Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
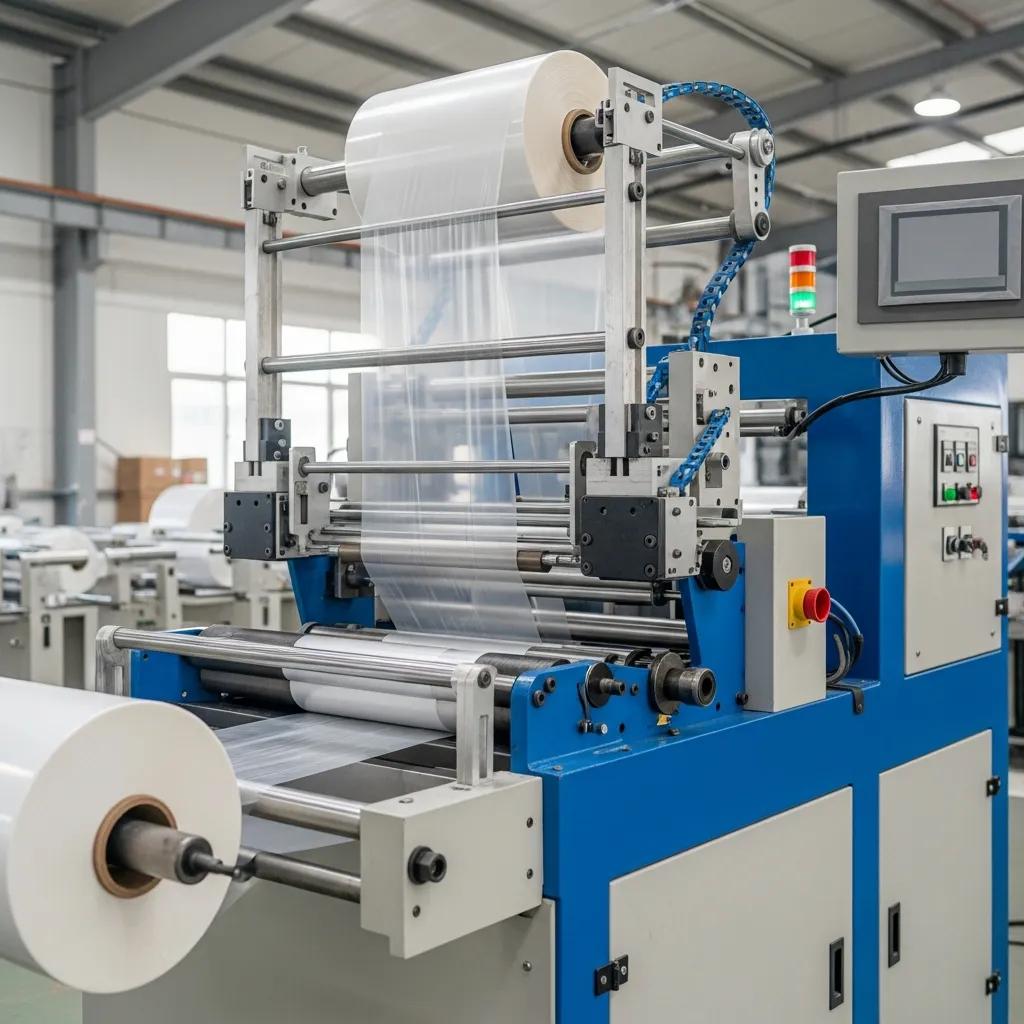

Durable bottom sealing plastic bag machines are specialized bag making systems that form, seal and cut bags from a continuous film web, producing strong bottom-seal bags suited for heavy-duty applications. These machines combine precise heat-sealing, robust mechanical construction, and automated control systems to deliver high throughput and repeatable seal integrity for LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE and similar films. For manufacturers targeting heavy-duty garbage bags, retail sacks or industrial liners, choosing the right bottom sealing machine determines final product strength, production uptime and cost per bag. This guide explains what bottom sealing machines are, how they work, which materials they handle, how to choose and customize equipment in South Africa, common troubleshooting steps, auxiliary devices that boost efficiency, and how these machines integrate into a full production line. Readers will find practical checklists, comparison tables and maintenance protocols designed to shorten commissioning time and reduce rejects while aligning sealing parameters to film properties and downstream handling requirements.
Durable bottom sealing plastic bag machines are bag-making machines that produce bags with a reinforced bottom seal, using a combination of controlled heat, pressure and cutting to create a load-bearing seam. This mechanism ensures bags carry heavier loads without seam failure and supports higher abrasion and puncture resistance in end-use. Key features that define durability include heavy-gauge sealing bars, reinforced frames, stable temperature control, and precise web handling to avoid misalignment during sealing. These features together deliver higher first-pass yield and consistent bag geometry for automated downstream packaging and winding systems.
The principal design elements that contribute to durability are mechanical robustness, sealing accuracy and automation:
Manufacturers also calibrate dwell time and pressure to film type and thickness, and incorporate control panels for repeatable recipes. Below is a brief credibility note: Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) manufactures bottom sealing machines and supports simple operation, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service and customization options, backed by final inspection and warranty terms. Understanding these core features leads naturally into the machine’s operational sequence and material compatibility.
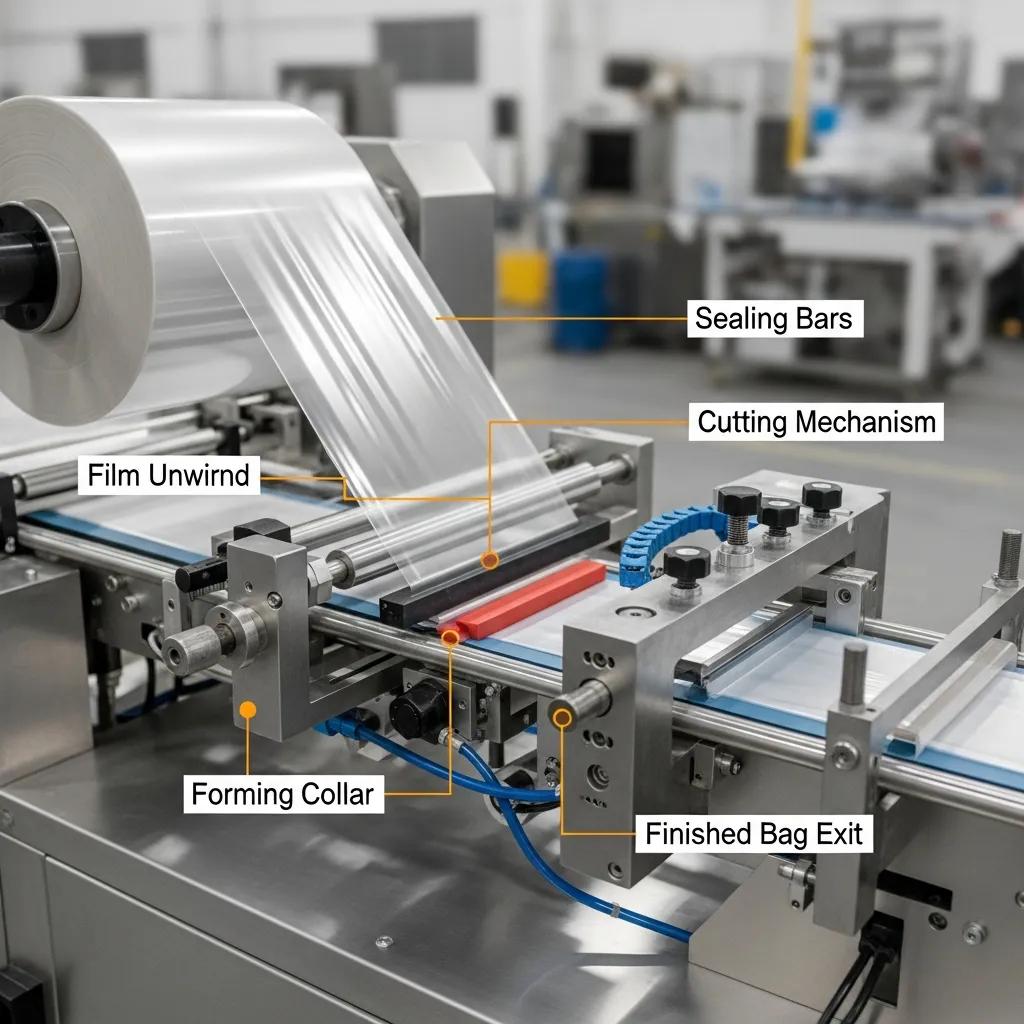
Bottom sealing machines operate by feeding a film web, registering it, creating a bottom seal, and cutting to length in a synchronized cycle that balances heat, pressure and timing. First, the film web is unwound, tensioned and aligned using rollers and edge guides to ensure consistent edge position for sealing. Next, the sealing bar (or bars) engages at controlled temperature and pressure for a precise dwell time to create a hermetic bottom seam; thermocouple feedback and PLC control keep the seal within target parameters. The cutting mechanism—either a flying knife for continuous motion or a timed cutter for intermittent motion—separates individual bags while preserving the integrity of the newly formed seam. Finally, finished bags are discharged to a stacker or rewind unit depending on downstream handling, with integrated sensors verifying seal quality and bag length.
This stepwise flow demands coordinated servo or pneumatic actuation with closed-loop control to prevent wrinkles, weak seals or mis-cuts that cause rejects. Proper machine setup and recipe storage on the control panel reduce changeover time and support repeatable production, which in turn improves overall line efficiency and lowers unit cost.
Bottom sealing machines are compatible with common thermoplastic films such as LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE and polypropylene films when thermal properties and thickness fall within the machine’s specification range. Typical thickness ranges for durable bags vary from thin retail films (~10–20 µm) up to heavy-duty garbage or industrial liners (>80–120 µm), and the sealing temperature and pressure must be matched to the polymer to avoid cold seals or burned seams. Material-specific adjustments include lowering temperature for LLDPE to avoid melt-through and increasing dwell time for thicker HDPE webs to ensure full fusion.
| Film Type | Typical Thickness Range | Typical Sealing Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| LDPE / LLDPE | 20–120 µm | 120–180°C |
| HDPE | 10–100 µm | 110–160°C |
| PP (monolayer) | 20–80 µm | 140–200°C |
This compatibility matrix helps operators set initial parameters, but fine-tuning through test seals and destructive peel tests yields final setpoints. Material handling tips—such as maintaining consistent web tension, avoiding dust contamination and conditioning rolls to humidity—further reduce sealing defects and align with the film supplier’s specifications.
Selecting the correct heavy duty bottom sealing machine requires mapping production targets, film properties, automation needs and local service capabilities to machine specifications. Begin by defining required production output (bags/min or kg/hr), film width and thickness, desired bag dimensions and any printing/handle features. Next, evaluate machine speed, web width capacity, film thickness range, power needs and automation level (manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic), as well as serviceability and spare parts availability. Considering ROI, balance upfront capital cost against expected throughput gains, reject reduction and labor savings.
The following decision checklist summarizes primary selection criteria:
Below is a comparative EAV table to help buyers match model specs to requirements.
| Model Class | Key Specification | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| High-speed bottom sealer | Speed | Up to 60 bags/min (model dependent) |
| Heavy-duty sealer | Web width | 600–1600 mm range |
| Versatile automatic sealer | Film thickness range | 10–120 µm |
This comparison clarifies trade-offs between speed, width and material flexibility; customers with on-site extrusion should align film output rates to sealer throughput to avoid bottlenecks. After evaluating technical fit, consider local after-sales presence and lead times: Plastic Bag Machine South Africa highlights customization, local sales presence in major cities and competitive pricing with sample delivery within 3 days and bulk lead times of 15–25 days, which can shorten commissioning timelines for South African manufacturers. If you want a tailored quote or demo, request machine specifications and customization options that map directly to your production scenario to validate ROI and delivery timing.
Automatic bottom seal bag machines deliver measurable benefits in throughput, consistency, safety and labor efficiency compared with manual or semi-automatic systems. Automation replaces manual timing and operator intervention with programmed recipes, resulting in more consistent seal quality, fewer human-induced errors and higher overall OEE (overall equipment effectiveness). Operators benefit from reduced repetitive tasks, while management sees lower rejection rates and more predictable production costs. Automated machines also enable advanced features such as flying knife cut, servo-driven web handling and electronic registration for printed films, which together support higher-speed operation without compromising bag integrity.
These benefits translate directly into ROI: increased output per shift and reduced material waste improve unit economics and support competitive pricing for end customers in busy markets.
Customization tailors machine features—such as extended sealing bar length, flying knife integration, spine seal options or advanced PLC packages—to specific bag formats and use-cases, improving performance and reducing rework. For example, flying knife systems enable continuous high-speed cutting for long bags, while spine or gusset configurations improve load distribution for heavy waste bags. Custom PLC recipes and HMI layouts speed changeovers and help operators maintain optimal setpoints when switching materials or sizes. Although customization increases lead times and cost, the resulting reduction in rejects and faster changeovers often justifies the investment for high-mix or specialized product lines.
These tailored changes should be specified early in procurement so engineering teams can validate mechanical interfaces and electrical requirements before fabrication.
Bottom seal bag machines most commonly encounter sealing failures, cutting defects and web alignment issues; diagnosing these quickly prevents extended downtime and scrap accumulation. A structured troubleshooting approach begins with a diagnostic checklist covering temperature setpoint accuracy, seal pressure/dwell consistency, blade sharpness and web tension. Systematic checks—starting with the simplest variables (settings and consumables) and progressing to sensors and drive components—resolve most issues within a single shift. Preventive maintenance such as scheduled seal bar inspection, blade replacement cycles and control system backups reduces the frequency of these problems over time.
The following numbered checklist provides a practical diagnostic order:
A recommended preventive maintenance schedule includes daily visual checks, weekly blade and guide inspection, and monthly control-system backups. Keeping spare consumables—seal bar covers, blades, thermocouples—on-site reduces mean time to repair and maintains throughput targets. Addressing root causes rather than symptoms helps sustain first-pass yield and aligns with quality control checkpoints upstream and downstream.
Sealing problems usually stem from temperature mismatch, uneven pressure or contamination on sealing surfaces; resolving them requires methodical parameter checks and surface maintenance. First, confirm the controller’s setpoint and the thermocouple reading match and recalibrate if necessary, since an uncalibrated sensor can hide over- or under-heating. Next, inspect seal bar faces for polymer buildup or damage—cleaning and replacing covers restores uniform contact and heat transfer. Finally, adjust pressure and dwell time incrementally while performing peel tests until the seal exhibits acceptable strength without film thinning or burn-through.
Following these steps resolves most incomplete seals and prevents the need to cycle through more invasive mechanical checks, leading directly to cutter and alignment diagnostics when sealing is consistently correct.
Cutting defects typically result from dull blades, misalignment or incorrect cutter timing relative to web feed; addressing these requires blade inspection, timing checks and safe replacement procedures. Start by inspecting blade edges for nicks or dullness and replace blades on a scheduled interval based on runtime and processed material. Verify cutter alignment with the seal line and adjust mounting brackets or guide plates to ensure a clean shear. Check the drive timing or encoder feedback between web feed and cutter actuation to eliminate off-length cuts or jagged edges.
Always follow lockout-tagout procedures during blade maintenance to protect technicians; consistent blade care minimizes rejects and preserves bag edge integrity for downstream punches or handles.
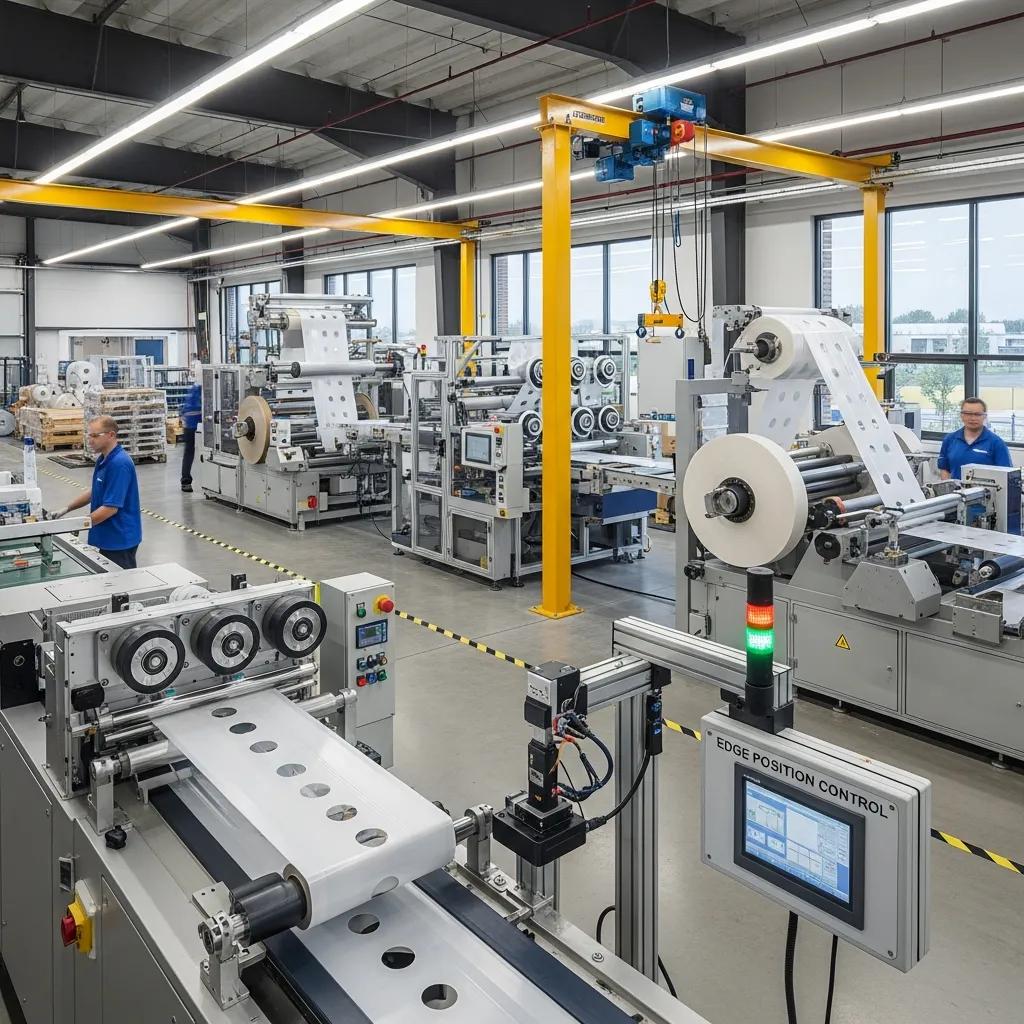

Auxiliary devices such as edge position control (EPC), puncher units and rewind/palletizing systems significantly enhance yield and downstream handling, reducing waste and manual labor. EPC systems actively track web edges or printed registration marks and adjust lateral position to maintain accurate seals and print alignment; this is essential when running printed films or narrow tolerances. Puncher devices apply handles, vents or hanging holes while rewind units form finished rolls or stacks ready for packing, each improving packaging throughput and consistency. Retrofit compatibility should be assessed when adding devices to older machines to ensure mechanical and electrical integration is feasible.
Below is a comparison table summarizing common auxiliary devices, their functions and compatibility considerations.
| Device | Function | Compatibility / Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Edge Position Control (EPC) | Maintains lateral web alignment | Reduces waste on printed webs; sensor-based feedback |
| Puncher (handles/vents) | Creates handles, vents or hanging holes | Adds functionality for retail/garbage bags |
| Rewind / Winder | Forms rolls or stacks finished bags | Simplifies downstream packaging; supports various core sizes |
These auxiliary options reduce manual rework and enable finished formats that meet retail or industrial specifications, and they should be selected based on product mix and end-use handling.
Edge Position Control (EPC) systems actively monitor web position with optical or ultrasonic sensors and command lateral actuators to correct drift, ensuring seals and printed registration remain accurate. EPC is critical for printed or multi-lane webs where even small lateral deviations create misregistration and scrap; the system reduces off-spec production and conserves expensive printed materials. Tuning EPC requires setting appropriate sensor thresholds, feedback loop gains and actuator travel limits to match film stretch characteristics and machine speed. Properly configured, EPC reduces waste, improves print-to-seal registration and supports higher-speed runs without operator intervention.
Puncher devices add bag features—such as handles, vents or hanging holes—during the bag-forming cycle, enabling finished products that match retail or waste-handling requirements and increasing product value. Different puncher designs handle single or multiple punch types and must be synchronized with the cutter to place features precisely. Rewind units take finished bags and form them into rolls or stacks using controlled tension and core handling, which eases packaging and shipping logistics. Selecting puncher and rewind equipment involves matching type and capacity to production rates and ensuring electrical and mechanical interfaces align with the sealer’s control system.
These auxiliary devices streamline packaging flows, reduce manual sorting and enable ready-to-ship roll formats that save floor space and labor.
A heavy duty plastic bag production line integrates blown film extrusion upstream, optional flexo printing, bottom sealing and winding/recycling downstream to balance throughput and material quality across the entire process. The blown film extruder supplies a consistent web with defined width, thickness and melt characteristics; any variability here affects sealing setpoints and final bag strength. Flexo printing, if present, must be carefully registered to the sealer using EPC systems to avoid misprints and to ensure ink drying or curing does not contaminate seal zones. Downstream, rewinders, stackers and recycling units handle finished goods and trim; throughput matching between components avoids bottlenecks and ensures continuous operation.
| Process Stage | Integration Point | Key Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Blown film extrusion | Film width/thickness consistency | Throughput and film tensile properties |
| Flexo printing | Print registration & drying | Ink compatibility with seal area |
| Bottom sealing | Seal temperature & cut timing | Matches film and downstream speed |
Balancing these stages involves specifying extruder output rates to match the sealer’s rated capacity and coordinating PLC recipes across machines to maintain consistent bag length and seal quality. Quality control checkpoints—such as inline seal testers and optical inspection—catch deviations early and feed back to extrusion or printing parameters to stabilize output.
Blown film extrusion produces the base film whose physical properties—gauge uniformity, melt index and additive package—determine the bag’s strength and sealability; choosing appropriate resin blends and co-extrusion layers enhances puncture resistance and tensile strength. Extrusion parameters, including die gap, haul-off speed and cooling, control gauge profile and molecular orientation that influence tear resistance. For durable bags, co-extrusion with reinforcing layers or additives can increase impact resistance without excessive thickness. Throughput matching between the extruder and sealer is critical to avoid film backlog or starvation on the bag-making line.
Flexo printing adds branding and regulatory information to films but introduces registration and ink-compatibility challenges that affect sealing if not managed. Accurate registration requires precise web tracking and EPC, and inks must be chosen to dry or cure without leaving residues in the seal area. Printing speed affects sealer timing and may require buffer unwind/rewind to decouple speeds between printing and bag forming. Ensuring inks, coatings and antistat treatments do not impair heat transfer or adhesion at the seal zone prevents rejects and maintains production flow.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa (operating as Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd.) positions itself as a one-stop manufacturer and supplier of plastic bag production equipment in South Africa, offering a range that includes blown film extrusion, plastic bag making machines, flexo printing machines, plastic recycling machines and bottom sealing machines. The company emphasizes simple operation, perfect performance and easy maintenance as core product attributes, and it supports customers with timely after-sales service and one-stop customization including logo, labeling and packaging options. Quality controls include 100% final inspection and defective rate control between 1–3%, while a two-year warranty on timer switches and an in-house R&D and engineering team provide technical assurance for tailored solutions.
The company also highlights production and delivery advantages: multiple production lines for timer switches (16 lines), claims of competitive pricing, fast sample delivery within three days and bulk order lead times of 15–25 days, plus sales presence across major South African cities such as Gqeberha, Soweto, Cape Town and Johannesburg. These attributes aim to reduce lead times and simplify procurement, especially for manufacturers requiring customization or rapid ramp-up.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa’s validated UVPs focus on operational simplicity, maintainability and quality assurance: final inspection across all machines, defective rate control (1–3%) and a specific two-year warranty on timer switches. Their R&D and engineering team supports customization and new product development while offering one-stop services that cover logo, labeling and packaging integration. After-sales workflows emphasize timely service and spare parts availability, designed to shorten downtime and keep production lines running.
Competitive pricing and faster delivery reduce total acquisition and operational costs by lowering inventory needs, accelerating production ramp-up and shortening time to market for new bag SKUs. Rapid sample delivery (within three days) enables faster validation and pre-production testing, while bulk lead times of 15–25 days shorten procurement cycles compared to long import lead times. For manufacturers, these timelines and pricing claims help improve cash flow, accelerate order fulfillment and reduce the risk associated with extended downtime during equipment changeovers.
These advantages make a pragmatic case for sourcing integrated equipment with local customization and service capability to support heavy-duty bag production in South Africa.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on being a leading manufacturer of plastic bag making machines. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that our customers receive the best machinery tailored to their specific production needs. By choosing us, you are partnering with a company that has established itself as a trusted name in the industry.
Our extensive range of plastic bag machinery includes options for various applications, from shopping bags to biodegradable solutions. We understand the importance of efficiency and reliability in production, which is why our machines are designed for optimal performance, ensuring your business can meet market demands effectively.
Our plastic bag machines are engineered to provide numerous advantages, including ease of operation, low maintenance costs, and high productivity rates. These features make them ideal for businesses looking to enhance their manufacturing processes while keeping operational costs low.
Additionally, our machines are equipped with advanced technology that ensures consistent quality in production. With energy-efficient designs and robust construction, our equipment not only meets but exceeds industry standards, providing you with a competitive edge in the market.
We have had the pleasure of serving over 1000 satisfied customers across various regions, each with unique needs and challenges. Our commitment to customer satisfaction is reflected in the positive feedback we receive, showcasing the effectiveness of our machines in real-world applications.
From small start-ups to large manufacturing plants, our clients have successfully integrated our machinery into their operations, leading to increased productivity and profitability. These success stories underscore our dedication to providing tailored solutions that foster growth and innovation.
As a forward-thinking manufacturer, we continuously invest in research and development to bring the latest innovations to our plastic bag machines. This commitment allows us to offer cutting-edge technology that enhances production efficiency and reduces waste.
Our innovations include features such as automated controls, real-time monitoring systems, and environmentally friendly production processes. By adopting these advancements, our clients can not only improve their operational efficiency but also align with global sustainability goals.