Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M

A three layer bubble film machine produces co-extruded air bubble film that combines multiple polymer layers into a single, high-performance protective film, delivering enhanced cushioning and dimensional stability for transit and storage. This article explains how three-layer co-extrusion works, what materials and process controls produce reliable LDPE/LLDPE bubble wrap, and why manufacturers and packagers in South Africa are adopting multi-layer air bubble film for fragile and high-value goods. Readers will learn the mechanical and material reasons a three-layer configuration outperforms single- and double-layer films, the primary protective benefits (burst strength, shock absorption, anti-static and UV options), and the typical machine features that drive efficient in-house production. We also map industry use-cases across electronics, agriculture and industrial parts; provide specification and ROI guidance for procurement; and show how local distribution and after-sales services translate technical benefits into lower total cost of ownership. Throughout this guide you will find practical lists, comparison tables, and stepwise investment guidance designed for technical buyers evaluating three layer bubble film extrusion lines, automatic bubble wrap machines, or high-speed bubble film production options.
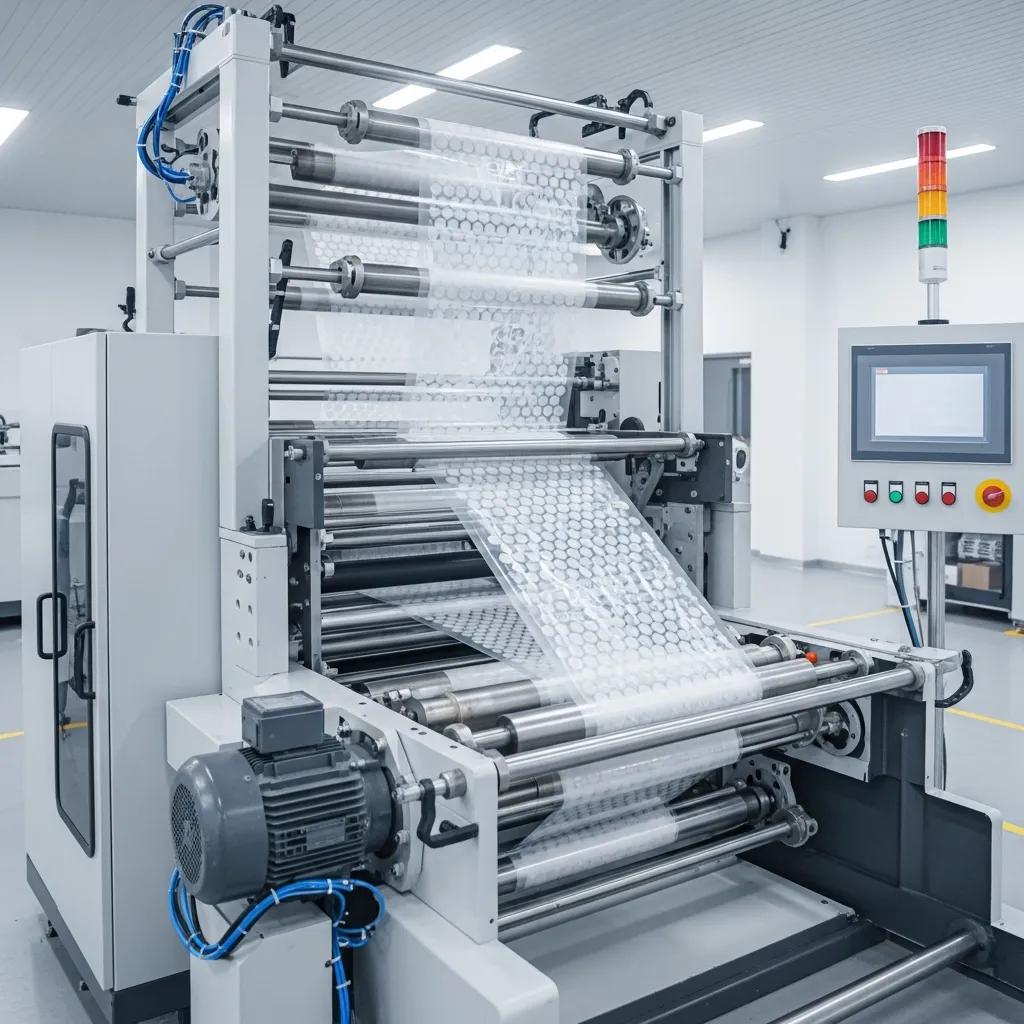
A three layer bubble film machine is specialized film extrusion equipment that co-extrudes three polymer streams to form a laminated sheet with an air-cushion core and protective outer skins, enabling improved mechanical performance and tailored properties. The machine uses multiple extruders feeding a multi-manifold die where streams are combined and shaped, then a bubble-forming roller set creates the characteristic pockets of trapped air before sealing and winding, which produces an LDPE or LLDPE-based bubble wrap with controlled thickness and bubble geometry. This configuration separates the functional roles of layers—outer skins resist abrasion and handling, while an inner layer optimizes bubble strength or recycled-content cost balance—so manufacturers can tune films for cushioning, puncture resistance, or recyclability. Understanding these components and process variables helps procurement and production teams specify a line that meets throughput, film width, and performance targets while enabling consistent quality for large-scale packaging operations.
The fundamental components of such a machine, including the extruder and multi-channel die, are critical for achieving the desired multi-layer structure and performance.
Multi-Layer Extrusion Machine Components
extruder, the connecting mechanism, the rotatable adapter and the multi-channel die are the same as was in the case with the multi-layer
5 Sheet and Film Extrusion Processes and Process Control
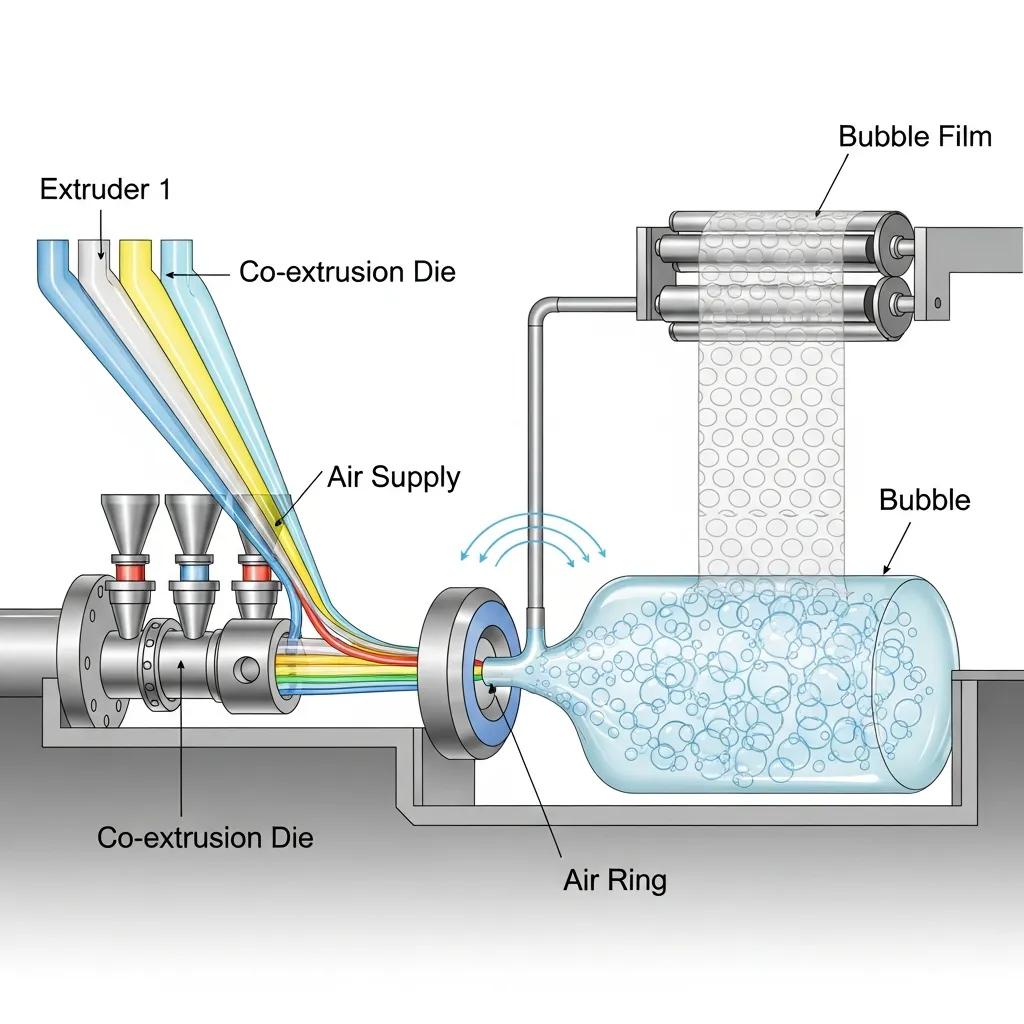
Co-extrusion combines molten polymer streams through synchronized extruders into a single die, blending materials without chemically mixing them to maintain distinct layer functions and mechanical properties. Each extruder melts and meters a specific resin—typically LDPE or LLDPE for outer and core layers—while screw speed, melt temperature, and die-gap settings control layer thickness and interlayer adhesion, which are essential for bubble fusion and burst strength. The molten laminate passes over a bubble-forming roller that creates cavities which are subsequently sealed by a lamination/calendering station; precise air pressure and cooling rates determine bubble uniformity and long-term stability. Modern three layer bubble film machines include PLC controls and sensor feedback to stabilize these variables, reducing scrap and ensuring reproducible film performance across long production runs.
The intricate process of forming the air bubble film involves precise control over the bubble’s expansion and orientation, as highlighted by recent research.
Bubble Film Blowing Process & Orientation
Film blowing is commonly carried out by forming a bubble into a bubble that increases in diameter and orients the film in the
Mechanical recycling and design of multi-layer packaging: constraints, opportunities and challenges, 2023
LDPE and LLDPE are the primary resins for bubble film due to their balance of flexibility, heat-sealability, and impact resistance, with LLDPE typically offering higher tensile strength and puncture resistance for thinner films. In a three-layer design, manufacturers commonly use LLDPE or a higher-strength blend for one or both outer layers to resist abrasion and handling, while the inner core can be a softer LDPE or a formulated recycled-content blend to reduce material cost while preserving cushion. Incorporating recycled plastics requires careful rheological matching and often a compatibilizer or adjusted processing temperatures to maintain layer adhesion and bubble integrity. Additives such as anti-static agents, UV stabilizers, or slip/antiblock masterbatches are introduced at compounding to give the finished bubble film application-specific properties like electronics-safe handling or outdoor weathering resistance.
Three-layer bubble film delivers superior protective performance by combining optimized outer skins with a resilient air core, resulting in higher burst strength and consistent cushioning that reduces product damage during handling and transit. The layered design enables material efficiency—thin, high-strength outer layers protect while a tailored core provides most of the cushioning—so packagers can often reduce overall material use compared with heavier single-layer films without sacrificing protection. Multi-layer constructions also allow function-specific additives (anti-static, UV resistance) to be localized in the layer where they are most effective, creating multi-functional packaging films without complex downstream coatings or laminations. These characteristics translate into fewer returns, lower replacement costs, and operational savings through faster packing and reduced secondary protection material needs.
This section highlights the primary performance and cost benefits of three-layer air bubble film:
These benefits lead directly to measurable supply-chain improvements and lower total packaging cost by reducing damage rates and enabling more compact, efficient packing operations.
| Protective Feature | Measurable Attribute | Practical Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Air Bubble Film (three-layer) | Burst strength (kPa) — higher than single layer | Fewer transit failures and reduced returns |
| Outer skin reinforcement | Abrasion resistance (index) — improved handling durability | Longer shelf life and less surface wear |
| Anti-static outer layer | Surface resistivity (Ω/sq) control | Safe packaging for electronics, reducing ESD risk |
The table maps film attributes to real-world benefits so procurement teams can compare specifications to expected operational outcomes. Understanding these mappings helps align film selection with damage-reduction and cost-avoidance targets.
After assessing these technical benefits, manufacturers often seek local supply and technical support to realize them in production. Plastic Bag Machine South Africa operates as a representative and distributor for Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. and supplies bubble film machines and related extrusion lines; their offering emphasizes simple operation, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service, and cost-effective durable machinery. For technical buyers wanting to translate the benefits above into production outcomes, requesting a technical consultation or quote from a knowledgeable distributor is a natural next step to match film performance to application needs.
Improved burst strength and controlled bubble geometry directly reduce damage rates by absorbing impact energy and preventing punctures that lead to product failure, which lowers replacement and return processing costs. Quantitatively, even modest reductions in transit damage—measured as a percentage of total shipments—translate into significant cost savings when factoring product value and handling expenses; this makes stronger bubble film a high-leverage packaging upgrade. Operationally, stronger three-layer films can allow packers to eliminate redundant cushioning layers or dense void-fill materials, speeding packing lines and reducing labour per parcel. These efficiencies compound across high-volume operations to shorten payback periods for in-house bubble film production and reduce total cost of ownership in the long term.
Multi-layer bubble films provide an array of protective features that can be combined in one production run through material selection and layer-specific additives, creating versatile films for diverse applications. Shock absorption derives from the trapped-air core geometry, while abrasion resistance is supplied by tougher outer layers; anti-static agents mitigate electrostatic discharge risks for electronics, and UV stabilizers protect goods stored or shipped in sun-exposed environments. Manufacturers can therefore specify films with a combination of properties—e.g., high burst strength plus anti-static protection—without resorting to additional laminations or coatings, simplifying supply chains and reducing unit costs.

Several South African industries gain immediate value from three-layer bubble film due to the combination of enhanced cushioning, functional additives, and material efficiency, making it suitable for a wide range of packaging and protection tasks. Electronics manufacturing and distribution demand anti-static and clean films to protect sensitive components; agriculture and fresh produce benefit from cushioning and breathability options that reduce bruising and spoilage; industrial supply chains need puncture-resistant films for heavy parts and irregular shapes. The ability to customize bubble size, film thickness, and additives allows suppliers and manufacturers to specify film that addresses the particular handling and environmental challenges of each sector.
Key industry applications include:
These industry mappings show how three-layer bubble film is not a one-size-fits-all product but a configurable packaging solution that reduces damage and optimizes logistics for each vertical.
In electronics, bubble film must combine consistent thickness control, clean-film processing, and effective anti-static performance to protect components and assemblies from mechanical shock and electrostatic discharge. Typical solutions specify anti-static outer layers with controlled surface resistivity and medium-to-small bubble sizes to conform to component geometries while still providing cushion. Quality controls focus on particulate cleanliness, dimensional consistency, and layer adhesion tests to ensure long-term ESD protection and mechanical reliability. Packaging engineers often pair three-layer bubble film with conductive or static-dissipative foams for high-value shipments to achieve multi-tiered protection without complicating the packing workflow.
For agricultural packing, bubble film provides cushioning for fruit and cut produce, reducing bruising and post-harvest losses while enabling lighter secondary packaging that preserves cold-chain efficiency. Industrial uses include wrapping machined parts, protecting painted surfaces, and preventing chafing during transport of metal components; here the priority is puncture resistance and abrasion protection afforded by reinforced outer skins. In both domains, three-layer designs allow the inner layer to be optimized for cost or recycled content while outer layers deliver the necessary mechanical properties, creating an effective balance between sustainability goals and protection performance. Adopting in-house production for these films enables faster specification changes and better inventory control for high-volume packers.
Three layer bubble film machines are film extrusion equipment designed with multiple extruders, a multi-manifold co-extrusion die, precision bubble forming rollers, perforation and sealing stations, and a winding and slitting system to deliver finished rolls at target widths and bubble patterns. Core specification categories buyers evaluate include production capacity (kg/h), maximum film width, bubble diameter and pitch options, control systems (PLC, HMI), and available automation such as automatic core loading or roll change subsystems. Advanced lines also offer IoT-capable monitoring for process parameters and predictive maintenance alerts; these features reduce downtime and deliver consistent quality in high-speed bubble film production. Selecting the correct balance of automation, throughput and tooling flexibility determines final throughput, labour requirements, and life-cycle operating costs.
Understanding the complete system, from raw material feeding to the final winding, is crucial for appreciating the complexity and efficiency of modern industrial three-layer film extrusion lines.
Industrial Three-Layer Film Extrusion Systems
The industrial cast three-layer film extrusion line system with automatic raw material feeders are presented in supplementary files (Figures S1 and S2).
Overview of the cast polyolefin film extrusion technology for multi-layer packaging applications, D Matykiewicz, 2023
Below are typical automation and specification features found on modern three-layer lines:
This list illustrates how automation and well-chosen mechanical components increase output while reducing operator variability and scrap.
| Machine Component | Attribute | Typical Value / Range |
|---|---|---|
| Extruder capacity | Output per line | 150–400 kg/h (typical ranges) |
| Film width | Maximum usable width | 800–1600 mm (configurable) |
| Bubble size | Diameter / pitch | 10–25 mm / 15–50 mm (standard options) |
The table provides a quick comparison of key attributes to help technical buyers screen lines by throughput, film width and bubble geometry before requesting detailed datasheets or model specs.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa represents and distributes bubble film and blown film extrusion equipment as a local partner for buyers; their product positioning highlights simple operation, perfect performance, easy maintenance and timely after-sales service—attributes buyers often prioritize when evaluating automation and high-speed production equipment. For procurement teams comparing automatic bubble wrap machines and three-layer co-extrusion lines, these supplier qualities can shorten installation cycles and reduce early-life support costs.
Automation reduces manual interventions and standardizes film quality through recipe control, automated tension management and roll handling, which directly lowers labour costs and minimizes human error in long production runs. High-speed production increases throughput measured in meters per minute and kg/h, enabling reduced unit production cost when demand justifies the line capacity; the relationship between uptime, speed and yield determines realized cost per roll. Monitoring features and predictive maintenance alerts further reduce unplanned downtime by identifying wear or drift in processing variables before product becomes out-of-spec. Together, these improvements strengthen just-in-time supply capabilities for large packers and reduce safety stocks tied to externally sourced protective films.
Customization is driven by tooling—bubble forming rollers, perforation cylinders and die widths—allowing buyers to specify bubble diameter, pitch, and roll perforation patterns for sheets or rolls optimized to their packing processes. Standard bubble sizes cover a practical range for electronics, household goods and industrial parts, while bespoke tooling can produce specialized bubble geometries for unique cushioning profiles; lead time for custom tooling varies with complexity. Perforation patterns determine whether rolls separate into sheets easily or remain continuous for automated packing; sample configurations often include micro-perforations for produce or single-sheet perforation for retail-ready packaging. Early engagement with machine suppliers reduces lead time and ensures tooling and perforation choices align with downstream packing equipment and workflows.
Investing in a three layer bubble film line requires a structured procurement approach: assess production volumes and film specifications, match machine throughput and tooling options to those needs, evaluate total cost of ownership including energy and maintenance, and verify local installation and after-sales capability. A stepwise procurement process helps buyers prioritize CAPEX vs OPEX trade-offs and ensures machines are sized correctly for both current and forecasted demand. Important financial considerations include expected material savings from optimized films, labour reductions through automation, and the payback period calculated from damage-reduction and per-unit production cost improvements. Engaging a local distributor early clarifies installation schedules, operator training, spare parts logistics and service-level expectations.
Consider the following investment steps as a practical roadmap:
| Investment Item | Metric | Estimated Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Machine CAPEX | Purchase price | Primary upfront cost (varies by capacity) |
| Energy consumption | kW per hour | Ongoing operating expense affecting OPEX |
| Material savings | kg of film saved per month | Reduces variable costs and shortens payback |
| Downtime reduction | % uptime improvement | Increases productive output and revenue capture |
This ROI-style table helps buyers model payback scenarios by mapping investment items to measurable metrics and estimated impacts, making it easier to compare offers and justify capital allocation.
Major cost drivers include machine CAPEX, energy and material consumption, labour and the expected reduction in damage and returns once higher-performance film is in use; the balance between CAPEX and the unit cost reduction from producing optimized films in-house determines payback. To estimate ROI, calculate monthly production capacity multiplied by per-unit material savings plus reductions in damage-related costs, then compare cumulative savings to the machine purchase and installation costs; typical payback windows depend heavily on utilization rate and the value of protected goods. Also account for spare-part stocking, preventive maintenance schedules and potential efficiency gains from automation when modeling TCO. A rigorous, scenario-based approach reveals the sensitivity of payback timelines to throughput, scrap rates and energy pricing.
Local distributors typically provide installation and commissioning, operator training, spare parts provisioning and hotline support to minimize downtime and accelerate ramp-up to steady-state production. Expect installation to include on-site testing with factory-trained technicians, process recipe transfer, and hands-on operator sessions focused on changeover, preventive maintenance and troubleshooting. Spare parts planning should encompass wear items for extruders, rollers and sealing units, plus recommended SLA response times for critical components to reduce extended outages. For buyers in South Africa, a distributor that emphasizes timely after-sales service and straightforward maintenance ensures the technical benefits of three-layer bubble film machines translate into predictable production and a lower total cost of ownership; Plastic Bag Machine South Africa positions its sales and service in line with these expectations and can provide tailored quotes, installation planning and training arrangements on request.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.