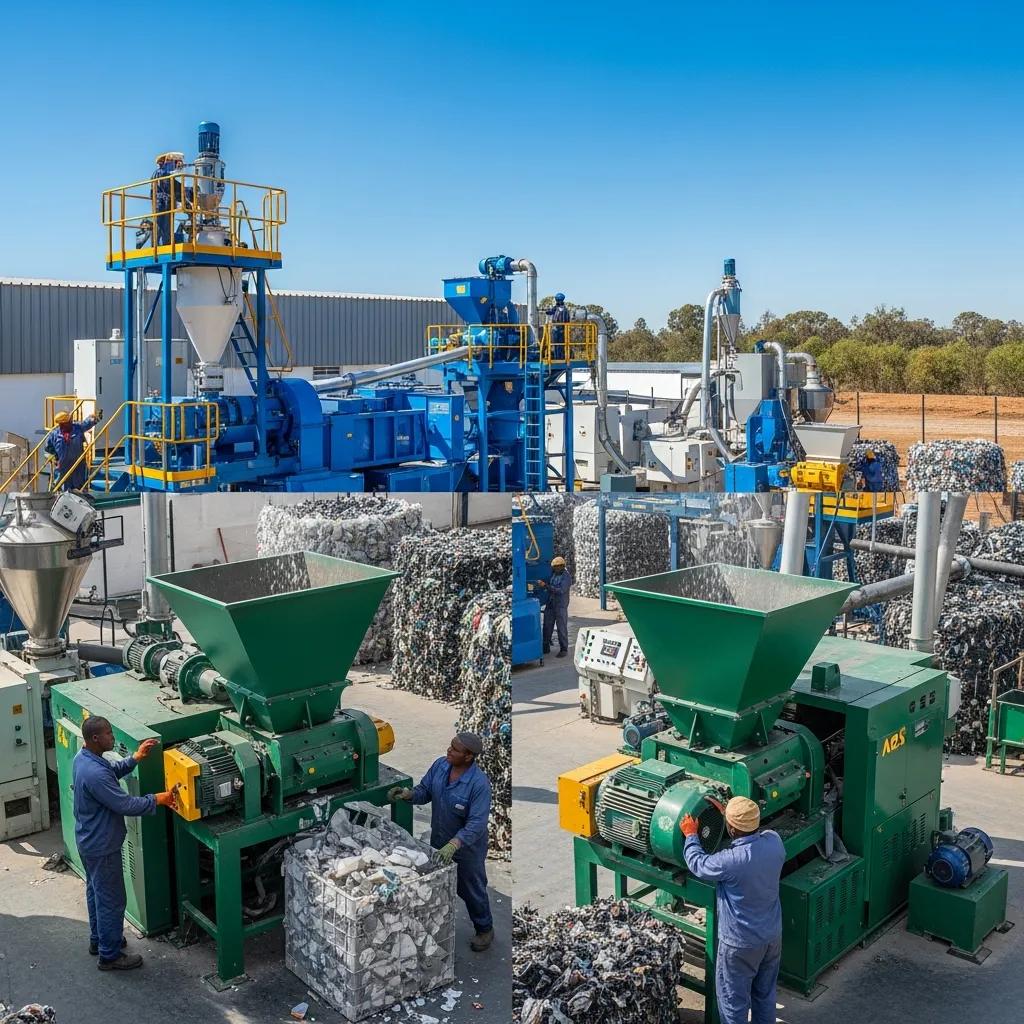

Plastic recycling solutions for Polokwane businesses means deploying the right combination of industrial recycling equipment to convert local plastic waste into usable flakes or pellets that local manufacturers can buy or reuse. This guide explains what machines are commonly used, how they work, what plastics they process, and practical steps to start a commercial recycling line in Polokwane and broader Limpopo. Many businesses face rising disposal costs and inconsistent feedstock quality; mechanical recycling provides a route to lower raw-material costs, create new revenue streams, and meet emerging regulatory expectations under circular-economy policies. The article covers core machine types and maintenance, the economics and environmental benefits of recycling in Limpopo, polymer-specific workflows for PET/HDPE/LDPE/PP/PVC, step-by-step commissioning advice, and funding options including UNDP-style grants. Throughout, we reference machine categories such as plastic pelletizer machines and industrial plastic shredders relevant to Polokwane operators, and explain how to match capacity and output quality to local markets and buyers.
Key plastic recycling machines for Polokwane businesses are industrial shredders, granulators, washing lines, extrusion pelletizers, and separation/air-classification units that collectively convert mixed waste into flakes or pellets for resale or in-house use. Each category performs a defined role: shredders reduce size; washing removes contaminants; granulators refine particle size; pelletizers convert melt into uniform pellets; separation units improve output quality. Choosing the right first machine depends on feedstock form, target output (flakes vs pellets), and available utilities. Below is a concise mapping of machine → core function → typical plastics processed to help readers quickly identify which equipment starts a commercial line.
This short comparison clarifies first-step choices and leads into more detailed equipment descriptions below.
| Machine Type | Core Function | Typical Plastics Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Shredder | Size reduction for bulky or film waste | LDPE film, PP woven sacks, mixed rigid plastics |
| Granulator | Fine size control for consistent flake feed | PET bottles, HDPE drums, PP parts |
| Washing Line | Remove labels, adhesives, and contaminants | PET, HDPE, mixed post-consumer plastics |
| Plastic Pelletizer | Extrude and cut molten plastic into pellets | rPET, rHDPE, reprocessed LDPE/PP |
This table helps buyers decide whether to start with size reduction or move straight to pelletizing based on their feedstock quality and market goals. The next subsections detail pelletizers and shredders so operators can match machines to local industrial demands.
Plastic pelletizer machines convert cleaned and dried plastic flakes into uniform pellets by melting polymer through an extruder screw and cutting strands into granules, producing feedstock suitable for injection molding and extrusion. The core components include the screw & barrel, die head, cutter, and downstream pellet dryer; control of melt temperature and residence time dictates pellet quality measured by melt flow index and moisture content. Typical small-to-medium commercial pelletizers produce tens to a few hundred kilograms per hour depending on screw diameter and line design, making them suitable for local manufacturers seeking rPET or rHDPE feedstock. Pelletized outputs lower transport costs and expand marketability compared with bulk flakes, and pelletizers can be paired with filtration and vacuum venting to improve purity. Understanding pellet quality metrics is crucial when targeting South African processors that expect consistent diameter, low contamination, and controlled moisture.
This operational overview of pelletizers sets the stage for selecting shredding and pre-processing equipment required to produce suitable feed for extrusion-based pelletizing.
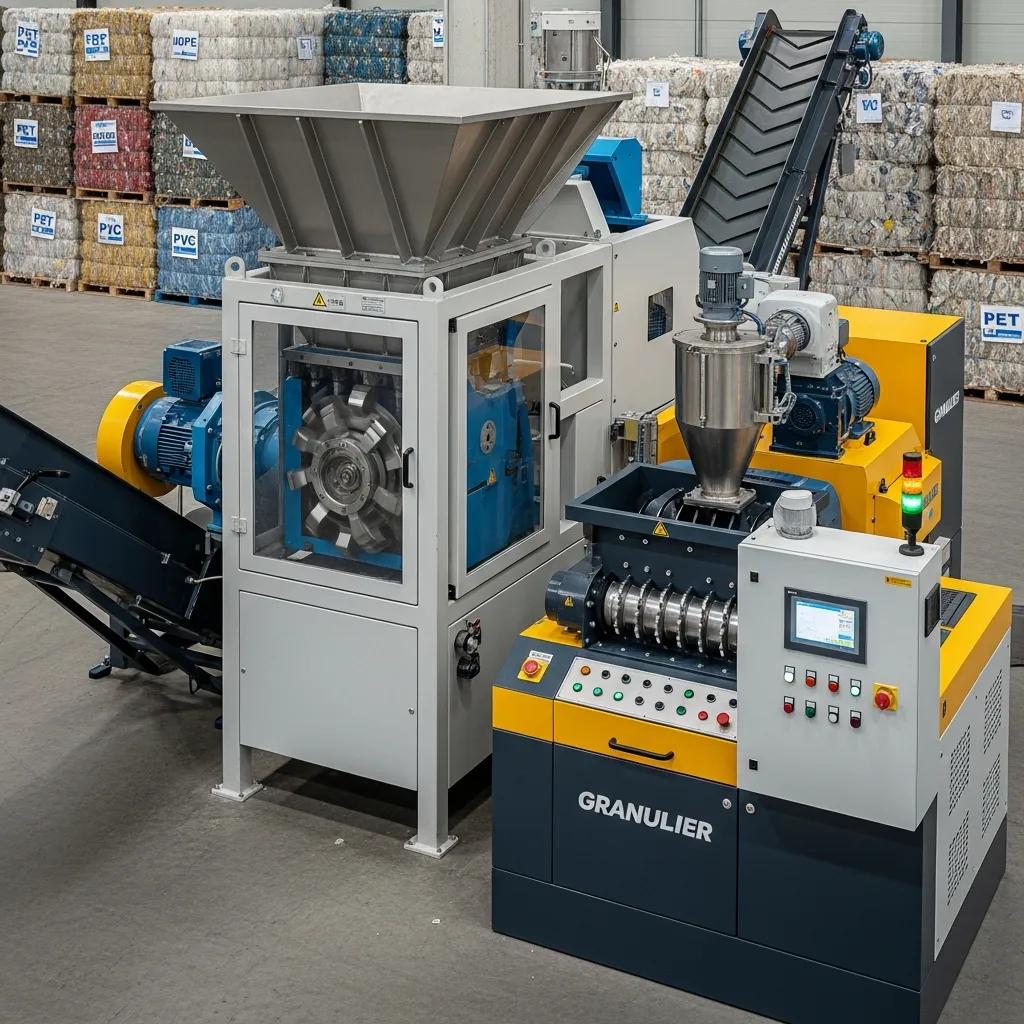

Industrial plastic shredders and granulators are designed to reduce feedstock to a controlled particle size while accommodating different plastic forms and contamination levels; shredders handle bulky and film materials while granulators create finer, uniform flakes for washing and extrusion. Blade design, rotor speed, and screen sizing determine throughput and output size, while feed throat design influences the ability to process film versus rigid items. Typical considerations for Limpopo operations include noise attenuation, power supply compatibility, and maintenance schedules for blade sharpening and monitoring cutting gaps. Safety features such as access interlocks and emergency stops are essential in commercial environments, and matching machine capacity to expected daily volumes prevents bottlenecks upstream of pelletizing. Proper selection of shredder or granulator ensures that downstream washing and extrusion processes receive consistent feed, which improves final pellet quality and reduces downtime.
Understanding shredding capacity and compatibility helps businesses choose the right upstream equipment before investing in washing or pelletizing lines.
Polokwane businesses should invest in plastic recycling solutions because recycling delivers direct cost savings, new revenue potential, and alignment with environmental and regulatory trends that increasingly favor circular economy practices. Economically, recycling cuts disposal fees and reduces reliance on virgin polymer purchases by creating in-house feedstock or saleable pellets. Environmentally, recycling diverts waste from landfills and lowers lifecycle emissions compared with virgin resin production. Regulators and buyers are prioritizing Extended Producer Responsibility and recycled content, so early investment can provide competitive advantage and reputational benefits. The table below summarizes business benefits and environmental impacts to help decision makers weigh the case and estimate potential outcomes.
These quantified benefits illustrate why a planned investment in recycling machinery can be commercially and socially advantageous for local firms.
| Business Outcome | Attribute | Value or Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Saving | Disposal and raw-material reduction | Lower operational costs and improved margins |
| Environmental Benefit | Landfill diversion and emissions reduction | Reduced local environmental burden and better ESG profile |
| Market Opportunity | Supply of rPET/rHDPE to local industry | Access to manufacturers in Johannesburg and Cape Town markets |
This benefits table supports assessing ROI and leads into the economic breakout that follows, which quantifies savings drivers and return factors.

Economic benefits from plastic recycling arise through several channels: avoided disposal fees, reduced raw-material purchases, and income from selling recycled pellets or using them internally. Key drivers include scale of throughput, consistent feedstock supply, and local demand for recycled material; higher utilization and stronger quality control increase realized value per kilogram. Payback periods vary but are often shortened by grants and by integrating recycling with existing production to offset virgin resin purchases. Operational costs include energy, labor, maintenance (blade sharpening, screen changes), and utilities; optimizing these can improve margins. Businesses should model scenarios using expected daily input tonnes, recovery yield, and local pellet prices to estimate realistic outcomes and determine whether to start with shredding and washing or to invest directly in a pelletizing line.
Understanding these economic levers prepares operators for conversations with suppliers and financiers about equipment sizing and expected returns.
Plastic recycling contributes to environmental sustainability in Limpopo by diverting significant volumes of plastic from landfills, reducing local pollution, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared with producing virgin polymers. Mechanically recycling PET and HDPE into pellets reduces energy consumption and embodied carbon per unit of polymer when compared to virgin resin production, which supports corporate sustainability targets and municipal waste-reduction goals. Local recycling also reduces transport-related emissions by shortening supply chains when recycled feedstock is used regionally. Community benefits include job creation across collection, sorting, and processing stages and support for informal waste aggregators who can integrate into formalized supply chains. These environmental contributions strengthen a company’s social license to operate and help meet both regulatory expectations and buyer procurement requirements.
This environmental framing clarifies why investment decisions must weigh both financial and ecological outcomes when planning recycling capacity.
Recycling machines in Polokwane can process PET, HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PVC with polymer-specific adaptations in pre-sorting, washing, and extrusion processes that address contamination and melting characteristics. PET bottles typically go through bottle-to-bottle mechanical recycling workflows to produce rPET suitable for packaging or fiber, while HDPE and LDPE require different shredding and washing treatments for film versus rigid forms. PP and PVC are recyclable but often face additive and contamination challenges that require careful sorting and sometimes specialized filtration. The table below maps common polymers to processing steps and typical output quality to assist buyers in matching machines to their feedstock types.
This mapping helps businesses prioritize equipment purchases by feedstock prevalence and desired end-use quality.
| Polymer | Typical Processing Steps | Typical Output Quality |
|---|---|---|
| PET | Collection → Sorting → Washing → Flaking → Pelletizing | High-quality rPET pellets for packaging or fiber |
| HDPE | Sorting → Shredding → Washing → Extrusion | rHDPE pellets with good stiffness for containers |
| LDPE | Sorting → Shredding → Washing → Extrusion | Lower-density pellets for film extrusion or blending |
This table clarifies which machines are essential for each polymer and previews expected marketable outputs before drilling into polymer-specific workflows.
PET recycling in Polokwane follows a bottle-to-bottle pathway: collection, color sorting, label and cap removal, washing, flaking, drying, and pelletizing, producing rPET that local converters can reintroduce into packaging or fiber production. HDPE and LDPE processing diverge by form—rigid items are shredded and granulated for higher-value applications, while film requires pre-compaction and specialized washing to remove cling and adhesives. PP and PVC are handled with stringent sorting to limit contamination; PP can be reprocessed into non-food applications, while PVC often requires dedicated lines due to chlorine content. Local recycling relies on a network of aggregators and sorting centers to ensure feedstock quality, and machines must be selected to handle the most common waste streams a business expects to receive. Proper pre-sorting and washing are critical steps that directly influence final pellet acceptance by South African manufacturers.
This polymer workflow description leads into quality expectations for recycled outputs and how producers can meet buyer criteria.
Recycling machines produce two main commercial outputs: flakes and pellets, each with defined quality metrics such as moisture content, contamination level, and melt flow index (MFI) that determine suitability for various industrial applications. Flakes are typically used where downstream processing will recondition material, while pellets are preferred by injection molders and extruders for consistent feeding and dosing. Quality assurance involves sieving, float-sink separation, washing efficiencies, and moisture removal to meet buyer specifications. South African manufacturers commonly require low contamination and consistent pellet diameter for reliable processing; achieving these standards often requires filtration during extrusion and vacuum venting to remove volatiles. Testing for MFI, color consistency, and residual contaminants is part of acceptance criteria for local industry buyers.
Understanding output quality helps businesses design process controls and testing regimes that align with the needs of regional converters and OEMs.
Starting a recycling operation in Polokwane begins with a structured assessment—conduct a waste audit, quantify volumes by polymer, and determine desired output quality—then progress to equipment selection, site preparation, installation, and training. A clear specification document that captures feedstock variability, target throughput (kg/h), and electrical and water utilities is essential to get accurate equipment proposals and to secure funding. The ordered steps below provide a high-level implementation roadmap for businesses ready to move from concept to commissioning and commercial production.
Following a defined procurement and commissioning sequence reduces hidden costs and speeds time-to-production for new recycling lines.
This ordered checklist helps readers visualize the practical sequence of actions and leads into detailed selection and installation guidance.
Selecting and installing recycling equipment requires defining required capacity, verifying available utilities (power, water, drainage), evaluating footprint and noise constraints, and planning for spare parts and maintenance access. Procurement should specify guaranteed throughput and output quality, warranty terms, and after-sales service to minimize downtime. Site preparation includes concrete pads, access for material delivery, ventilation, and connections for electrical and water services; commissioning involves calibration, test runs, and operator training focusing on safety and quality control. Operators should establish maintenance schedules for blade sharpening, screen replacement, and extruder screw inspection to sustain consistent outputs. Documenting these steps in a project execution plan ensures sequence clarity and smoother handover to production teams.
These practical procurement and installation tasks naturally lead to where businesses can find technical support and supplier consultation for each phase.
Businesses can find support from equipment suppliers, local waste aggregators, industry associations, and grant-advisory organizations that guide project development, feedstock sourcing, and permit requirements. Suppliers often provide site assessment, equipment matching, installation, and operator training as part of a one-stop service, while aggregators supply sorted feedstock and assist with collection logistics. Industry associations offer technical guidance and networking to connect processors with local buyers in cities such as Johannesburg and Cape Town. For operators seeking turnkey assistance, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers plastic recycling machines and related solutions, R&D and one-stop customization, and claims simple operation, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service, plus quality assurance measures including 100% final inspections and a two-year warranty on certain components.
This supplier-and-support overview points to practical next steps, including requesting detailed equipment specifications and quotes for site-specific proposals.
Funding and grant opportunities for plastic recycling in South Africa include government programs, international development grants, and specialized small-grant calls that support circular-economy projects and infrastructure. Programs often prioritize projects that demonstrate scalability, environmental impact, job creation, and alignment with municipal waste strategies. Applicants need to assemble technical equipment specifications, realistic budgets, and environmental impact statements to improve chances of success. Below is a brief guide to preparing grant-ready documentation and the typical application steps used by successful applicants.
This funding overview prepares businesses to gather the documents and partner support necessary for competitive applications and follows with concrete steps to access grants.
| Funding Element | Required Documentation | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Specs | Detailed machine lists and capacities | Enables accurate costing and procurement planning |
| Environmental Impact | Waste diversion estimates and emissions benefits | Demonstrates project sustainability and compliance |
| Business Case | Market demand and financial projections | Shows project viability and scalability |
This table outlines the documentation most often requested by grant evaluators and transitions to practical steps on accessing specific grants.
To access government and UNDP-style grants, businesses should monitor open calls, prepare a coherent project narrative that outlines objectives and measurable outcomes, and attach technical equipment specifications and cost estimates. The application process typically involves registration, proposal submission, technical reviews, and due-diligence checks; applicants should factor timelines and co-funding requirements into project plans. Suppliers can assist by providing detailed machine specifications, production capacities, and formal quotes to include in proposals, which strengthens technical credibility. For example, referencing recent small-grant calls can help applicants align project scopes with funder priorities and anticipate documentation expectations during proposal drafting.
Securing supplier-backed technical documentation is often a deciding factor in award decisions, so early engagement with equipment providers is recommended.
Eligibility criteria commonly include formal business registration, a clear environmental or social impact, and evidence of project scalability or replicability; funders evaluate technical feasibility, financial sustainability, and alignment with policy priorities. Typical application steps are: identify a suitable call, prepare a project plan and budget, collect technical specs and supplier quotes, submit the proposal, and respond to any clarifications during evaluation. Common pitfalls include underestimating operating costs, omitting detailed equipment specs, and failing to demonstrate local partnerships for feedstock or offtake. To improve success rates, applicants should provide robust technical appendices and letters of support from local aggregators or buyers.
This eligibility summary leads naturally into frequently asked operational and regulatory questions local businesses ask when planning recycling investments.
Polokwane businesses frequently ask about machine costs, expected returns, regulatory compliance, output quality, and supplier support; concise answers help decision makers prioritize next steps. Understanding capital versus operating costs and how to secure feedstock and buyers is central to early-stage planning. The short Q&A items below address the most common practical questions and provide direct, actionable responses to move a project from interest to implementation.
These focused answers help clear common decision bottlenecks so businesses can proceed to technical consultations or funding applications.
The benefits include reduced waste disposal costs, potential revenue from pellet or flake sales, and supply security for in-house manufacturing; costs include capital expenditure for equipment, installation, utilities, and ongoing maintenance such as blade servicing and extruder screw inspection. Capital costs vary widely with capacity and automation level; operating costs are driven by energy, labor, and consumables. Businesses should run sensitivity analyses using projected daily tonnes, recovery rates, and local recycled-material prices to estimate payback. Careful planning, supplier warranties, and maintenance agreements mitigate operating risk and improve lifecycle economics.
This cost-benefit framing sets up the regulatory context that follows, which businesses must address when launching operations.How Do Local Regulations Affect Plastic Recycling Operations?
Local regulations, including Extended Producer Responsibility frameworks and municipal waste bylaws, affect permitting, reporting, and acceptable end-uses for recycled material; businesses must ensure compliance with environmental permits, waste transporter registrations, and workplace safety rules. Engagement with the Department of Forestry, Fisheries and the Environment and municipal authorities is necessary to confirm permit requirements and reporting obligations. Common compliance steps include preparing environmental management plans, demonstrating safe effluent handling for washing lines, and maintaining records for material flows. Early regulatory consultation reduces delays and ensures operations meet legal and market expectations.
These regulatory considerations complete the practical guidance Polokwane businesses need before contacting suppliers or applying for grants.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.