Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
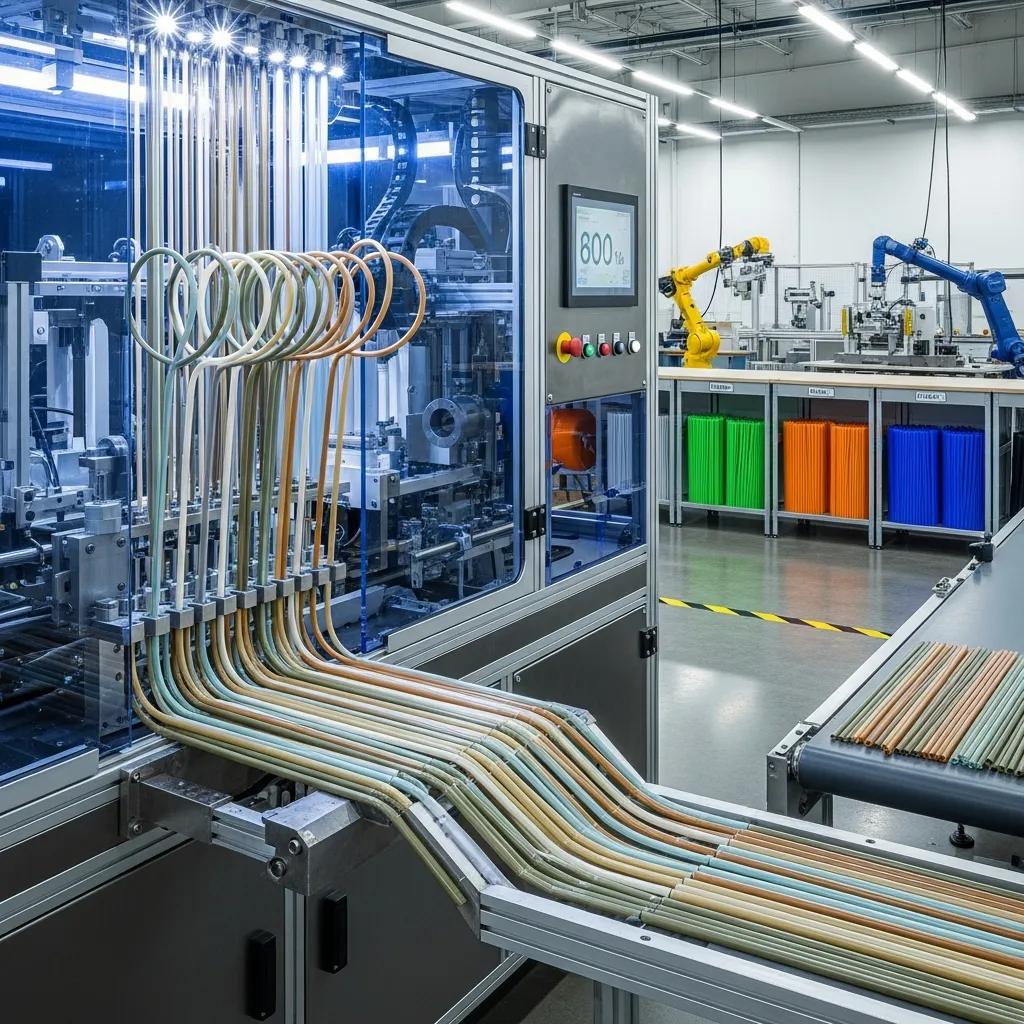

Drinking straw machines are industrial systems that form, cut, and finish straws from polymers or paper, and they are increasingly sought by manufacturers and entrepreneurs in Bloemfontein looking to supply cafes, beverage producers, and packaging companies. This guide explains the main machine categories, sustainable options, high-speed automation benefits, local procurement paths, business setup considerations, and essential accessories so you can evaluate equipment and scale production thoughtfully. Many buyers must balance throughput, material compatibility, and compliance with evolving South African demand for biodegradable options; this article offers practical comparisons, specifications, and purchasing checklists to simplify that process.
You will learn how plastic extrusion, paper forming, and PLA/PHA systems differ in operation and cost structure, what to look for in high-speed lines, and how accessories such as cutters and packagers integrate into an automatic straw production line. Practical tables and lists highlight machine attributes, performance metrics, and accessory compatibility to speed decision-making. Following these sections, specific guidance shows where to request quotes and what after-sales support to expect when sourcing machines for delivery to Bloemfontein.
Drinking straw machines available to South African buyers fall into three main categories—plastic extrusion, paper forming, and biodegradable-material systems—each defined by feedstock, machine architecture, and end-use suitability. Plastic straw extrusion machines melt and shape polymer resins like PP and PE through an extruder and downstream forming tools to deliver high-throughput, low-cost straws; paper straw making machines wrap, glue, and cut paper tubes for compostable single-use applications; biodegradable straw machines process PLA, PHA or agricultural materials using controlled drying and temperature profiles to retain bio-polymer properties. Understanding these distinctions helps manufacturers choose equipment that matches market demand, regulatory requirements, and production scale. The short table below compares core attributes to help you narrow options quickly before examining model-level specs.
| Machine Category | Material Compatibility | Typical Production Capacity | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Extrusion | PP, PE | 200–800 pcs/min (model dependent) | High-volume beverage and food service suppliers |
| Paper Forming | Food-grade paper, adhesive | 60–300 pcs/min | Eco-focused cafés, retail packaging |
| Biodegradable Systems | PLA, PHA, agricultural feedstocks | 50–300 pcs/min | Brands seeking compostable certifications |
This comparison highlights that plastic extrusion favors the highest throughput while paper and biodegradable systems prioritize environmental attributes, leading naturally to a closer look at plastic extrusion features and paper forming mechanics.
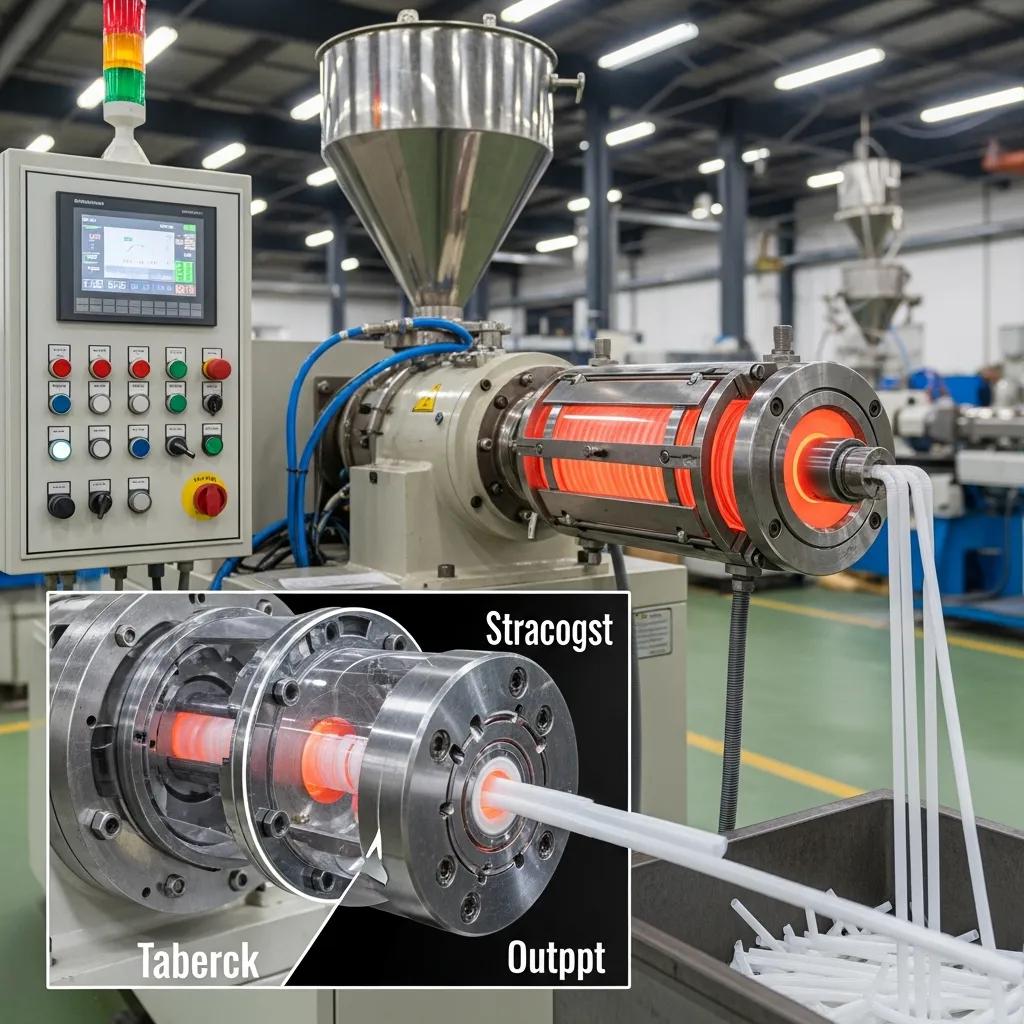
Plastic straw extrusion machines use an extruder with a precisely engineered screw, feed throat and heating zones to melt and homogenize PP or PE resins, then push material through a die to form continuous tubing that is cut and optionally bent. Typical specifications include screw diameters tailored to throughput, motor power rated for steady-state extrusion, and PLC control panels for process consistency; these features produce output ranging from low hundreds to several hundred pieces per minute depending on model. Maintenance centers on nozzle and die wear, screw inspection, and timely spare parts like cutters and sensors to sustain uptime, and many manufacturers offer 100 percent final inspection during production to ensure quality. For buyers focused on long runs, consider energy consumption, footprint and ease of tooling changes for diameter or color shifts—these choices influence operating cost and product flexibility, and they lead into comparisons with paper straw forming.
Paper straw making machines feed printed or plain paper rolls through gluing, forming mandrels, and cutting stations to deliver a range of diameters and lengths suitable for hot and cold drinks, with tooling that supports multi-layer constructions for strength. Production rates typically range from several dozen to a few hundred pieces per minute depending on machine size and whether drying and printing modules are integrated; required raw materials include food-grade paper, approved adhesives, and core tooling. Paper straw lines have different maintenance needs than polymer extruders: adhesive system cleanliness, drying efficiency, and forming mandrel wear are primary concerns, and sourcing consistent paper rolls is critical for product quality. Given rising consumer demand for biodegradable options, many buyers weigh the lower lifecycle impact of paper straws against their slightly higher per-unit cost and supply-chain considerations.
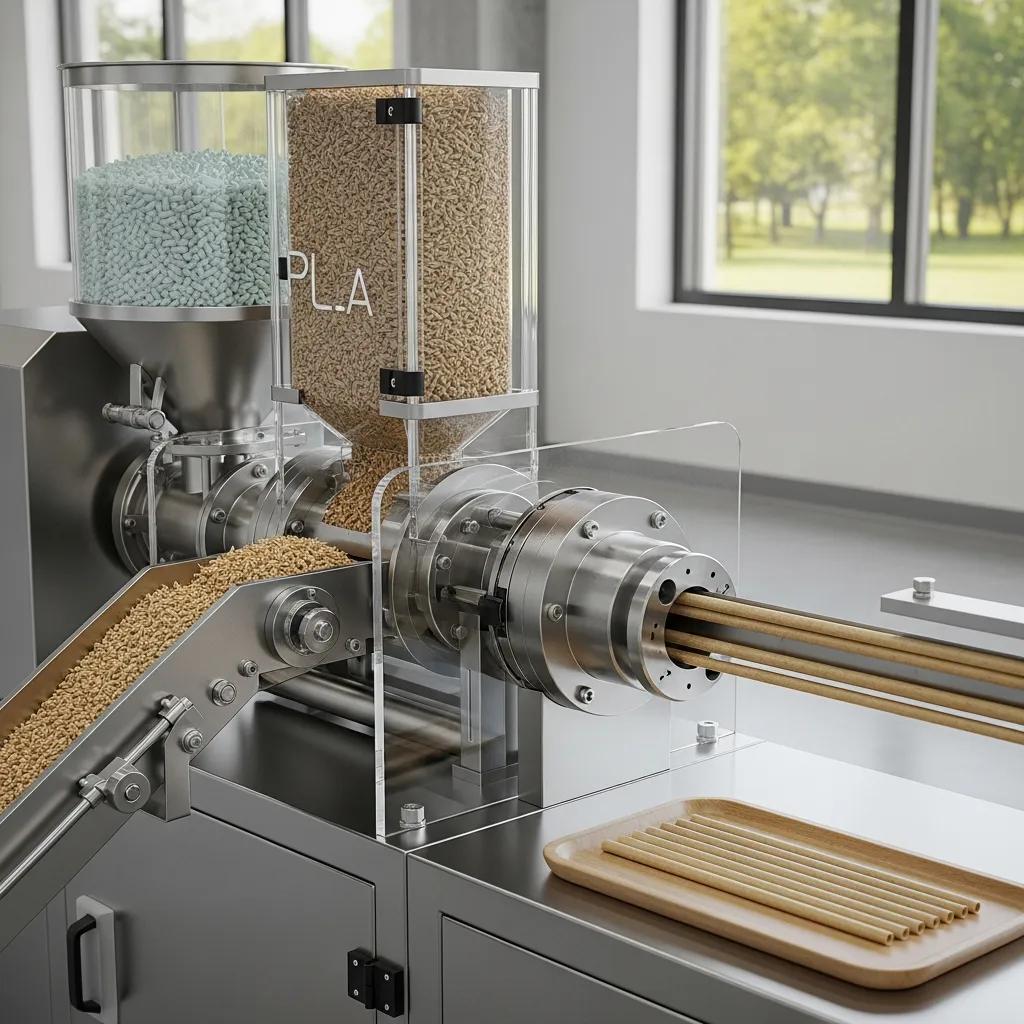

Biodegradable straw machines enable production from compostable polymers and agricultural byproducts by adapting extrusion and forming parameters to the material’s thermal sensitivity and physical properties, producing straws with reduced environmental persistence. These systems treat PLA and PHA differently from PP/PE: lower melting points, need for moisture-controlled feeding, and careful cooling to prevent deformation are central to processing; the result is straws that meet growing consumer and regulatory expectations for compostability. The environmental advantage is twofold: lower plastic pollution risk and market alignment with retailers seeking sustainable packaging, which can translate to premium product positioning. The following subsections detail technical approaches for PLA/PHA and using rice or sugarcane feedstocks so manufacturers understand practical trade-offs and equipment adaptations.
PLA and PHA straw production requires careful drying of pellets, controlled extruder temperature profiles, and sometimes retrofit components such as vacuum calibrators and specialized dies to maintain dimensional stability, because these biopolymers display narrower processing windows than conventional plastics. Typical machine adaptations include material dryers before the hopper, accurate heater zones on the extruder, and calibration units to ensure roundness and wall thickness, which together support consistent output and acceptable mechanical properties for drinking use. Production capacities are often lower than identical-size PP lines due to slower safe-processing speeds, but modern biodegradable straw machines preserve finish quality and reduce post-processing scrap when operated within specifications. Understanding these constraints helps planners estimate CAPEX and establish realistic throughput expectations for eco-focused product lines.
Converting agricultural byproducts such as rice husk derivatives or sugarcane fibers into straw-like products often involves preprocessing steps—drying, grinding, and pelletizing—followed by adapted extrusion or forming that accommodates heterogeneous feedstocks and higher filler content. These machines include robust feeders and screw designs tolerant of fibrous material, and they may use binders or coatings to meet strength and food-safety requirements; throughput varies with feedstock quality and preprocessing investment. The sustainability trade-off is that while agricultural-material straws can reduce reliance on synthetic polymers and circular waste, they demand additional upstream processing and quality control to ensure uniform product properties. For manufacturers, evaluating feedstock availability, preprocessing costs, and end-market acceptance is essential before choosing agricultural-material-based straw equipment.
High-speed drinking straw machines deliver large throughput, tight dimensional tolerances, and automation that lowers labor costs while improving unit economics and consistency for high-demand production environments. The principal performance drivers are a reliable extruder or forming head, precision cutting units, synchronized bending modules (if required), and an advanced control panel for recipe management; these combine to reduce cost-per-unit and shrink lead times for large orders. Buyers should prioritize energy efficiency, spare-parts availability, and footprint-to-throughput ratios when comparing models because these parameters determine operating expense and scalability. To illustrate practical choices, the table below compares representative high-speed attributes, and the subsequent sections explain automation benefits and customization options to help purchasers match production goals to machine capabilities.
| Model Class | Throughput (pcs/min) | Automation Level | Typical Footprint | ROI Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry High-Speed | 200–350 | Semi-automatic | Medium | Lower CAPEX, moderate payback |
| Industrial High-Speed | 350–800+ | Fully automatic | Large | Best for long-term high-volume runs |
| Flexible High-Speed | 150–500 | Modular automation | Variable | Good for mixed-product businesses |
This comparison shows how throughput and automation scale together, prompting a closer look at how automation affects staffing and quality control on the line.
Automation increases throughput by coordinating extruder output, cutting cycles, and packaging modules to eliminate bottlenecks and reduce manual intervention, which in turn cuts labor costs and minimizes human error-related defects. Typical throughput improvements range widely by model class, but even modest automation can boost effective production by 20–50 percent compared with manual-fed lines, and consistent cycle timing improves downstream packaging synchronization. Automated systems also enable recipe recall for different straw diameters and materials, improving changeover speed and reducing scrap; this reliability supports predictable lead times for customer orders. When selecting automated features, assess serviceability, control system openness for updates, and spare-parts lead times, since these factors influence uptime and the real-world production advantage.
Customization options include diameter and wall-thickness tooling, color feeding, multi-layer co-extrusion for strength, and integration of bending or printing modules, which allow brands to differentiate products and address diverse customer requirements. Material compatibility considerations require checking extruder torque, barrel design, and thermal control capabilities to handle PP, PE, PLA or paper-based inputs without frequent retooling, and tooling kits must be accessible for fast swaps. Custom tooling and multi-material capability increase upfront costs and spare-part needs, but they expand product offerings and open higher-margin niches like premium or branded straws. Properly planned customization minimizes tooling downtime and ensures that supply of spare parts and maintenance aligns with production schedules.
Local procurement in Bloemfontein typically involves evaluating suppliers for product range, delivery logistics, spare-part provisioning, and after-sales service to ensure machines run reliably in your operating environment. When sourcing, ask targeted questions about lead times, warranty coverage, spare-parts lists, and whether the supplier performs pre-shipment inspections and testing; these items determine total landed cost and time-to-production. For buyers who prefer working with an established manufacturer, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) lists drinking straw machines among its product categories and emphasizes simple operation, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service, and quality control such as 100 percent final inspection during production. Their value proposition includes two-year warranty provisions on timer switches and competitive pricing enabled by scale, and their logistics model notes fast delivery for samples and standard bulk production—factors that influence vendor selection for Bloemfontein-based operations.
Choosing a local partner requires a supplier checklist that covers response times, spare-parts availability, and the ability to arrange technician support or remote troubleshooting; these elements reduce downtime and protect production forecasts. Ask suppliers about typical service response SLAs, stock levels of wear parts like cutters and dies, and whether they offer installation assistance or operator training to accelerate commissioning; verifying such claims through references or case examples helps validate readiness. Consider logistics such as customs handling, inland freight to Bloemfontein, and local workshop access for repairs, since these practicalities affect total ownership cost. Assessing these operational details will lead naturally to a precise request-for-quote that captures required machine specs and service commitments.
A focused request-for-quote (RFQ) should list required machine specifications, expected throughput, material types, tooling needs, desired warranty terms, lead time, and spare-part lists to enable apples-to-apples comparison between suppliers. Include questions about pre-shipment testing, installation support, training for operators, and ongoing technical support arrangements so you can evaluate total service offerings rather than just headline price; this clarity prevents scope gaps during delivery. When reviewing quotes, compare warranty coverage (including specifics like two-year warranty on timer switches if offered), spare-part lead times, and whether the supplier conducts 100 percent final inspection prior to shipment; these attributes materially affect long-term reliability. With a clear RFQ and service checklist, you can select a supplier who matches production goals and provides predictable after-sales support for Bloemfontein operations.
Starting a straw manufacturing venture in Bloemfontein requires matching local market demand to production capacity, selecting appropriate equipment, and planning for regulatory and supply-chain requirements to ensure profitability and compliance. Key considerations include identifying target customers—cafés, beverage producers, event caterers and retail packaging firms—estimating initial order volumes, and choosing machines that balance CAPEX with projected demand. Financial planning must account for facility costs, utilities for extrusion or paper drying, operator wages, and spare-part inventories, while equipment choices influence scalability and operating expense. The next subsections outline market trends and offer a stepwise investment checklist that entrepreneurs can use to build a pragmatic business plan for local manufacturing.
Demand in South Africa has been shifting toward eco-friendly straw solutions as retailers and consumers prefer compostable and paper alternatives, and this trend has increased opportunities for manufacturers who can deliver certified biodegradable products. Growth segments include specialty cafés seeking branded paper straws, beverage bottlers wanting custom-diameter plastic or PLA straws, and wholesale packaging suppliers needing automated production lines for stable supply. Recent market dynamics favor automated production to achieve consistent quality and to meet bulk order timelines, and targeting a mix of B2B customers provides steadier revenue than relying solely on retail channels. Understanding these buyer categories informs equipment selection and marketing strategy for a Bloemfontein-based manufacturer.
A practical equipment investment checklist includes floor-space allocation for extrusion or paper-forming lines, reliable electrical supply and climate control for material storage, ventilation for extrusion processes, and an inventory plan for critical spare parts like cutters, dies, and control modules. Typical CAPEX items are the main extrusion or forming machine, auxiliary dryers or gluing units, cutting and packaging modules, tooling sets for different diameters, and funds for installation and operator training; financing options may include equipment leasing or supplier financing where available. Plan workforce training and maintenance routines to maximize uptime, and align production scale with forecasted order volumes so you avoid oversized investment that slows cash flow. With a clear investment plan and conservative demand estimates, entrepreneurs can stage growth and add capacity as orders scale.
For buyers seeking equipment and procurement support, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers one-stop solutions from concept to mass production with strong R&D capabilities and claims of over 1700 machines installed globally; their model emphasizes competitive pricing through large-scale production, fast delivery for samples and standard bulk orders, and easy maintenance—attributes that can streamline startup timelines and reduce implementation risk.
Accessories and downstream modules such as precision cutters, bending units, and automated packaging machines significantly impact overall throughput, product quality and the ability to ship finished goods directly from the production line. Adding the right accessories reduces manual finishing, improves consistency, and allows producers to offer value-added formats like pre-bent or shrink-wrapped straw packs; compatibility between accessory modules and the main extrusion or forming line is essential to avoid bottlenecks. The EAV table below compares common accessory modules by function and maintenance demands so buyers can prioritize purchases that deliver the greatest uptime improvement.
| Accessory Module | Primary Function | Compatibility & Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Unit | Slices continuous tubing to length | Requires matched stroke rate; periodic blade replacement |
| Bending Module | Forms angled straws | Synchronization with cutter needed; occasional servo tuning |
| Packaging Machine | Wraps or bags finished straws | Throughput must match upstream; regular conveyor checks |
This comparison underscores that accessory selection must align with extruder speed and product format to maintain balanced line performance.
Cutting units range from mechanical guillotines to high-speed rotary cutters and must be matched to the machine’s throughput to avoid accumulation or jamming; feed sensors and synchronized drives help maintain tight tolerances. Bending modules add value by creating pre-angled straws for certain markets, though they introduce additional control complexity and spare-part needs for servo elements. Packaging options include simple bagging and more advanced automated wrapping or cartoning machines that enable direct-to-retail packaging; selecting packaging that matches production cadence ensures continuous flow and lowers handling labor. When integrating accessories, ensure spare parts and maintenance intervals are planned to sustain target production levels.
Planned maintenance routines focus on regular inspection of the extruder screw and barrel, replacement cycles for cutting blades and wear parts, lubrication of bearings, and firmware updates for control panels to prevent unexpected downtime. Critical spare parts to stock locally include cutting blades, heating elements, sensors, and common electrical components to enable rapid repairs; maintaining a small inventory reduces lead-time exposure and production interruptions. Establishing a predictable maintenance schedule and training operators to perform daily checks improves machine longevity and aligns with supplier after-sales service expectations, which together maintain steady output and protect margins.
For accessory and spare-part inquiries, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) lists straw-cutting, bending, and packaging modules among its offerings and highlights timely after-sales service, competitive pricing, two-year warranty elements on specific controls, and fast sample delivery—capabilities that help manufacturers minimize downtime and secure replacement parts when needed.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.