Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
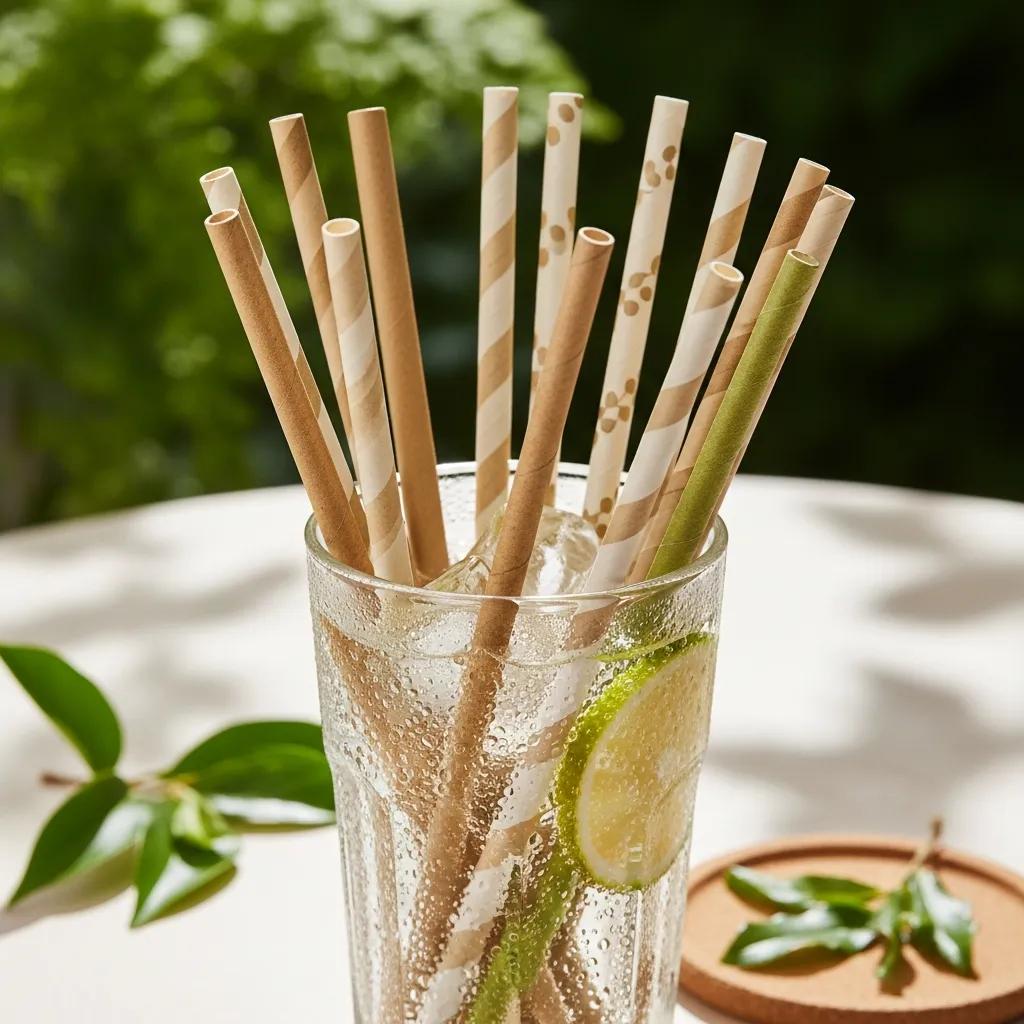

Eco-friendly biodegradable drinking straw production transforms single-use disposables into compostable, lower-impact products by using bioplastics like polylactic acid (PLA) and food-grade paper combined with specialized manufacturing equipment. This guide explains the machines, materials, and end-to-end processes required to produce compostable drinking straws, and it shows how manufacturers can align production choices with regulatory drivers and market demand. Readers will learn how PLA straw extrusion lines differ from automatic paper straw machines, which biodegradable feedstocks suit different beverages, and how production workflows—from material prep to cutting and packaging—deliver consistent quality. The article also covers South Africa–specific market signals, troubleshooting, buying criteria, and maintenance planning so entrepreneurs and manufacturing managers can assess CAPEX/OPEX implications and scale production responsibly. Throughout, we use target terms such as compostable drinking straw making machine, biodegradable drinking straw machine, PLA straw extrusion line, and paper straw machine to map practical decisions to equipment options for sustainable manufacturing.
Eco-friendly biodegradable drinking straw machines are manufacturing systems designed to convert renewable feedstocks into single-use straws that break down under composting conditions, replacing conventional fossil-plastic straws. These machines fall into two primary categories: PLA straw extrusion lines that melt and shape bioplastic into rigid tubes, and paper straw manufacturing equipment that spirals and bonds food-grade paper into durable, liquid-resistant tubes. Both machine types control critical process variables—temperature, adhesive application, and dimensional tolerance—to produce straws that meet food-safety and performance standards while minimizing waste. By using specialized moulding heads, cooling, and cutting units, these systems deliver consistent diameters and wall thicknesses suitable for hot and cold beverages. Understanding these machine families clarifies investment choices for manufacturers seeking sustainable product lines.
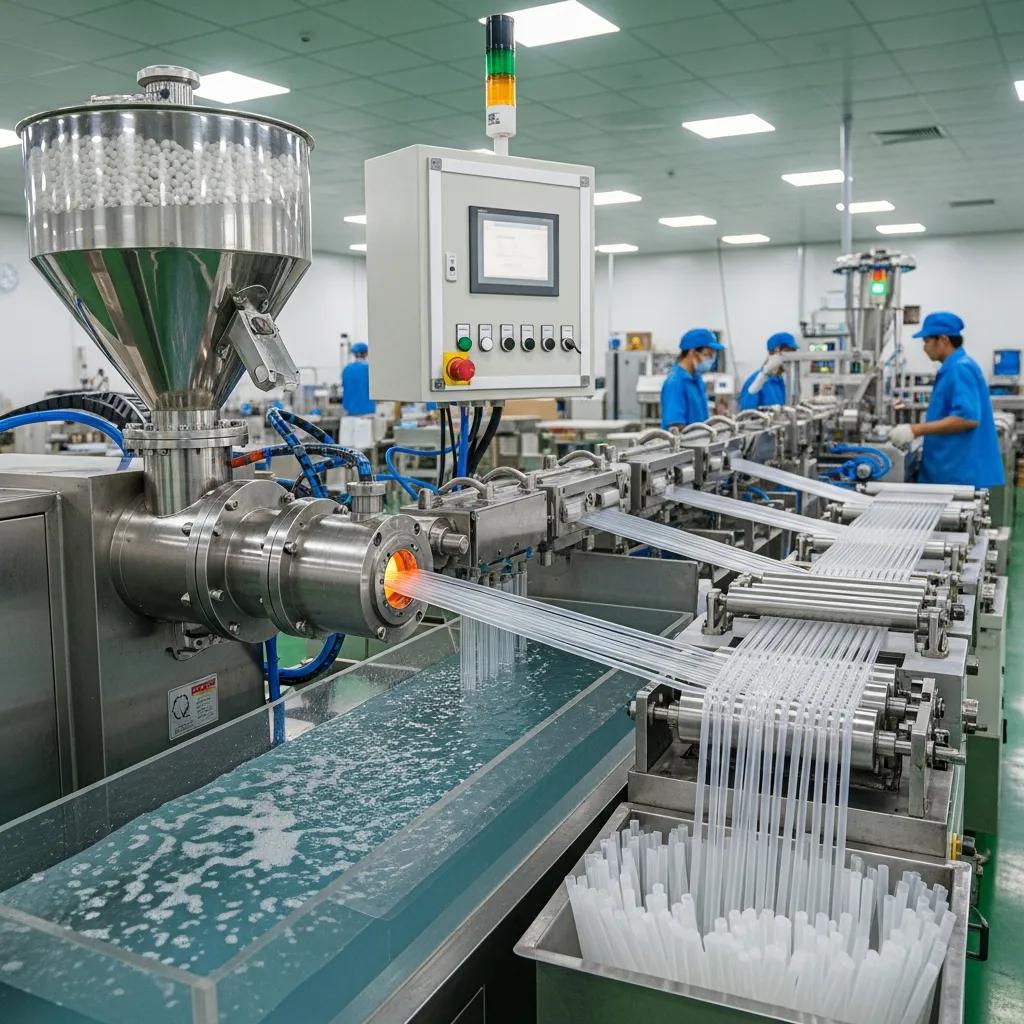

PLA straw making machines operate by converting polylactic acid resin into continuous tubular profiles through a controlled extrusion and forming process that preserves mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy. The process begins with material drying to remove moisture, followed by melting in an extruder where screw speed and barrel temperature control melt homogeneity and throughput; the molten PLA is then pushed through a sizing die or moulding head to form a straw profile. After extrusion, a cooling tank or air-cooling array stabilizes the shape while hauling units maintain tension and speed control prior to precision cutting; quality checkpoints monitor diameter, wall thickness, and surface finish to reduce rejects. Operators tune screw RPM, die gap, and haul-off speed to balance rigidity and flexibility for end-use; troubleshooting commonly addresses die build-up, inconsistent melt flow, and thermal degradation. Clear process control yields reproducible compostable drinking straw machine output suitable for packaging and private-label supply.
Optimizing PLA Straw Production: Addressing Macular Defects in Manufacturing
The PLA (polylactic acid) straw macular quality problems were analyzed, and the optimization scheme of PLA straw production process was proposed. The main factors affecting the formation of macular defects in straw production are cleaning frequency, material viscosity, and extrusion temperature. The optimization scheme of PLA straw production process is to improve the cleaning frequency, adjust the material viscosity, and control the extrusion temperature.
Manufacturing process analysis and optimization of polylactic acid straw based on improving macular defects, 2023
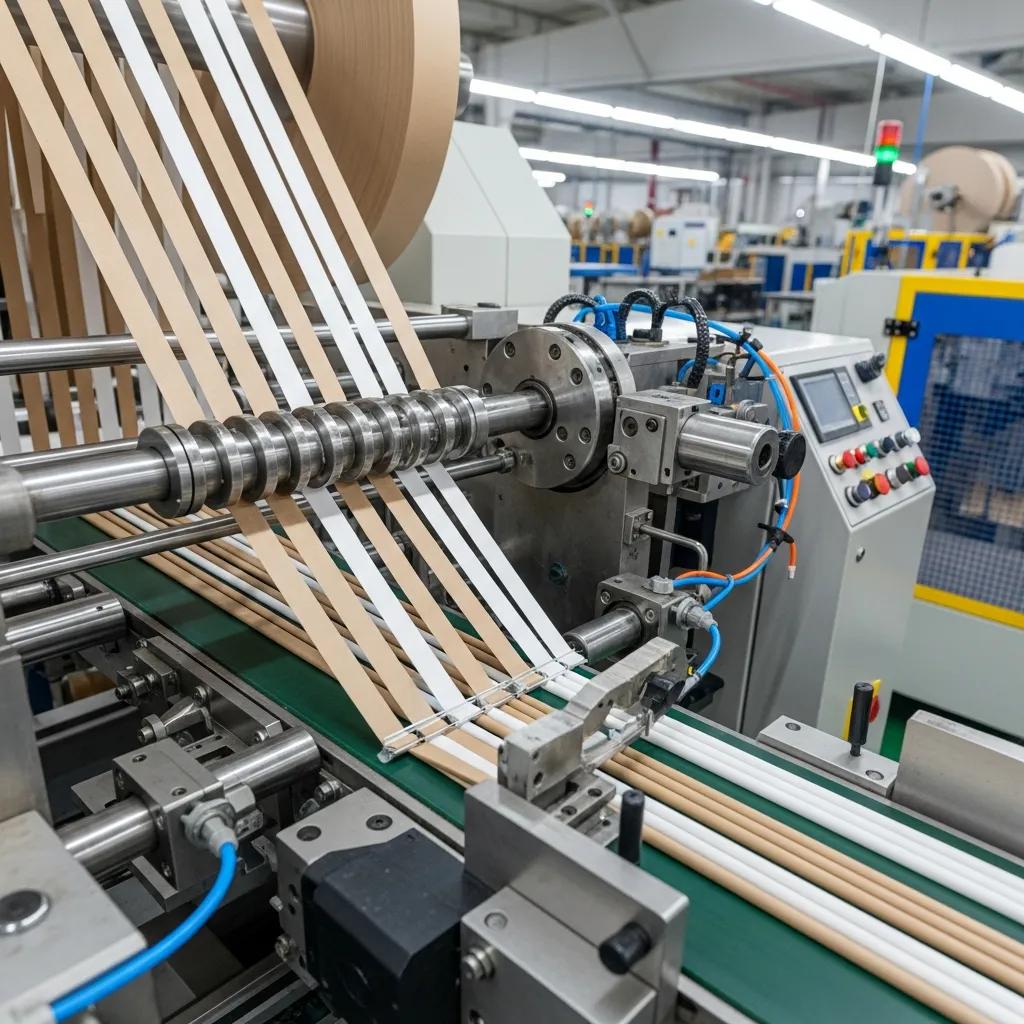

Paper straw manufacturing equipment uses spiraling heads to wind food-grade paper strips around mandrels while applying a food-safe adhesive and curing the seam to create a sturdy, moisture-resistant tube suitable for beverages. Raw paper rolls are precision slit into strips, guided to a spiraling head where seam overlap and glue application are controlled to ensure seam integrity and consistent inner diameter; drying tunnels and controlled curing zones remove moisture and stabilize the adhesive bond. High-speed machines incorporate trimming, end-finishing, cutting, and optional printing modules so branded straws and packaging can be completed inline, while seam strength and moisture resistance tests validate performance. Machine variables that influence output include strip width, glue viscosity, spiraling head speed, and drying temperature; adjusting these factors balances production rate with seam durability and tactile finish for different beverage temperatures.
Superhydrophobic and Degradable Cellulose Paper Materials for Eco-Friendly Straws
Cellulose-based materials are considered to be green and sustainable substitutes for plastics. However, their hydrophilicity and water instability limit further applications. Herein, ethyl cellulose (EC) and hydrophobic SiO2nanoparticles (NPs) were employed to prepare hydrophobic SiO2@EC/P materials by dipping-spraying method. A series of cellulosic papers with various hydrophobicity (water contact angle (WCA) from about 90° to 166°, and contact angle hysteresis (CAH) less than 5°) were fabricated by varying the amount of SiO2NPs. The dry and wet strength of the modified paper increased by 72.3% and 916.7%, respectively. Soaking test shows that the SiO2@EC/P straws remain intact after being placed in different beverages and water at the temperature of 0 to 90 °C for 2 h. Furthermore, these straws can be completely degraded after being buried into the soil for 200 days. Therefore, SiO2@EC/P materials are promising alternative materials for plastic straws. The potential application of SiO2@EC/P materials would effectively alleviate the ‘white pollution’ problem.
Fabrication of superhydrophobic and degradable cellulose paper materials for straw application, CM Ewulonu, 2022
Biodegradable drinking straws are made from a limited set of bio-based feedstocks selected for food safety, processability, and biodegradability under composting conditions; the main options are PLA, food-grade paper, starch blends, and edible or seaweed-based materials. Each material brings trade-offs: PLA offers thermoplastic processing and rigidity for cold and warm drinks but requires industrial composting to meet compostability claims, while paper offers broad compostability and recyclability depending on coatings and glue. Alternative feedstocks, such as starch blends and seaweed-derived polymers, provide niche applications (e.g., edible or water-dispersible straws) and can reduce reliance on land-intensive crops if sourced responsibly. Selecting material depends on regulatory definitions of compostability, desired product lifespan in use, processing compatibility with extruders or spiraling heads, and end-of-life infrastructure available to customers.
Different biodegradable materials used for drinking straws are compared below to help manufacturers match feedstock to product requirements.
| Material Type | Source / Form | Biodegradability & Composting Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Fermentation-derived lactic acid (corn/starch) → polymer pellets | Industrial composting required for complete biodegradation; strong, thermoplastic behavior for extrusion |
| Food-grade Paper | Virgin or recycled pulp in coated/uncoated rolls | Broadly compostable; seam integrity depends on adhesive and coating choices; suitable for spiraling machines |
| Starch Blends (PLA-starch, PHA blends) | Plant starch blended with bio-polymers | Biodegradability varies by formulation; may be suitable for home or industrial composting depending on blend |
| Seaweed / Edible Polymers | Algae or seaweed-derived gels | Emerging feedstocks for edible or water-dispersible straws; process integration still developing |
This comparison highlights material readiness and processing implications; manufacturers should align feedstock selection with available composting infrastructure and product positioning.
Sustainable Biodegradable Straws from Agricultural Waste: An Alternative to PLA
However, the manufacturing of PLAS needs sugar-based feedstocks (eg, corn starch), which compete with food production. In summary, waste rice stalk was used to convert into biodegradable straws by redistribution of the components of rice stalk, which can be used as a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics and PLA.
Sustainable straws from agricultural waste fibers with excellent toughness, water resistance, and biodegradability, SY Leu, 2024
A complete biodegradable straw production line sequences material handling, forming, cooling or drying, hauling, cutting, finishing, and packaging to convert raw feedstock into packed straws ready for distribution. For PLA extrusion lines, key stages include drying, extrusion and die forming, cooling and dimensional control, hauling and tension control, precision cutting, and optional printing or packaging modules. For paper straw lines, the workflow centers on roll unwinding, strip slitting, glue metering and spiraling, drying/curing, seam strength verification, cutting, and packing. Each stage contributes to throughput, yield, and energy consumption; integrated quality control systems check diameter, wall thickness, seam bond, and surface finish to reduce customer complaints and reworks. Understanding how stages interact helps manufacturers model CAPEX/OPEX, plan for spare parts, and optimize yield for different product SKUs.
Numbered steps summarize the general production flow so manufacturers can visualize an end-to-end line:
These steps frame the production responsibilities operators must manage to maintain consistent quality and throughput; the following table maps equipment stages to typical machine units and expected operational focus.
| Production Stage | Typical Machine Unit | Primary Operational Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Material Prep | Dryer / Roll Unwinder | Moisture control, consistent feed rate |
| Forming | Extruder + Die / Spiraling Head | Shape accuracy, glue/seam application |
| Stabilization | Cooling Tank / Drying Tunnel | Dimensional stability, adhesive curing |
| Hauling & Cutting | Haul-off Unit + Cutter | Tension control, precise length |
| Finishing & Packing | Printing + Packager | Branding, protective packaging |
PLA straw extrusion begins with feedstock drying to below recommended moisture levels to prevent hydrolytic degradation, then controlled melt in a single- or twin-screw extruder where residence time and temperature profile determine melt quality. The molten PLA enters a sizing die or mandrel assembly that shapes the inner and outer diameters; immediately after forming, cooling—by a water bath or air gap—fixes the geometry and prevents ovality. Downstream, a haul-off mechanism maintains constant linear speed while sensors monitor diameter and wall thickness; a precision cutter delivers final lengths and may integrate counters for packaging. Operators implement QA steps at drying, extrusion, and post-cooling stages to detect die build-up, surface imperfections, or dimensional drift and to ensure compliance with food-contact requirements.
Paper straw spiraling begins by unwinding parent rolls and slitting them into uniform strips, which are then guided into a spiraling head that winds strips around a mandrel while a food-grade adhesive is applied to the seam. The spiraled tube passes through a drying or curing section where heat and airflow set the adhesive and stabilize the tube; seam overlap and glue distribution are tuned to achieve required seam strength while minimizing internal roughness. After curing, a trimming and cutting station delivers final lengths and optional end-finishing, and inline tests verify moisture resistance and seam integrity to ensure beverage performance. Production speed depends on glue curing rate, drying energy, and spiraling head precision; balancing these parameters helps manufacturers scale output without sacrificing durability.
Producing biodegradable straws in South Africa presents clear commercial benefits driven by regulatory pressure on single-use plastics, growing hospitality and retail demand for sustainable packaging, and opportunities for private-label manufacturing and contract production. Local manufacturers can capitalize on decreasing acceptance of conventional plastic straws by offering compostable alternatives to restaurants, hotels, packaged beverage brands, and events, using either PLA or paper-based products tailored to end-use requirements. Supply-chain considerations—sourcing certified food-grade materials and ensuring access to industrial composting or recycling channels—shape product positioning and pricing power. Entrepreneurs assessing investment should evaluate demand in key sectors, expected price premiums for compostable items, and logistics for raw materials and finished goods across South Africa.
The South African market context and supplier options point to practical next steps for buyers:
For manufacturers seeking turnkey production lines or a supplier with a broad machinery portfolio, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa operates as a representative of Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. and supplies Drinking Straw Machine models alongside complementary equipment such as plastic bag making machines, blown film extrusion, flexo printing machines, and plastic recycling machines. Their stated service offerings include final inspection during production, two-year warranty on timer switches, R&D support, one-stop service from innovation to mass production including branding and new product development, large production capacity, competitive pricing through scale, and timely after-sales service. Manufacturers interested in a tailored equipment quote or catalogue for South African operations are encouraged to request a formal quotation and discuss turnkey options.
Single-use plastic restrictions and municipal-level bans increase demand for certified biodegradable alternatives and create procurement opportunities for compliant suppliers, especially within hospitality and government tendering for food-service items. Regulations often define acceptable materials and required compostability or biodegradability certifications; manufacturers must confirm product claims align with those legal definitions and that end-of-life infrastructure exists to support composting or industrial processing. Compliance also influences sourcing decisions—importing certified PLA pellets or ensuring paper complies with food-contact and migration limits—and shapes labelling and marketing claims. Producers who build traceability, certification documentation, and clear disposal instructions into their product packaging gain access to regulated contracts and institutional buyers.
Market trends in 2024 show steady adoption of compostable straws across food service and retail, with manufacturers capturing margin through private-label contracts and differentiated, branded offerings; payback periods depend on utilization, product mix, and material costs. Key variables affecting ROI include machine throughput and uptime, raw material price volatility (PLA vs paper pulp), labor and energy costs, and the ability to secure higher-margin contracts for premium or branded straws. Manufacturers should model scenarios based on conservative utilization estimates and include spare-parts provisioning and training in OPEX assumptions. Scaling strategies—starting with a single-line for local distribution and expanding to multiple lines as demand grows—mitigate risk while capturing early market share.
Choosing and maintaining eco-friendly drinking straw machines involves evaluating production capacity, material compatibility, automation features, ease of changeover, and after-sales support to ensure sustained throughput and quality. Key technical features include production capacity in pieces per minute, precise temperature and screw controls for PLA lines, spiraling head tolerances and glue metering for paper lines, footprint and power requirements, and optional modules such as flexo printing and automated packaging. Maintenance planning covers scheduled preventative inspections for extruder screws, die cleaning, adhesive pump servicing, spare knife blades, and wear parts for haul-off units; a documented spare-parts list and access to technical support reduce downtime risk. Choosing a supplier with robust R&D, quality inspection processes, warranty terms, and commissioning services shortens ramp-up time and improves early yields.
Before listing model attributes, here is a concise checklist of features buyers should prioritize when comparing machine offers.
This checklist guides initial vendor screening and should be followed by factory acceptance tests and pilot runs to validate claims against real feedstock and product specifications.
| Machine Model Category | Key Attribute | Typical Supplier Value |
|---|---|---|
| Small-scale PLA Extruder | Production capacity (pcs/min) | Modular low-to-medium throughput; compact footprint |
| High-speed Paper Straw Machine | Automation & printing | High throughput with optional flexo printing module |
| Turnkey Production Line | After-sales support | Commissioning, training, and spare-parts list included |
Compare shortlisted machines using performance trials and request supplier references for commissioning and spare-parts responsiveness to reduce operational risk.
When evaluating PLA and paper straw machines, prioritize robust process controls, material handling systems that protect feedstock integrity, and modular automation that allows printing and packaging integration. For PLA lines, essential features include accurate drying systems, reliable screw designs for melt homogeneity, precision die assemblies, and effective cooling to minimize dimensional variance. For paper lines, look for precise slitting, controlled glue metering with food-safe adhesives, adjustable spiraling heads, and efficient drying tunnels to maintain seam strength at speed. Optional modules—flexo printing for branding, automatic bagging for retail-ready packs, and inline quality inspection—enhance value but should be weighed against budget and utilization forecasts.
Good suppliers provide comprehensive services including site assessment for electrical and ventilation requirements, installation and commissioning, operator training, documentation, and a spare-parts kit to support early operations. Installation typically covers mechanical alignment, electrical integration, safety interlocks, and performance verification against agreed test runs; training includes operation, routine maintenance, and basic troubleshooting. After-sales support elements to negotiate include warranty terms, availability and lead times for critical spare parts, remote diagnostic assistance, and optional on-site service contracts. Having a clear service-level agreement and documented parts list helps reduce downtime and ensures predictable maintenance budgeting.
For manufacturers desiring integrated supplier capabilities, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa represents Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. and emphasizes one-stop service from innovation to mass production, R&D support, final inspection during production, and timely after-sales service; potential buyers should request a quotation and discuss commissioning and spares planning when evaluating turnkey offers.
Prospective buyers commonly ask about cost drivers, lead times, operational yields, regulatory compliance, and the basic steps to produce compostable straws; clear answers help set realistic expectations for procurement and operations.
Below are concise FAQ-style answers addressing top buyer concerns.
Cost questions are best handled by evaluating specific configurations and service packages rather than relying on list prices; key pricing factors include production capacity, level of automation, optional printing and packaging modules, shipping and import duties, and the extent of commissioning and training required. Buyers should request a formal quotation that itemizes machine components, spare parts, warranty terms, and lead times so total cost of ownership can be modeled over expected throughput. Negotiating on service-level agreements, spare-parts arrangements, and training days often yields better predictability than focusing on headline machine price alone. For accurate quotations and catalogue options tailored to South African operations, request a supplier proposal.
Biodegradable straw manufacturing follows two succinct processes depending on material: for PLA, the steps are material drying → extrusion through a die, cooling, hauling, and cutting; for paper, the steps are roll slitting → adhesive application and spiraling → drying/curing → cutting, testing and packing. Quality control occurs at multiple points—after forming for dimensional checks, after curing for seam strength, and post-cutting for final length and surface finish—to ensure product performance. These concise workflows are the foundation for operational plans, CAPEX/OPEX modelling, and supplier acceptance testing during purchase.
This numbered summary aligns with featured snippet expectations and guides buyers toward validating supplier process capabilities during factory acceptance tests.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on being a leading manufacturer of plastic bag making machines. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that our customers receive the best machinery tailored to their specific production needs. By choosing us, you are partnering with a company that has established itself as a trusted name in the industry.
Our extensive range of plastic bag machinery includes options for various applications, from shopping bags to biodegradable solutions. We understand the importance of efficiency and reliability in production, which is why our machines are designed for optimal performance, ensuring your business can meet market demands effectively.
Our plastic bag machines are engineered to provide numerous advantages, including ease of operation, low maintenance costs, and high productivity rates. These features make them ideal for businesses looking to enhance their manufacturing processes while keeping operational costs low.
Additionally, our machines are equipped with advanced technology that ensures consistent quality in production. With energy-efficient designs and robust construction, our equipment not only meets but exceeds industry standards, providing you with a competitive edge in the market.
We have had the pleasure of serving over 1000 satisfied customers across various regions, each with unique needs and challenges. Our commitment to customer satisfaction is reflected in the positive feedback we receive, showcasing the effectiveness of our machines in real-world applications.
From small start-ups to large manufacturing plants, our clients have successfully integrated our machinery into their operations, leading to increased productivity and profitability. These success stories underscore our dedication to providing tailored solutions that foster growth and innovation.
As a forward-thinking manufacturer, we continuously invest in research and development to bring the latest innovations to our plastic bag machines. This commitment allows us to offer cutting-edge technology that enhances production efficiency and reduces waste.
Our innovations include features such as automated controls, real-time monitoring systems, and environmentally friendly production processes. By adopting these advancements, our clients can not only improve their operational efficiency but also align with global sustainability goals.