Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
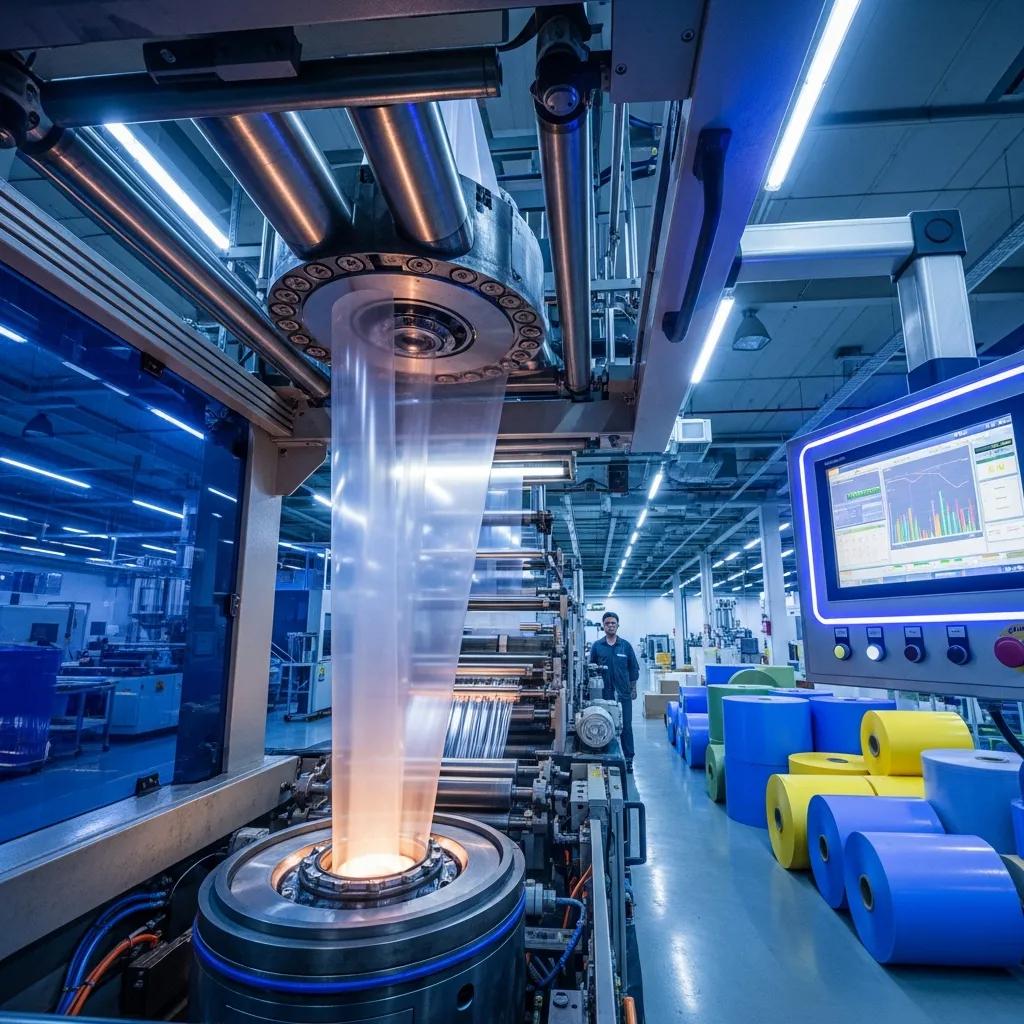

High-performance HDPE blown film machines produce thin, strong plastic film by extruding molten HDPE resin through a circular die and inflating a continuous tubular bubble that cools, collapses and winds into roll stock suitable for bags and packaging. This guide explains the blown film extrusion process, key hardware and resin considerations, machine types (monolayer, multi-layer, and high-speed lines), typical applications, and how to interpret technical specifications when sourcing equipment in South Africa. Manufacturers and buyers need clarity on throughput, film width, thickness control and automation to balance product quality against operating cost; this article addresses those decisions with practical checklists and specification tables. Readers will find a comparative EAV table of machine classes, recommended machine-to-application mappings, sample model specification formats, and procurement guidance tailored to South African operations. Throughout, we integrate concise supplier notes to show how local vendors supply turnkey blown film extrusion solutions, spare parts and complementary converting equipment while keeping the primary focus on technical decision-making and performance optimization.
HDPE blown film extrusion converts HDPE resin pellets into continuous film by melting, extruding through a circular die, inflating a controlled air bubble and cooling the film before collapsing and winding it. This process relies on controlled melt flow, die design and bubble stability to deliver consistent thickness, mechanical strength and optical properties; precise control of air ring cooling and haul-off tension produces repeatable gauge and lay-flat. The immediate benefit is a flexible manufacturing route for producing high-strength, low-gauge films used in bags and packaging, where HDPE’s stiffness and toughness improve handling and performance. Understanding these fundamentals enables buyers to specify machine features that control film properties rather than compensating for poor process equipment later. This technical foundation leads naturally into the specific hardware that composes a modern blown film extrusion line.
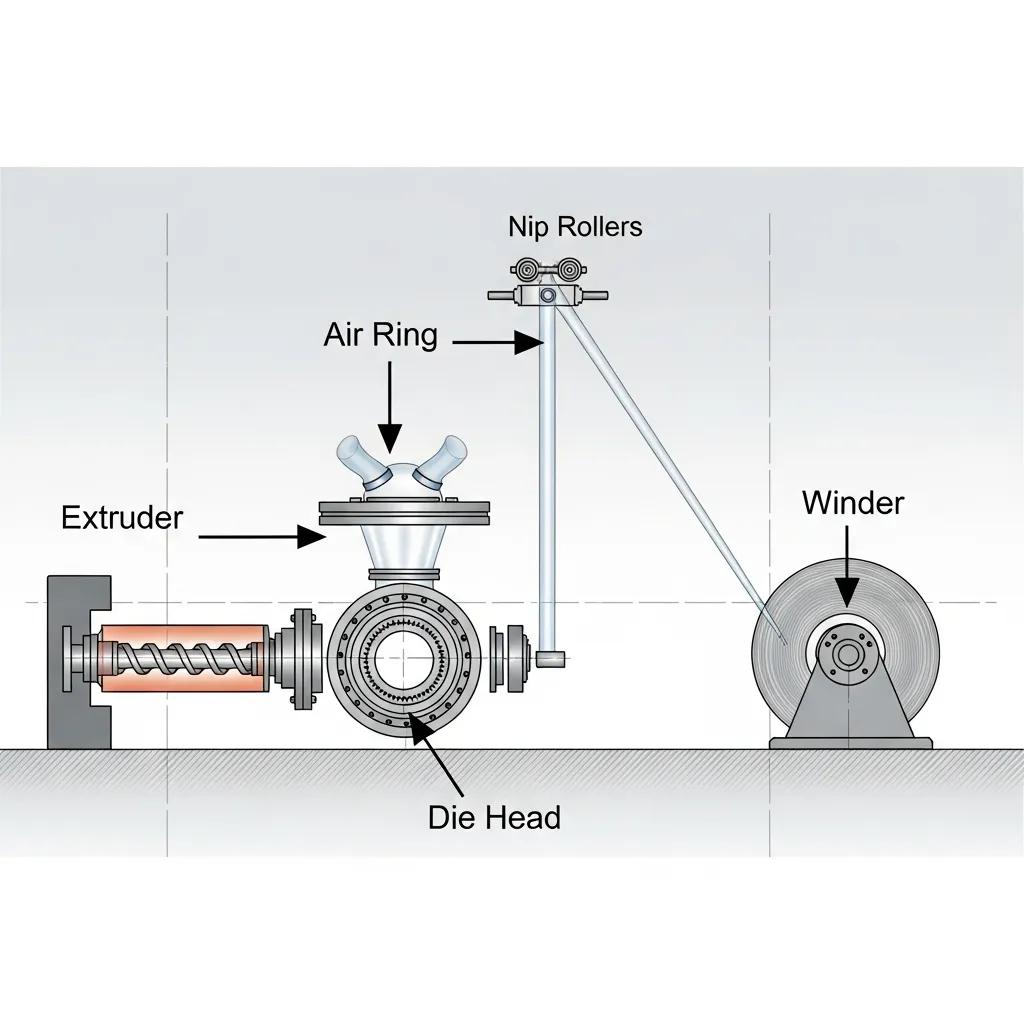
A blown film extrusion line consists of interdependent components that jointly determine film quality and productivity: the extruder, die head, air ring/cooling system, haul-off unit, collapsing frame, winder and automation controls. The extruder’s screw design and L/D ratio dictate melt homogeneity and throughput; the die head (rotary or flat-face) defines bubble stability and film uniformity. The air ring provides forced cooling and influences bubble cooling profile, while haul-off and winder systems manage drawdown rate and roll formation; thickness gauges and defect detectors complete inline quality control. These components form the meronymic structure of the machine—parts whose individual performance directly impacts finished film attributes—and selecting optimized subsystems reduces scrap and improves process windows. Proper component selection and integration set the stage for comparing machine types and configurations.
The next section compares machine architectures so buyers can match production goals to the right blown film equipment class.
HDPE resin properties—density, molecular weight distribution, and Melt Flow Index (MFI)—directly influence extrusion behavior and final film characteristics such as tensile strength, stiffness, and sealability. Lower MFI grades provide higher melt strength and better mechanical properties for heavier gauges, while higher MFI resins ease processing for thin-gauge high-speed lines; blends with LLDPE or LDPE modify flexibility and tear resistance. Additives like slip agents, anti-block, and UV stabilizers further tailor surface performance and longevity; correct dosage and dispersion prevent processing issues such as haze or die drool. Selecting the right resin grade and additive package reduces the need for process compromises and helps achieve target film properties consistently. With resin selection clarified, manufacturers can evaluate machine types that best convert chosen materials into market-ready film.
High-performance HDPE blown film machines fall into three practical categories: monolayer lines for standard bag stock, multi-layer co-extrusion lines for tailored properties and high-speed lines optimized for throughput and low gauge production. Each class balances capital cost, operational complexity and film functionality; monolayer lines are simpler to run, multi-layer lines permit functional layering (barrier, tie layers) and high-speed systems increase kg/hr output while demanding advanced cooling and control. Choosing between them depends on product portfolio, required film properties and expected return on investment. Below is a comparative EAV-style table to help buyers weigh outputs and configuration trade-offs across common machine types.
| Machine Type | Typical Output (kg/hr) | Layer Configuration | Typical Film Width | Typical Thickness Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolayer HDPE blown film machine | 50–300 | Single layer | 300–1200 mm | 10–100 microns |
| Multi-layer HDPE co-extrusion machine | 80–450 | 3–7 layers | 400–2000 mm | 10–200 microns |
| High-speed film blowing machine | 200–1200 | Mono or co-extruded | 600–3000 mm | 8–80 microns |
This EAV table highlights how layer configuration and throughput align with product needs and process complexity. The following subsections examine advantages and speed-related improvements.
Monolayer lines offer lower capital expenditure, simpler screw and die setups, and easier troubleshooting, making them ideal for producers focusing on basic bag stock and commodity films. Multi-layer co-extrusion machines enable property engineering—combining core strength layers with printable outer skins or barrier/tie layers—to meet more demanding packaging specifications or reduce material use through targeted layer performance. Operationally, multi-layer systems require synchronized extruders, more complex die heads and tighter process control, but they unlock product differentiation such as improved puncture resistance or printability. Maintenance and operator training requirements increase with layer count, so manufacturers should balance the market premium for multilayer films against higher OEE demands. After evaluating layer benefits, many buyers next consider throughput and how high-speed lines change production economics.
Advantages summary:
Understanding these trade-offs guides selection of the correct machine class for your product mix.
High-speed lines increase throughput primarily through mechanical upgrades—higher-torque extruders, optimized screw geometry for improved melting and conveying, robust gearboxes and stronger drive systems—and by integrating advanced air ring designs and faster chill/cooling profiles to stabilize thinner bubbles. Automation systems including PLC process control, automatic width and thickness control, and closed-loop haul-off reduce manual adjustments and minimize scrap, enabling consistent low-gauge production at higher m/min. KPI improvements typically include substantial kg/hr gains, reduced waste per ton of output and improved OEE when combined with reliable maintenance practices. Investment in high-speed technology must be weighed against increased energy demand and tighter process windows; however, proper selection can deliver quick payback through lower material cost per unit and higher finished-product throughput.
Key high-speed features:
These efficiency improvements lead directly to application-specific recommendations for film use cases.
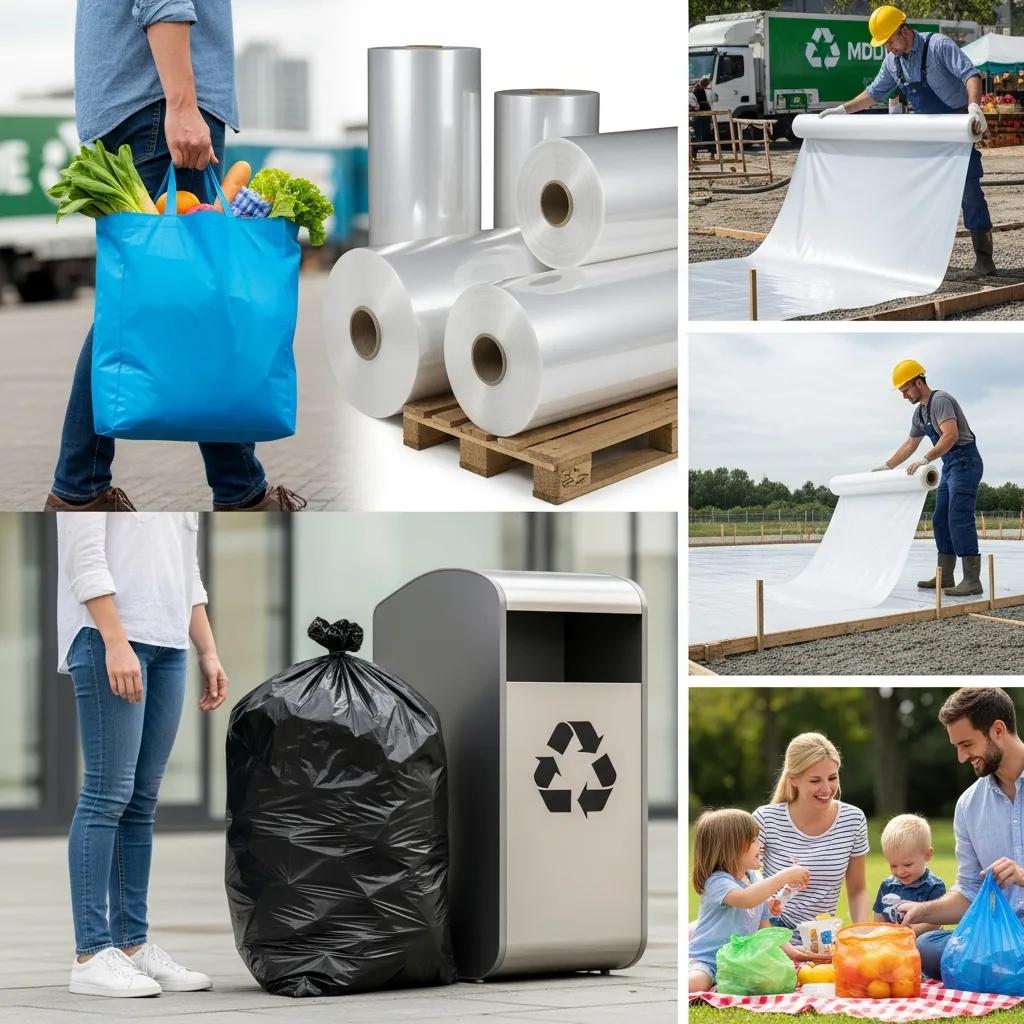

HDPE film from blown film machines serves multiple markets including shopping bags, garbage bags, industrial packaging, agricultural films and liners, each requiring tailored film properties such as tensile strength, puncture resistance and thickness. Matching the application to film properties and the appropriate machine class helps manufacturers optimize material consumption and production cost. The table below maps typical applications to recommended film properties and machine configurations so buyers can quickly match product demand to equipment capabilities.
| Application | Required Film Properties | Recommended Machine / Material |
|---|---|---|
| Shopping bags | Thin gauge, printable surface, adequate tensile strength | High-speed monolayer or 3-layer co-extrusion; HDPE/LLDPE blends |
| Garbage bags | High tear and puncture resistance, thicker gauge | Medium-output multi-layer line; high-strength HDPE grades |
| Industrial packaging | Wide width, heavy-gauge, high load capacity | Multi-layer co-extrusion, wide die heads |
| Agricultural films/liners | UV stability, weather resistance | Co-extruded layers with UV stabilizers |
This application mapping clarifies how film attributes drive machine selection and material choice. Next, specific application examples show how properties translate into processing and finishing decisions.
Shopping bags typically use thin-gauge HDPE with good printability and fold characteristics; these films prioritize appearance and cost-effectiveness and are produced on high-speed monolayer or lightweight co-extrusion lines. Garbage bags require thicker gauges and high tear/puncture resistance; producers often use multi-layer constructions or higher-density HDPE to improve toughness while managing cost. Industrial packaging—such as pallet wraps and heavy-duty sacks—demands wide-width production, heavier gauges and consistent tensile properties, making multi-extruder co-extrusion lines preferable. Each use case feeds back to extrusion settings, die choice and roll converting equipment needed for finishing, so aligning product targets with machine capability avoids rework or excessive scrap.
Typical production recommendations:
These application-specific requirements lead into customization and finishing options that allow brand and functional differentiation.
Customization spans flexographic printing for multi-color branding, addition of functional additives (UV stabilizers, anti-block, slip agents), colored or opaque films, embossed textures for appearance or anti-slip features, and converting services like slitting, perforating, gusseting and winding tailored to downstream bag machines. Integrating flexo printing units inline or offline enables high-quality graphics, while coordinated converting ensures roll widths and core sizes match bag-making equipment. Complementary equipment such as plastic bag making machines and flexo printing machines enable one-stop manufacturing workflows, and recycling pelletizers support material circularity in production. These customization routes increase product value and often justify selection of co-extrusion or higher-specification lines that support downstream finishing.
Customization options:
Knowing available customizations helps buyers specify machines that integrate effectively with converting and printing workflows.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating via Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) provides a one-stop supply of plastic bag production lines including blown film extrusion machines, plastic bag making machines, flexo printing machines and plastic recycling machines, positioning itself as a practical sourcing option for South African manufacturers. The company emphasizes simple operation, reliable performance and easy maintenance, and offers timely after-sales service in Gqeberha, Soweto, Cape Town and Johannesburg to support local uptime and parts availability. Quality measures include 100% final inspection and a two-year warranty on timer switches, while customization services cover logos, labels, packaging and new product development to match market needs. Buyers also benefit from competitive pricing, fast delivery—samples in three days and bulk orders in 15–20 days—and access to strong R&D and one-stop customization that links blown film lines to bag making, printing and recycling equipment.
Company value propositions:
The supplier profile above demonstrates practical procurement benefits and transitions into the specific support and warranty services buyers should expect.
After-sales services include on-site installation and commissioning, operator and maintenance staff training, spare parts sourcing and structured maintenance contracts to keep production lines running with minimal downtime. Timely after-sales service in key South African centers means faster response times for field visits and parts dispatch, and training programs reduce operator errors that commonly cause scrap or downtime. Regular maintenance schedules should include screw/barrel inspections, die cleaning, and calibration of thickness gauges to maintain film quality; suppliers that provide maintenance plans and reliable spare parts channels reduce total cost of ownership. These support elements help buyers maximize uptime and ensure consistent product quality, which then ties into delivery reliability and inspection practices described below.
Recommended support services:
Understanding service commitments clarifies the practical implications of procurement choices and delivery timelines.
Kingdom Machinery’s approach includes manufacturing quality control routines, sample and bulk delivery timelines, and logistics coordination to support South African customers; practical delivery claims specify three days for samples and 15–20 days for bulk orders, enabling predictable project planning. Quality assurance is backed by 100% final inspection before shipment, which reduces on-arrival defects and accelerates commissioning schedules at customer sites. The stated two-year warranty on timer switches provides a narrowly defined warranty assurance for specific components, and strong R&D supports customization requests such as logos, labels and new product development. These operational commitments help buyers align lead times, commissioning and product validation before scaling up production runs.
Delivery and QC highlights:
With supplier capabilities clarified, manufacturers can interpret technical specifications to finalize purchases.
Technical specifications define buyer expectations: output capacity (kg/hr), screw diameter and rpm, die size, film width and thickness ranges, and power consumption are core metrics that translate into daily production and energy costs. Interpreting model sheets requires understanding how screw diameter scales to throughput, how die width determines maximum lay-flat and roll width, and how gearbox/drive design influences stable operation at higher speeds. Energy efficiency and automation—variable frequency drives, PLC control, closed-loop gauge control—reduce kW/kg and lower labor intensity. The table below shows a representative model-format that buyers can request when comparing offers; use these fields to map vendor claims to in-plant production targets.
| Model | Screw Diameter / Power | Output (kg/hr) | Max Film Width | Film Thickness (microns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A (compact) | 45 mm / 30 kW | 80–150 | 600 mm | 10–80 |
| Model B (medium) | 65 mm / 55 kW | 180–350 | 1200 mm | 10–150 |
| Model C (high-speed) | 90–120 mm / 110–220 kW | 400–1200 | 2000–3000 mm | 8–80 |
This specification layout enables apples-to-apples comparisons across vendors and supports product-sourcing decisions. Next, we quantify how automation and efficiency features affect operating cost.
Typical output capacities vary by machine class: compact monolayer units may deliver 50–200 kg/hr suitable for small-run bag production, medium-class co-extrusion lines commonly yield 150–450 kg/hr for versatile product ranges, and high-speed lines can exceed 400–1,200 kg/hr for large-scale thin-gauge film manufacture. Film width scales with die design and collapsing frame geometry; standard widths run from several hundred millimeters to multiple meters for industrial films. Thickness ranges depend on die gaps, cooling rates and drawdown; thinner gauges (8–30 microns) generally require high-speed cooling and precise automation. Understanding these ranges lets buyers convert kg/hr into linear production metrics for planned gauge and roll dimensions.
Spec interpretation tips:
Translating specs into energy and automation savings clarifies total cost of ownership.
Energy-efficiency measures—optimized screw geometry, insulated barrels, and variable frequency drives—lower kW/kg consumed per tonne of film produced and reduce heat-related wear on components. Automation elements such as PLC-based recipe control, automatic thickness and width control, and automated roll changeover minimize operator intervention, reduce variability and cut scrap rates. Quantitatively, upgraded systems often show measurable percentage reductions in energy per kg and lower labor hours per shift; monitoring KPIs like kW/kg, scrap percentage and OEE provides a data-driven case for investment. Implementing these features alongside proactive maintenance and training yields compounded savings and improved predictability of production output.
Efficiency implementation checklist:
These performance metrics feed into buyer FAQs and procurement checklists that follow.
Buyers commonly ask how to match machine capacity to product plans, what costs to expect, which financing routes are practical and what installation and warranty terms should look like. A clear selection checklist—covering capacity, product specifications, material compatibility, footprint and after-sales support—simplifies decision-making, while understanding financing options (supplier credit, leasing, bank loans) helps spread capital expenditure. Installation planning must include operator training, spare parts provisioning and commissioning schedules that align with sample delivery and bulk lead times; asking suppliers for documented maintenance plans and spare-parts lists reduces surprises. The checklist below helps buyers prioritize procurement factors before requesting formal quotations or technical consultations.
Buyers should use this decision checklist when evaluating machine offers:
This checklist flows naturally into cost considerations and financing options that follow.
Selecting the right machine begins by defining product mix, target annual throughput, and quality parameters such as gauge tolerance and printability; then map those needs to machine class, layer capability and automation level. Starter manufacturers may prioritize compact monolayer machines for ease of use, medium-scale converters often choose multi-layer co-extrusion for product range, while high-volume producers require high-speed lines with advanced automation and energy optimization. Evaluate supplier service commitments, spare parts logistics and sample-to-bulk lead times to avoid production gaps; a supplier who offers one-stop solutions for blown film, bag making, printing and recycling improves integration and reduces vendor management overhead. Use the checklist above to frame technical questions during supplier discussions.
Buyer persona mapping:
Following persona-driven selection minimizes costly mismatches between machine capability and business goals.
Machine cost is driven by automation level, co-extrusion capability, die complexity and custom features; higher layer counts, wider dies and advanced automation increase capital expenditure, while simplified monolayer units reduce upfront cost. Rather than citing fixed prices, buyers should request tailored quotations that specify included features, spare parts packages and installation services to enable meaningful comparisons. Common financing approaches include supplier financing packages, equipment leasing and traditional bank loans; selecting financing depends on balance-sheet preferences and tax/timing considerations. Prepare financial comparisons that include expected energy consumption, maintenance and scrap rates to evaluate total cost of ownership rather than only purchase price.
Financing considerations:
At the end of procurement planning, buyers should request a technical consultation or quotation to validate configuration and lead times.
For a technical consultation or to request a quote and discuss complementary equipment such as plastic bag making machines, flexo printing machines and plastic recycling machines, request a technical consultation or quote through the supplier’s standard contact channels and provide your target film specifications, annual throughput and available factory footprint to accelerate accurate proposals.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.