Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
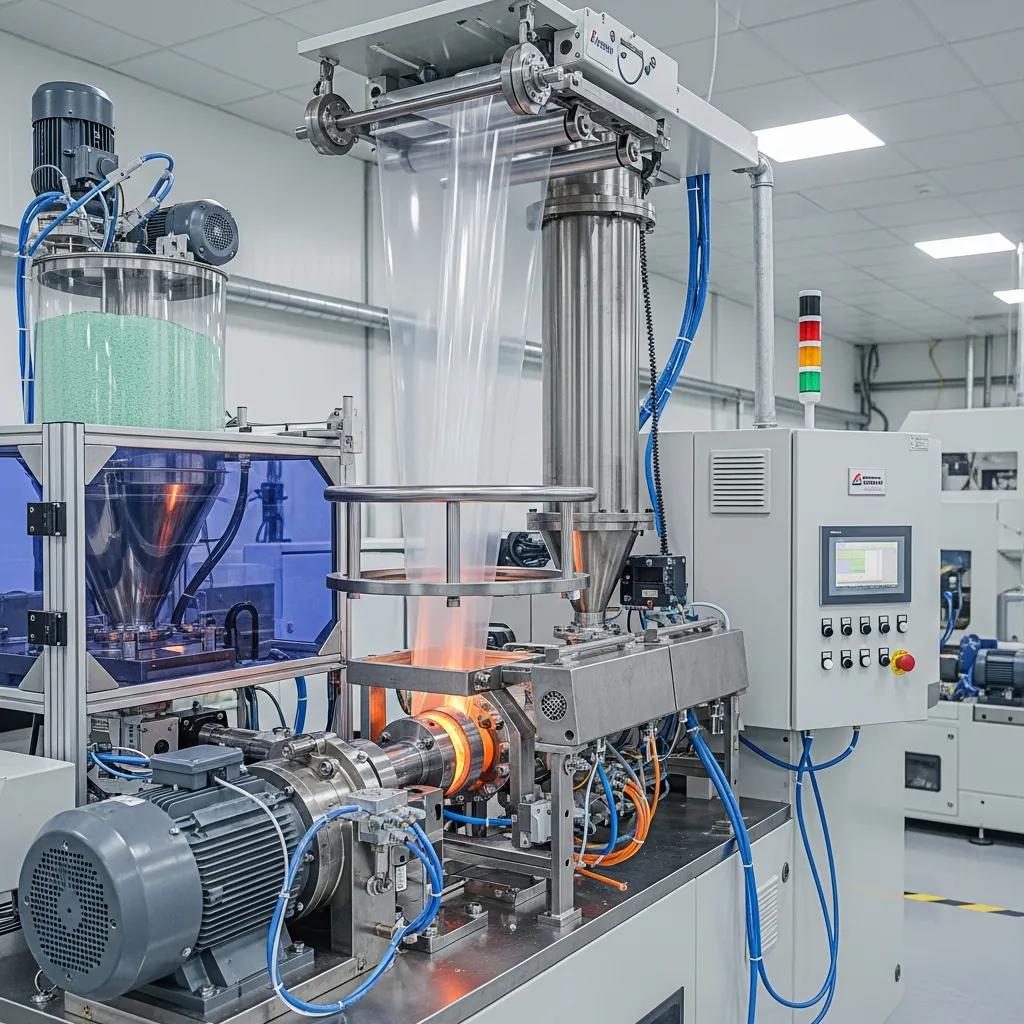

Blown film extrusion is a polymer extrusion process that converts molten resin into a continuous tubular film by forcing the melt through an annular die, inflating a stabilized bubble, cooling it and collapsing it for winding; this mechanism delivers flexible, mechanically balanced film suited to packaging and industrial uses. This guide explains how blown film is made, the critical machine components and process steps that affect gauge, clarity and strength, and how material choice (LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE, PP and blends) changes performance. Readers will learn the step-by-step production sequence, how each component—extruder, die head, air ring, nip rollers and winder—affects quality, and how to match machine capabilities to product requirements. The article also compares blown film with alternative methods, catalogs primary applications in food, consumer and agricultural markets, and reviews procurement criteria for buyers in South Africa. Practical checklists, EAV tables mapping steps to components and parameters, and supplier guidance are included to help technical teams and machinery buyers evaluate options and prepare for installation and scale-up.
Blown film extrusion is defined by melting polymer resin and forcing the melt through an annular die to form a continuous tubular film that is inflated with air into a bubble, cooled, collapsed and wound. The mechanism combines pressure-driven extrusion with film inflation and controlled cooling to produce oriented polymer layers that yield balanced mechanical properties and predictable gauge profiles. The principal benefit for manufacturers is flexibility: a single line can produce a wide range of film thicknesses, widths and multi-layer structures suitable for bags, shrink film and agricultural sheeting. Understanding the process fundamentals is essential for choosing extrusion equipment and tuning operating parameters for clarity, seal strength and tear resistance.
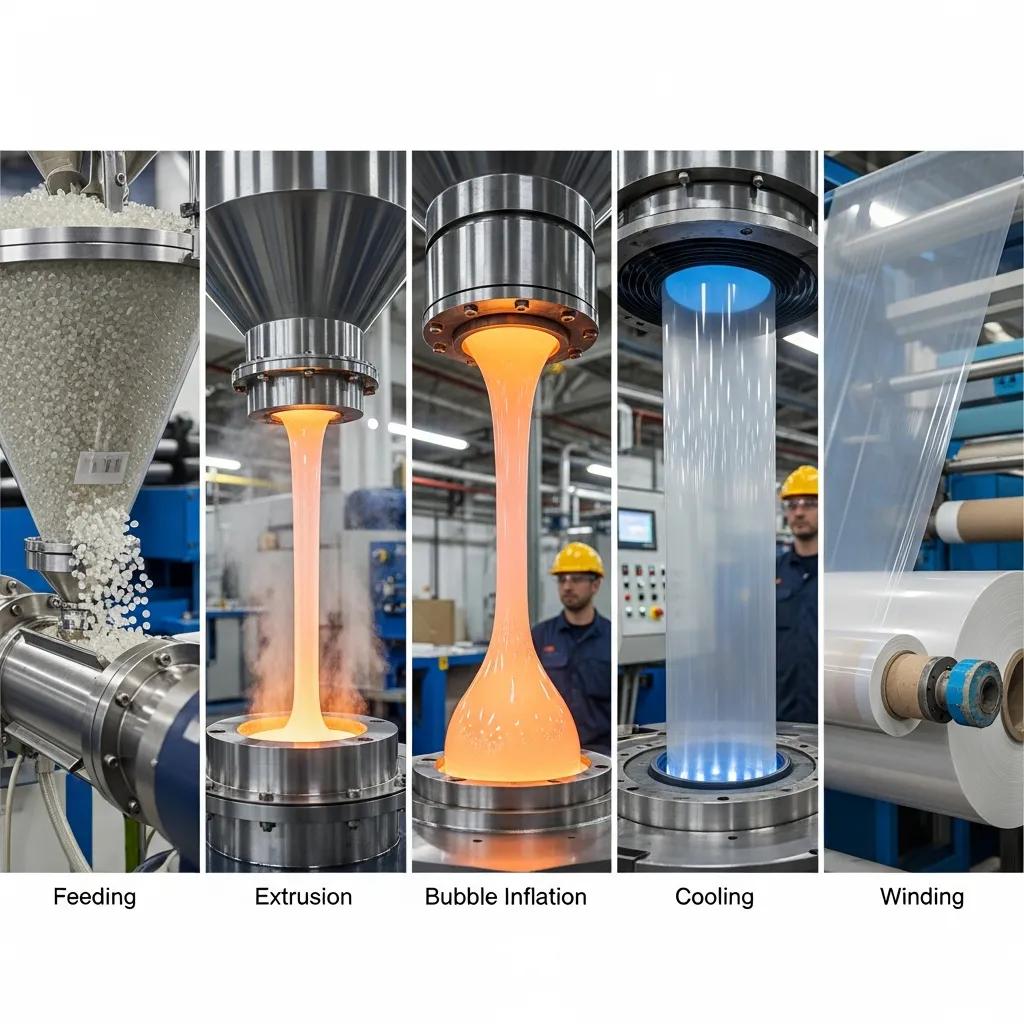

This subsection breaks the process into discrete operational steps, linking each to the components involved and expected outcomes to help operators and buyers set targets.
The table below maps these steps to the primary components and typical operating ranges so technical teams can compare expected parameters and tune processes during commissioning.
| Process Step | Key Components Involved | Typical Parameters / Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding & melting | Hopper, screw & barrel | Melt temp 160–230°C depending on polymer; consistent feed rate critical |
| Die extrusion | Annular die head, melt pump | Die gap controls throughput; melt pressure stable for uniform flow |
| Bubble inflation | Air ring, blow-up system | Blow-up ratio 2.0–3.0; influences film orientation and thickness |
| Cooling | Air ring, chill air, frost line control | Frost line height determines crystallinity; cooling rate affects clarity |
| Collapsing & winding | Nip rollers, winder, traversing system | Tension control and winding speed determine roll quality |
This mapping clarifies how each stage links to machine selection and process windows, which leads directly into selecting equipment components that influence those parameters.
A blown film line consists of functionally distinct components—extruder, die head, air ring, collapsing frame, nip rollers and winder—each shaping the film’s final properties and production efficiency. The extruder (screw diameter, L/D ratio and motor power) sets melt throughput and residence time, affecting dispersion and thermal stability. The annular die head design determines layer uniformity and coextrusion capability for multi-layer films; a quality die supports easy cleaning and channel balancing. The air ring and frost-line control are essential for consistent cooling and optical properties, while nip rollers and an accurate winder preserve gauge uniformity and roll quality. Selecting components requires matching capacity, control precision and serviceability to production goals.
| Component | Function | Selection Criteria / Buyer Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Extruder (screw & barrel) | Melts and conveys polymer | Select screw design for polymer type and output; consider motor sizing and gearing |
| Annular die head | Shapes melt into tubular film; enables coextrusion | Select for layer count, ease of maintenance and flow balancing |
| Air ring / cooling system | Controls cooling and frost line | Evaluate air distribution uniformity and adjustability |
| Nip rollers & collapsing frame | Collapse bubble and guide film | Material of rollers and tension control affect marking and surface finish |
| Winder & slitting units | Roll formation and finishing | Look for tension control, traversing precision and scrap handling |
These component definitions help buyers map functional needs to procurement decisions and prepare specifications for quotation requests, which is the next logical step when selecting a supplier or machine model.
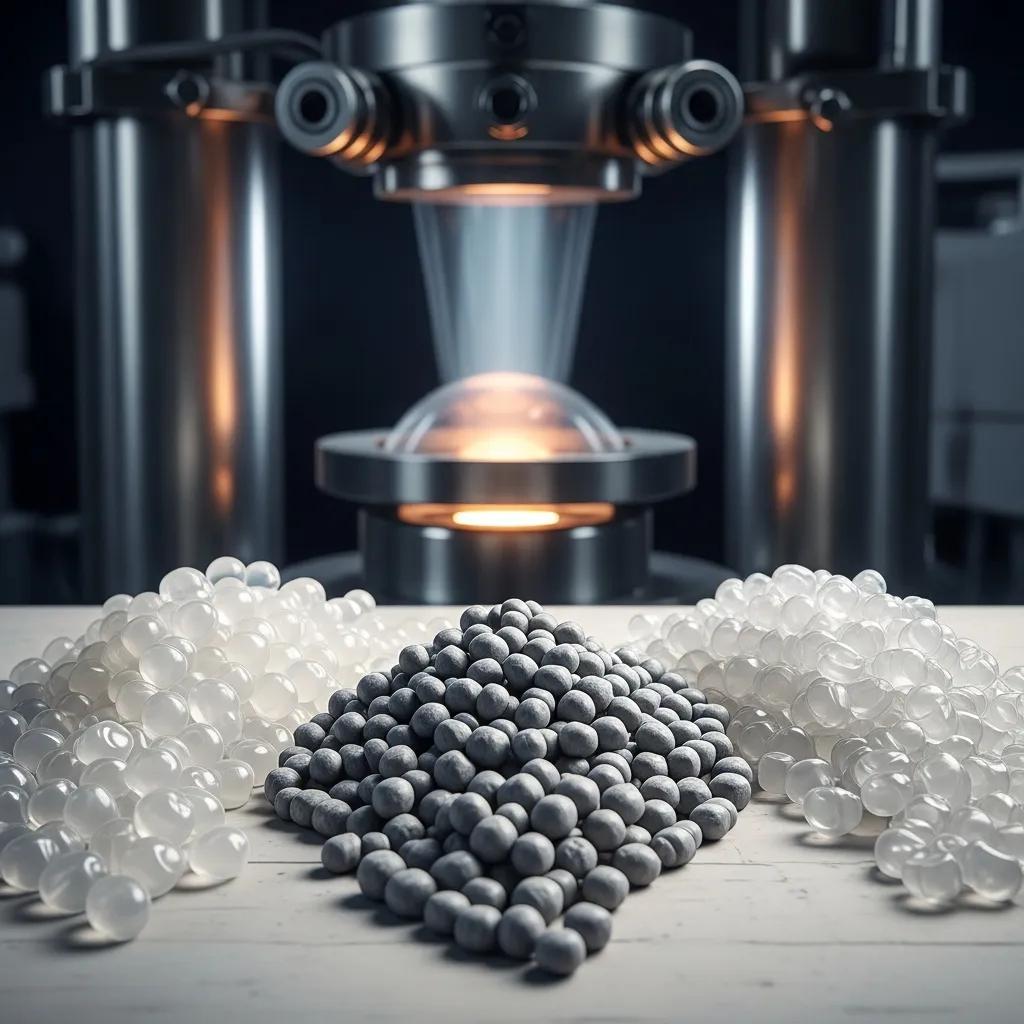

Raw material selection strongly influences mechanical performance, clarity, sealability and processability; typical blown film polymers include LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE and polypropylene, often used alone or in blends and coextruded layers. Material properties such as melt flow index, density, molecular weight distribution and additive packages determine required melt temperature, screw design and cooling strategy. Choosing the right polymer or blend for end-use—soft, clear consumer bags, robust industrial films or UV-stabilized agricultural sheets—minimizes waste and optimizes machine uptime. Understanding these relationships reduces trial runs during commissioning and helps specify extruder and die features.
This comparison summarizes the three primary polyethylene grades used in blown film and their typical applications so buyers can prioritize properties such as clarity, tensile strength and sealability.
| Polymer Type | Key Properties | Typical Applications / Film Performance |
|---|---|---|
| LDPE | High clarity, flexibility, good sealability | Soft retail and produce bags, twist-wrap films |
| HDPE | Higher stiffness, chemical resistance, lower clarity | Grocery bags, heavy-duty liners, industrial sacks |
| LLDPE | Superior toughness, puncture and impact resistance | Stretchable films, blends for better sealing and strength |
LDPE provides excellent optics and sealability, HDPE adds stiffness and cost-effectiveness for heavy-duty uses, while LLDPE offers toughness and puncture resistance that is often blended with LDPE to improve mechanical performance without sacrificing seal strength. These material choices guide screw selection, die design and cooling strategy during machine specification.
Polypropylene (PP) and other specialty polymers change film behavior by increasing stiffness, heat resistance and potentially improving barrier properties when used in coextrusion. PP offers higher melting point and tensile strength than many PEs, making it suitable when higher temperature resistance or stiffness is required; however, PP can have lower clarity and different sealing characteristics. Coextrusion allows PP or barrier layers (e.g., EVOH in specialized lines) to be combined with polyethylenes to tailor oxygen and moisture transmission. When selecting polymers beyond PE, buyers should ensure the extruder and die materials, screw configurations and temperature control ranges are compatible with the alternate polymer’s processing windows.
Blown film technology serves a broad spectrum of applications across consumer packaging, industrial protection, agriculture and specialized shrink or barrier films, owing to its adaptability to various thicknesses, layer constructions and additive packages. Packaging formats include shopping bags, produce bags, liners and printed flexible packaging; industrial uses cover pallet wrap, heavy-duty protection and bundling films; agricultural films include mulch, greenhouse and silage films that require UV stabilization. Being explicit about end-use requirements helps manufacturers set film specifications and determine whether single-layer or multi-layer coextrusion lines are needed.
The most common commercial applications include:
The following list breaks down common application categories and their typical film characteristics to guide production planning.
After evaluating these application requirements, manufacturers can align machine class (single-layer, multi-layer, high-speed) and material selection to meet specifications, then approach suppliers for models that match throughput and layer capabilities. For buyers in South Africa seeking machines suited to these markets, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (South African presence for Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) supplies a comprehensive range of blown film and accessory equipment—covering film for bags, shrink film and agricultural products—and offers customization, warranty terms and after-sales support that help bridge specification to production.
Food and consumer packaging demands films with consistent seal behavior, controlled oxygen and moisture transmission where necessary, and compatibility with printing and finishing. Food-contact-grade resins and proper processing (drying, contamination control) are critical to meet regulatory and safety requirements, while coextrusion can incorporate barrier layers for extended shelf life. Printability is achieved with surface treatment and proper tension control during winding to ensure registration and finish quality. These operational needs inform the selection of flexo-printing compatibility, chill and corona systems, and winding solutions during machine procurement.
Industrial films prioritize mechanical strength, puncture resistance and cost-effectiveness; agricultural films prioritize UV resistance and weathering stability. Typical thickness ranges vary widely: thin cling and shrink films may be under 20 microns, while greenhouse and silage films can be several hundred microns thick and often include UV and stabilizer additives. Material selection typically favors LLDPE or HDPE blends for strength, and processing adjustments—higher blow-up ratios, altered cooling and tailored screw designs—are used to reach required toughness and surface properties. Understanding these use-case driven production parameters enables manufacturers to specify relevant line components and polymer blends.
At the close of application selection, manufacturers can translate product specs into machine class choices and request tailored quotes; Plastic Bag Machine South Africa and Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. provide machines and add-on systems configured for film grades ranging from retail bag film to agricultural sheeting, and their product range and after-sales services can assist buyers in matching equipment to application needs.
Blown film extrusion offers clear advantages in film orientation, mechanical balance, and multi-layer coextrusion capability, but it also presents operational challenges such as lower line speeds versus some cast processes and sensitivity to bubble stability and operator skill. Advantages include uniform biaxial orientation leading to improved strength and toughness, flexibility in layer design for barrier or functional layers, and relatively low capital cost for small-to-medium lines. Disadvantages include higher scrap during startup, more operator-dependent control of the bubble and sometimes lower optical quality compared to cast film for certain polymers. Comparing these trade-offs helps manufacturers decide whether blown film is the optimal route for a given product.
The following lists summarize pros and cons to clarify decision-making:
A short comparison with cast film clarifies where blown film excels and where alternatives may be preferable:
Understanding these operational trade-offs lets buyers focus on required film properties and production economics when evaluating equipment.
Blown film’s primary benefits over cast film are mechanical toughness and the ability to produce multi-layer structures with balanced properties; biaxial orientation from the bubble process enhances tear resistance and elongation at break. Blown lines are also versatile across film thickness ranges and can be more cost-effective for small-to-medium production volumes. For applications requiring barrier layers or laminates, coextrusion enables a single-line solution that integrates barrier resins or recycled content. These advantages guide selection for food packaging, heavy-duty films and applications demanding durability.
Manufacturers should prepare for process control challenges such as bubble instability, gauge variation and contamination, and the need for precise frost-line and air ring adjustment.
Common failure modes include uneven die flow from poor melt distribution, unstable cooling leading to optical defects, and winding-related tension issues that cause telescoping or web breaks.
Mitigation strategies include robust melt filtration, regular maintenance of die and air ring, operator training, and automation or closed-loop controls to reduce variability.
Considering spare-parts availability and supplier training programs during procurement reduces downtime risk and supports long-term productivity.
Selecting the appropriate blown film extruder requires a checklist-driven approach: define production capacity (kg/hr), film width and thickness ranges, layer count, desired automation level and energy-efficiency targets. Clarify whether single-layer lines suffice or if multi-layer coextrusion (3-layer, 5-layer) is needed for barrier or strength. Evaluate control systems for precise speed, temperature and tension regulation, and confirm local after-sales service capability for installation, commissioning and spare parts. Considering power supply, factory footprint and staff skill-level helps avoid specification mismatches that can delay ramp-up.
The following procurement checklist helps buyers prioritize requirements before requesting quotes:
When technical requirements are established, supplier selection should assess machine features such as screw design, control systems, coextrusion heads and energy efficiency. Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (South African presence for Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) is a supplier option that emphasizes cost-effective machinery, comprehensive product range and after-sales service; Kingdom Machinery has installed machines across many countries, supports customization, and highlights outgoing quality control (100% final inspection) and warranty provisions that can be important in procurement decisions. Buyers should request detailed quotations, installation and training terms, and references for similar installations during the evaluation phase.
Machine categories range from compact single-layer lines for small-batch production to multi-layer coextrusion systems and high-speed lines for high-volume packaging. Key features to compare include screw diameter and L/D (affecting throughput), die head design and layer count, automation level of temperature and speed controls, and ancillary equipment such as chillers, corona treatment and flexo printing integration. Typical throughput ranges vary by class—compact machines suit low-to-moderate throughput, while industrial coextrusion lines provide higher kg/hr and integrated finishing. Evaluate footprint and modularity if future capacity expansion or additional layers are anticipated.
Sourcing options in South Africa include local representatives for international manufacturers, regional distributors and direct purchases from overseas manufacturers with local presence. Important evaluation questions to ask suppliers include warranty terms, the extent of installation and commissioning support, training provisions for operators and technicians, spare parts availability, and remote/online support capabilities. Confirm whether suppliers provide customization for local power conditions and factory layout, and request references or case studies of comparable installations. For buyers seeking an integrated one-stop supply with after-sales support and customization, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (South African presence for Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers blown film lines, printing and recycling machines, claims two-year warranty on specified components and provides 24-hour online support—attributes that can shorten ramp-up time and reduce downtime risk. Interested teams should prepare a clear specification and request detailed proposals and site visit arrangements from shortlisted suppliers.
Recent trends focus on sustainability, higher automation, integration of recyclates and advanced multi-layer coextrusion to meet barrier and functional requirements while reducing environmental impact. Manufacturers and OEMs are adopting energy-efficient motors, servo-driven extruders, and process controls augmented by IoT sensors for predictive maintenance and reduced scrap. Coextrusion chemistry advances allow incorporation of barrier layers and higher ratios of recycled content without sacrificing performance. These innovations improve economics and regulatory compliance and shape procurement priorities for new installations.
Sustainability drives material choices (recyclates, mono-material designs) and machine features (energy-efficient drives, improved melt-filtration to reduce rejects). Incorporating recyclate requires careful process control—adjusted screw profiles, temperature management and sometimes dedicated extruders—to maintain film properties; machine configurations that facilitate quick color/material changes reduce contaminated runs. Regulatory and market pressures in 2024–2025 increase demand for recyclable packaging and for machines that support circular-material workflows. Suppliers offering support for recyclate integration and energy reduction can accelerate customers’ sustainability roadmaps while maintaining productivity.
Automation improves repeatability and reduces operator dependence through closed-loop control of melt pressure, speed, temperature and winding tension, which directly reduces gauge variation and scrap. Multi-layer coextrusion is advancing with more compact, modular die heads capable of 3-layer to 7-layer constructions that enable barrier and functional layers while maintaining compact footprints. These advances deliver consistent product quality, faster changeovers, and improved ROI by lowering waste and increasing first-pass yield; buyers should assess control-system sophistication and recipe management when evaluating modern lines.
For manufacturers ready to move from specification to procurement, suppliers with strong R&D, diverse product ranges and reliable after-sales service can shorten commissioning time and improve long-term performance. Plastic Bag Machine South Africa and Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. emphasize a one-stop product range—from blown film machines to flexo printing and recycling solutions—and cite installation experience across many international markets plus ongoing online support to assist with commissioning and troubleshooting.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.