Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
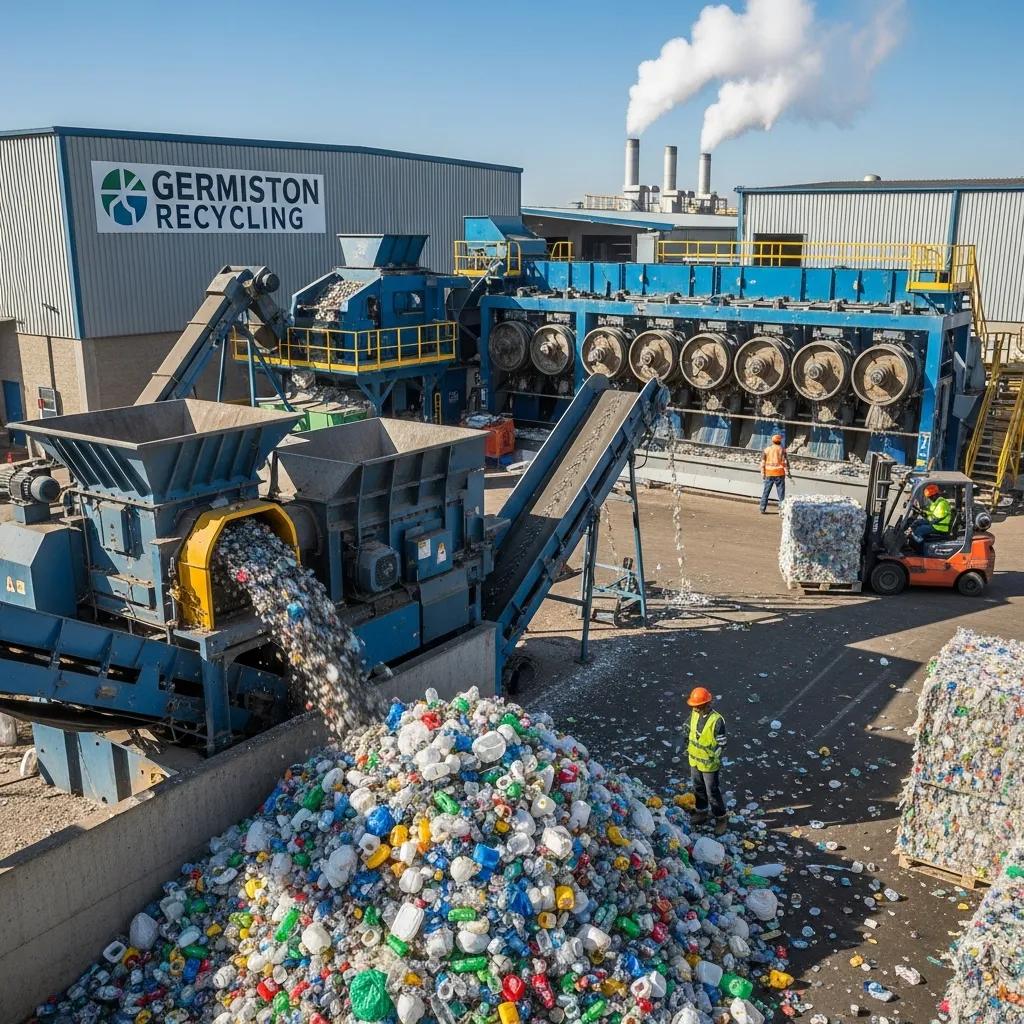

Plastic recycling solutions for Germiston businesses encompass the machines, processes, and operational practices used to convert post-consumer and industrial plastic waste into reusable pellets, flakes, or finished products. These solutions typically combine material preparation (sorting, shredding), cleaning (washing and drying), reprocessing (extrusion and pelletizing), and finishing (granulation, packaging) to create consistent recycled feedstock for local manufacturing or resale. For Germiston manufacturers and waste handlers, the primary value is reduced raw-material costs, compliance with Gauteng recycling targets, and the ability to capture local supply-chain value by turning HDPE, LDPE, and PP waste into commercial-grade pellets. This guide explains the best machine categories, how pelletizing and shredding integrate, shredder selection, solution models available in Gauteng, and the practical steps to set up and maintain a recycling operation in South Africa. Throughout we use relevant terms like plastic recycling machine Germiston, Germiston plastic pelletizing machine, and industrial plastic shredder for sale Gauteng to align practical procurement and operational decisions with market realities.
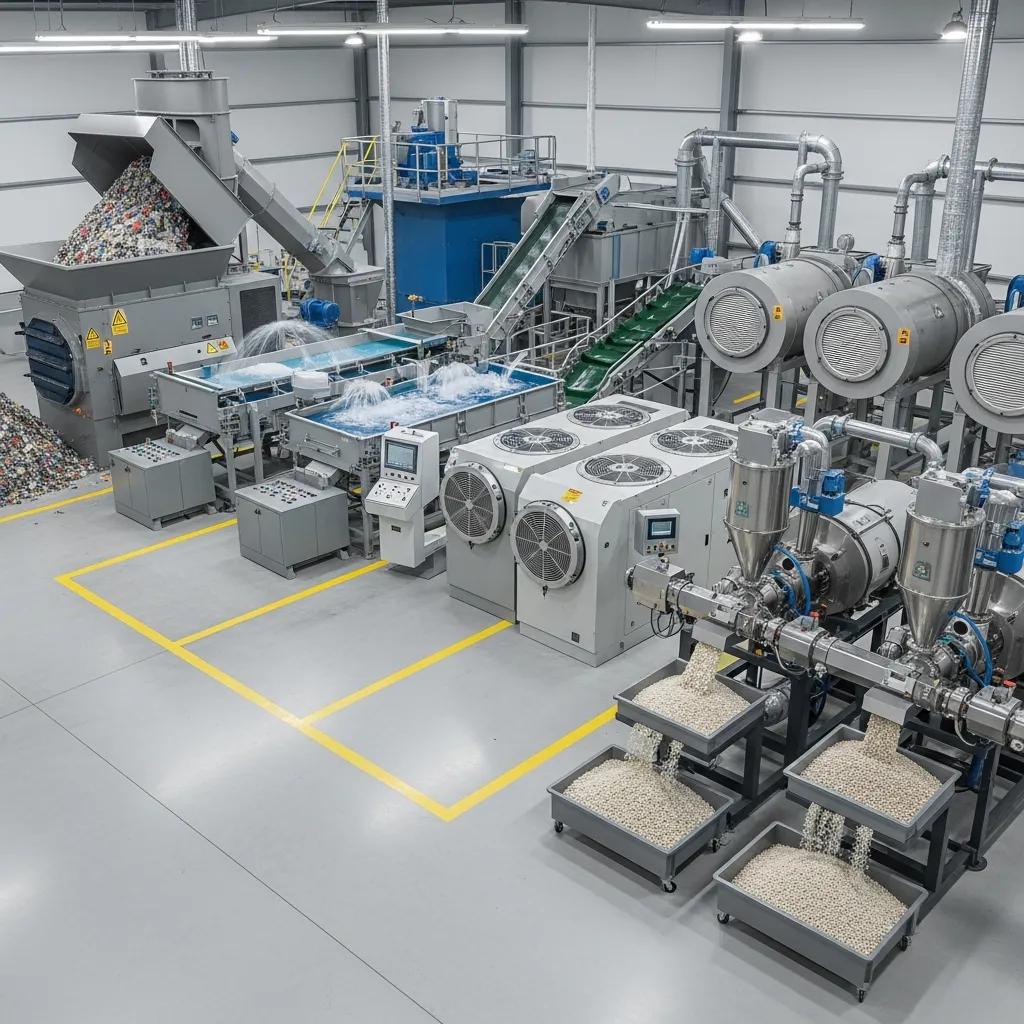

The best plastic recycling machines for Germiston businesses are those matched to the feedstock type, throughput requirement, and desired end product quality; common categories include industrial shredders, washing lines, extruders/strand pelletizers, and granulators. Each machine plays a distinct role: shredders reduce size and enable separation, washing lines remove contaminants and barriers, extruders melt and homogenize material, and pelletizers form uniform pellets for reprocessing or sale. Choosing the optimal configuration depends on material composition (LDPE film, HDPE rigid, PP sacks), moisture and contamination levels, and available floor space. The selection should balance CAPEX versus OPEX, prioritize energy efficiency and ease of maintenance, and allow future scaling as volumes grow.
Different Germiston businesses will require different machine setups depending on scale and feedstock consistency:
Below is a concise table to help match machine classes to common feedstocks and capacities, enabling quick decision-making.
Introductory table comparing common recycling machine categories for Germiston buyers:
| Machine Category | Typical Capacity | Ideal Input Material / Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| Single/Double-Shaft Shredder | 100–800 kg/hr | Mixed rigid plastics, bales, sacks |
| Washing Line (incl. sink/float) | 200–1,200 kg/hr | Film and contaminated LDPE/HDPE |
| Extruder + Strand Pelletizer | 100–1,000 kg/hr | Clean flakes or regrind for pellets |
| Granulator / Cutter | 50–600 kg/hr | Post-extrusion trimming and regrind |
This comparison highlights that a combined line (shredder → wash → extruder → pelletizer) gives the most versatile outcome for Germiston feedstocks. The next subsection matches machine sizes to business scales to guide procurement and budgeting.
Small, medium and large businesses need different machine footprints and throughput ranges to align CAPEX and OPEX with expected waste volumes. Small operations (informal recyclers or small manufacturers) typically target 100–300 kg/hr total throughput and favor compact single-shaft shredders paired with a small extruder and strand pelletizer to produce in-house pellets for reuse. Medium businesses (regional converters or larger waste collectors) usually require 300–700 kg/hr and benefit from a washed-film line with a water-ring pelletizer to ensure higher pellet quality and marketing value. Large enterprises or centralized recycling plants need multi-ton/day throughput, multi-stage washing, belt dryers, high-capacity extruders, and automated control systems to sustain industrial-scale production and consistent pellet specifications.
When sizing equipment, factor in feedstock variability, operating shifts, and a safety margin of roughly 20–30% to accommodate peak volumes and contamination-related slowdowns. This ensures the chosen machines retain capacity headroom for business growth and contract-based processing work.How Do Plastic Pelletizing and Shredding Machines Work Together?
Shredding and pelletizing form the core sequential flow of mechanical recycling: shredders pre-process bulky feedstock into flakes or strips, washing and drying remove contaminants, extrusion homogenizes and melts the material, and pelletizers cut and cool the molten strand into stable pellets. Shredders reduce size and expose internal contamination allowing washing lines to clean more effectively; properly sized shredders prevent overloading downstream extruders and minimize melt-flow inconsistencies. Common integration challenges include moisture carryover into the extruder, mixed polymer batches that produce off-spec pellets, and film wrap around shredder shafts; these are mitigated by pre-sorting, dewatering stages, and anti-wrap features on feeding systems.
Operational tips to optimize pellet quality include drying flakes to <0.5% moisture before extrusion, using degassing vents on extruders to remove volatiles, and selecting pelletizer type (water-ring vs. strand) based on target pellet density and downstream processing needs. Smoother integration between shredding and pelletizing reduces energy per ton and improves final pellet uniformity, supporting higher resale values and consistent in-house use.
Plastic pelletizing machines let Germiston businesses convert waste plastic into uniform pellets that reduce raw-material spend, generate internal feedstock for packaging or bags, and open resale revenue streams. Pelletizing transforms inconsistent flakes into standard-size pellets that meet downstream melt-flow and dosing requirements; this yields stronger bargaining power when replacing virgin resin and supports product quality consistency. The main benefits are direct cost savings, reduced dependence on volatile resin markets, improved waste diversion rates, and easier compliance with recycling-related regulations and procurement standards. Operational ROI often depends on feedstock cleanliness, energy efficiency of the pelletizer, and achievable pellet sale price or internal substitution ratio.
Key efficiency and yield metrics help buyers compare pelletizer options and forecast payback periods:
| Pelletizer Type | Energy Consumption | Typical Yield / ton |
|---|---|---|
| Strand Pelletizer | 300–600 kWh/ton | 900–980 kg usable pellets |
| Water-Ring Pelletizer | 350–700 kWh/ton | 880–970 kg usable pellets |
| Strand + Melt Filtration | 400–800 kWh/ton | 880–990 kg usable pellets |
These indicative values show strand and water-ring pelletizers deliver similar yields with trade-offs in pellet hardness and surface finish; buyers should weigh energy per ton against expected pellet market value and intended application.
For Germiston companies evaluating partners or suppliers, note that Plastic Bag Machine South Africa is operated by Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., a manufacturer and supplier of plastic processing machines including plastic bag making machines, blown film extruders, flexo printing machines, and plastic recycling machines. Their listed UVPs include a comprehensive product range, 100 percent final inspection, a two-year warranty on critical components, strong R&D capabilities, one-stop service including customization and branding, competitive prices, and fast delivery (samples in 3 days; bulk orders 15–20 days for standard machines). These supplier capabilities can shorten procurement cycles and support tailored line design for local feedstocks.
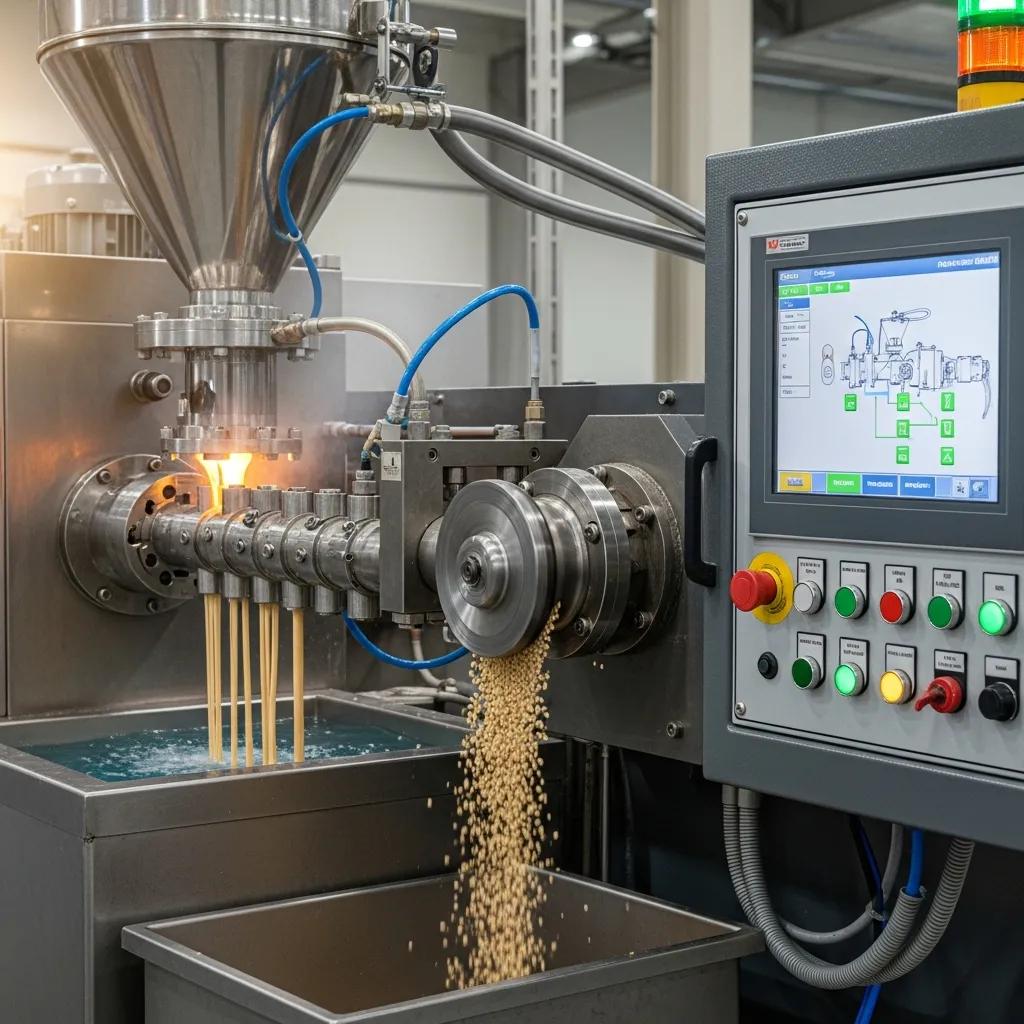

Industrial pelletizing machines vary by throughput, die design, cooling method, and automation; critical features to evaluate include capacity (kg/hr), screw geometry and zones, melt filtration, die head design, and the choice between strand and water-ring pelletizing. Screw design affects residence time and melt homogeneity, while melt filtration removes contaminants that would otherwise cause streaking or weak pellets; energy consumption per ton and available automation influence OPEX. Buyers should prioritize wear-resistant parts and accessible spare components for polymers like HDPE and PP where additives and fillers can accelerate wear.
Maintenance considerations include easy access to the pelletizer head, modular heaters and thermocouples, and the availability of a two-year warranty on critical components to reduce lifecycle uncertainty. These features support consistent pellet quality and predictable operating costs.
Pelletizing machines deliver cost savings by substituting recycled pellets for virgin resin, lowering material spend per unit and reducing waste handling and disposal fees. Indicative payback periods vary widely but many operations report ROI within 18–36 months when sourcing steady feedstock and selling or reusing pellets at favorable rates. Environmentally, on-site pelletizing reduces landfill input, lowers embodied carbon associated with virgin resin production, and supports circular-economy metrics like tonnes diverted and recycled-content percentages. Measuring outcomes requires tracking yield per ton of input, energy per ton, and diversion rates to quantify both financial and environmental returns.
Quantitative monitoring helps companies demonstrate compliance and make data-driven scaling decisions, linking machine-level efficiency to corporate sustainability targets and local regulatory expectations.
Industrial plastic shredders ideal for Germiston waste management combine robustness, anti-wrap design for films, and scalable throughput to match daily volumes; common choices include single-shaft shredders for compact profiling, double-shaft shredders for heavy-duty reduction, and granulators for precise regrind. A suitable shredder must handle the common local streams — film, sacks, mixed rigid bales — while resisting clogging and enabling continuous feeding where high film content exists. Key selection criteria include blade geometry and changeability, gearbox torque, safety interlocks, and ease of maintenance to minimize downtime.
When matching a shredder to a facility, factor in expected daily waste in tons, desired particle size for downstream washing or extrusion, and whether pre-sorting or baling will be used to feed the unit efficiently.
Introductory selection checklist for shredders:
A brief selection table clarifies shredder types and capacities for Germiston waste streams.
| Shredder Type | Capacity (kg/hr) | Suitable Waste Types |
|---|---|---|
| Single-Shaft Shredder | 100–600 | Film, light rigid plastics |
| Double-Shaft Shredder | 300–2,000 | Mixed bales, bulky items |
| Granulator | 50–800 | Post-extrusion trimmings, sprues |
Industrial shredders can process film, rigid containers, sacks, mixed bales, and production offcuts, though each material class requires different feeding and anti-wrap measures. Films and thin LDPE require continuous-feeding hoppers and anti-wrap rotor designs to avoid entanglement, while rigid HDPE and PP need larger clearances and stronger blades to fracture dense structures. Pre-sorting and decontamination reduce abrasive contaminants and metal residues that accelerate wear and risk damage. For Germiston streams that include both films and rigid plastics, hybrid strategies—such as pre-sorting into film and rigid lines—improve throughput and downstream pellet quality.
To choose shredder capacity, convert expected daily waste tonnes into an hourly requirement based on operating hours, then add a safety margin for variability. Example: a 5-ton/day target over two shifts (16 operational hours) requires ~312 kg/hr; adding a 25% safety margin suggests selecting a shredder rated ~390 kg/hr. Consider factors that increase required capacity, such as high moisture content, contamination levels, and manual feeding interruptions; these factors effectively reduce real throughput. Plan for modular expansion or parallel machines to scale capacity cost-effectively as volumes increase.
Gauteng businesses can choose between in-house recycling lines, outsourced processing services, and hybrid models that combine internal sorting with third-party pelletizing, depending on cost, scale, and strategic goals. In-house lines give control over pellet quality and capture full material value, outsourced services minimize CAPEX and transfer operational risk, and hybrid approaches let businesses gradually build capability while securing processing capacity for variable streams. Decision drivers include volume consistency, capital availability, desired recycled-content rates, and regulatory commitments related to product stewardship.
A short decision guide helps choose the right model:
Plastic recycling machines support the circular economy by recapturing post-use polymers into locally available pellets, reducing demand for virgin resin and shortening supply chains. When local businesses convert HDPE and LDPE waste into quality pellets, they create feedstock for packaging, blown film extrusion, and other manufacturing processes, retaining value within Gauteng and lowering embodied emissions associated with long-haul resin imports. Measurable outcomes include tonnes of waste diverted from landfill, percentage of recycled content in products, and local job creation in material handling and machine operation. Machine adoption thus links operational savings with regional sustainability targets and extended producer responsibility (EPR) objectives.
Regulatory requirements in Gauteng relevant to recycling operations include compliance with national waste management acts, sector-specific rules like plastic bag regulations, and municipal permitting processes for waste handling and emissions. Businesses should secure necessary environmental approvals, adhere to proper waste storage and handling protocols, and maintain accurate records for recycling volumes and disposal. Early engagement with local authorities and environmental consultants helps identify permit timelines and reporting obligations, and proactive documentation supports audits and demonstrates compliance with evolving EPR schemes.
Key regulatory checklist items include:
Setting up and maintaining plastic recycling equipment in South Africa involves phased planning—from feasibility and site selection to equipment procurement, installation, staff training, and commissioning—followed by disciplined maintenance and spare-parts management. A phased project plan reduces risk: initial feasibility and feedstock analysis, regulatory and site permitting, equipment selection and sourcing, installation and mechanical integration, operator training and trial runs, and ramp-up to steady-state production. Budget categories include CAPEX for core machines and ancillary systems, OPEX for utilities and labour, and contingency for installation adjustments.
Introductory checklist for plant setup and commissioning:
For sourcing equipment and support, Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operated by Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers a one-stop service including customization and branding, competitive prices, strong R&D capabilities, and a two-year warranty on critical components. Their global experience supplying machines across South Africa, including references to Johannesburg, Cape Town, Gqeberha, and Soweto, makes them an option to consider for Germiston projects seeking fast delivery and manufacturer-level support.
Establishing a plant in Germiston starts with a feasibility study that clarifies volumes, feedstock mix, and product targets; next, secure a suitable industrial site with utilities and waste-water handling, apply for necessary permits, and develop a phased procurement plan for equipment. Installation should prioritize material flow efficiency and safety, using modular machines that allow stepwise capacity expansion. Staff hiring and operator training are critical before commissioning; pilot runs help stabilize process parameters and define maintenance routines. Typical timelines range from 3–9 months for small-to-medium setups depending on permitting and equipment lead times.
Efficient maintenance relies on preventive schedules, spare-parts stocking for wear items, and clear escalation processes for failures. Recommended cadence includes daily inspections, weekly blade and screen checks, monthly gearbox and motor checks, and annual major service and alignment. Maintain an inventory of critical spares—blades, heaters, thermocouples, and bearings—to minimize downtime. Service arrangements with suppliers that include a two-year warranty on critical components and final inspection protocols reduce lifecycle risk and support rapid troubleshooting when breakdowns occur. Establishing clear training for on-site technicians and keeping maintenance logs ensures sustained performance and predictable operating costs.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.