Plastic Bag Making Machines for Sale in Pretoria
Plastic Bag Making M
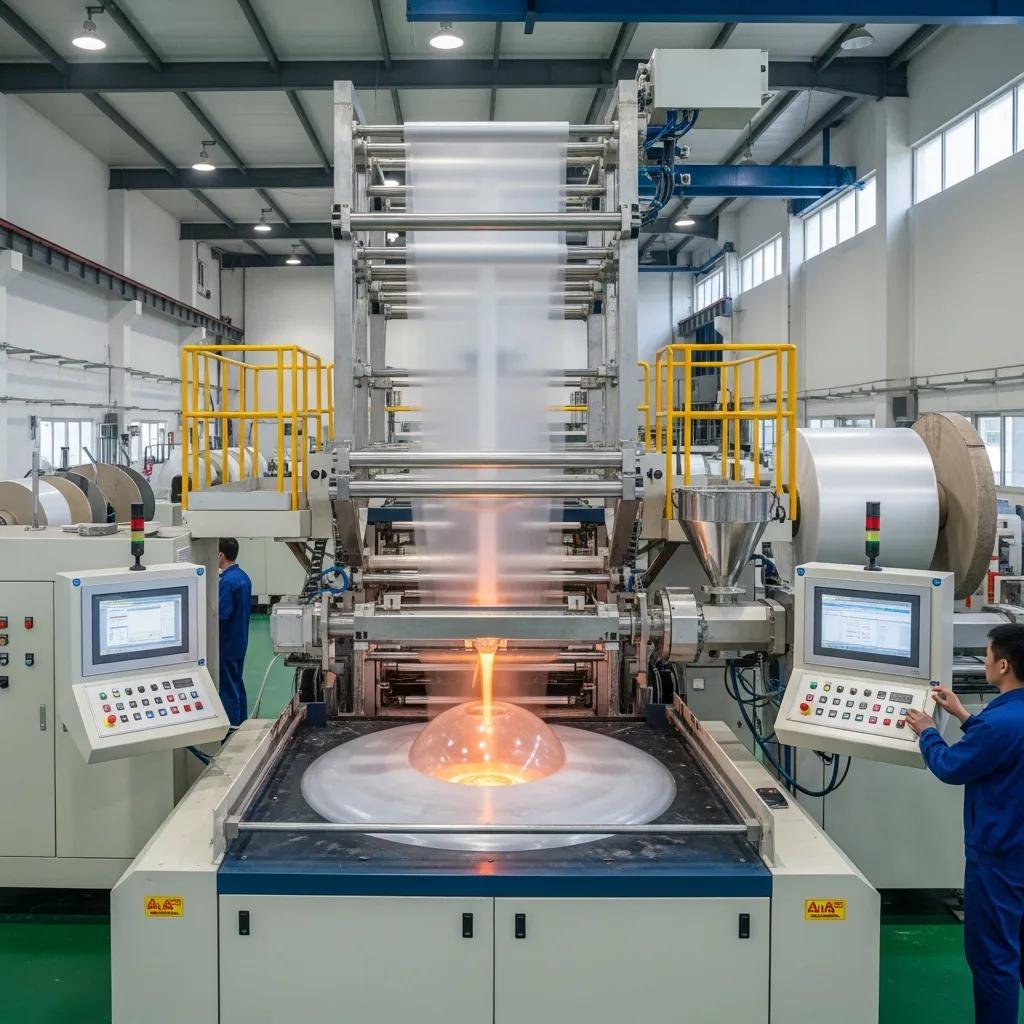

Blown film extrusion converts molten polymer into continuous tubular film by extruding through an annular die and inflating a stabilized bubble, producing flexible plastic film used across packaging and bag-making applications. This guide explains the types of blown film extrusion machines available in Pretoria and Gauteng, how the extrusion process works, what to expect on pricing and total cost of ownership, and where to source reliable suppliers with local support. Many manufacturing teams struggle to match machine capability to product requirements—gauge control, layer structure, and material compatibility directly affect yield and downstream processing. This article helps procurement and operations managers select the right machine class, compare monolayer versus multi-layer systems, and evaluate key features such as rotary die heads, automation, and energy efficiency. You will find clear comparisons of machine types, component breakdowns, price-range guidance, supplier evaluation checklists, and service expectations for installations in Pretoria and surrounding regions. Throughout, keywords like blown film extrusion Pretoria, plastic film blowing machine Gauteng, and monolayer blown film extruder are used to aid discovery and to align technical selection with local supplier capabilities.
Blown film extrusion machines in Pretoria range from basic monolayer extruders to sophisticated multi-layer co-extrusion lines designed for barrier and value-add films, with polymer-specific machines optimized for HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE, and PP. Monolayer machines offer simplicity and lower capital cost, while multi-layer co-extrusion plants (ABA, ABC configurations) combine different resins to deliver barrier, strength, or sealability advantages; choosing between them depends on product requirements for barrier, clarity, and mechanical performance. Specialized machines for HDPE, LDPE, and PP modify screw geometry, die design, and cooling to match processing windows and recycled-content handling, which affects throughput and film uniformity. The right selection balances production capacity, desired film properties, and downstream processes like printing and bag making. Below is a compact comparison table to help shortlist options based on typical production metrics and common applications.
This table compares core machine classes across capacity and application to simplify initial screening.
| Machine Class | Typical Production Capacity | Typical Film Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Monolayer Blown Film Extruder | 50–400 kg/hr | Basic shopping bags, garbage bags, liners |
| Multi-layer Co-extrusion Plant (3–7 layers) | 100–800 kg/hr | Barrier films, printed packaging, high-strength bags |
| Polymer-specific (HDPE/LDPE/PP) Line | 50–600 kg/hr | HDPE sacks, LDPE cling/packaging, PP heavy-gauge film |
This comparison helps buyers map product needs to machine capability; the next sections explore practical trade-offs between monolayer and multi-layer approaches and polymer-specific machine features.
A monolayer blown film extruder melts a single resin and forms film in one continuous process, providing cost-effective production for simple bag and film grades where barrier properties are not critical. Multi-layer extruders combine two or more polymers through co-extrusion to create films with tailored barrier, seal, and mechanical properties while often reducing material usage by placing functional layers strategically. Monolayer systems are easier to operate and maintain, lowering spare-parts complexity, whereas multi-layer systems deliver performance gains—like oxygen or moisture barriers—that can replace downstream lamination or coating steps. When selecting, consider production volumes, required film performance, and whether you need barrier or printable surfaces; these needs determine whether the additional capital and control complexity of co-extrusion is justified. Understanding this trade-off sets up the next topic: polymer-specific considerations that affect screw design and die configuration.
Machines tuned for HDPE, LDPE, and PP address each polymer’s melt strength, shear sensitivity, and cooling behavior by adjusting screw profiles, L/D ratio, die gap, and nip roll arrangements to achieve consistent gauge and mechanical properties. HDPE lines emphasize shear and cooling control for high-strength sacks; LDPE/LLDPE setups target clarity and sealability for retail and shrink films; PP extruders are configured for heavier-gauge industrial films where stiffness and heat resistance matter. Recycled polymer compatibility is rising in importance—machines with robust feeding, melting zones, and degassing options support pellet variability and additives. Selecting polymer-specific features improves yield and reduces scrap, which in turn impacts operating costs and downstream conversion quality. The following section explains the process mechanics and machine components that determine these outcomes.
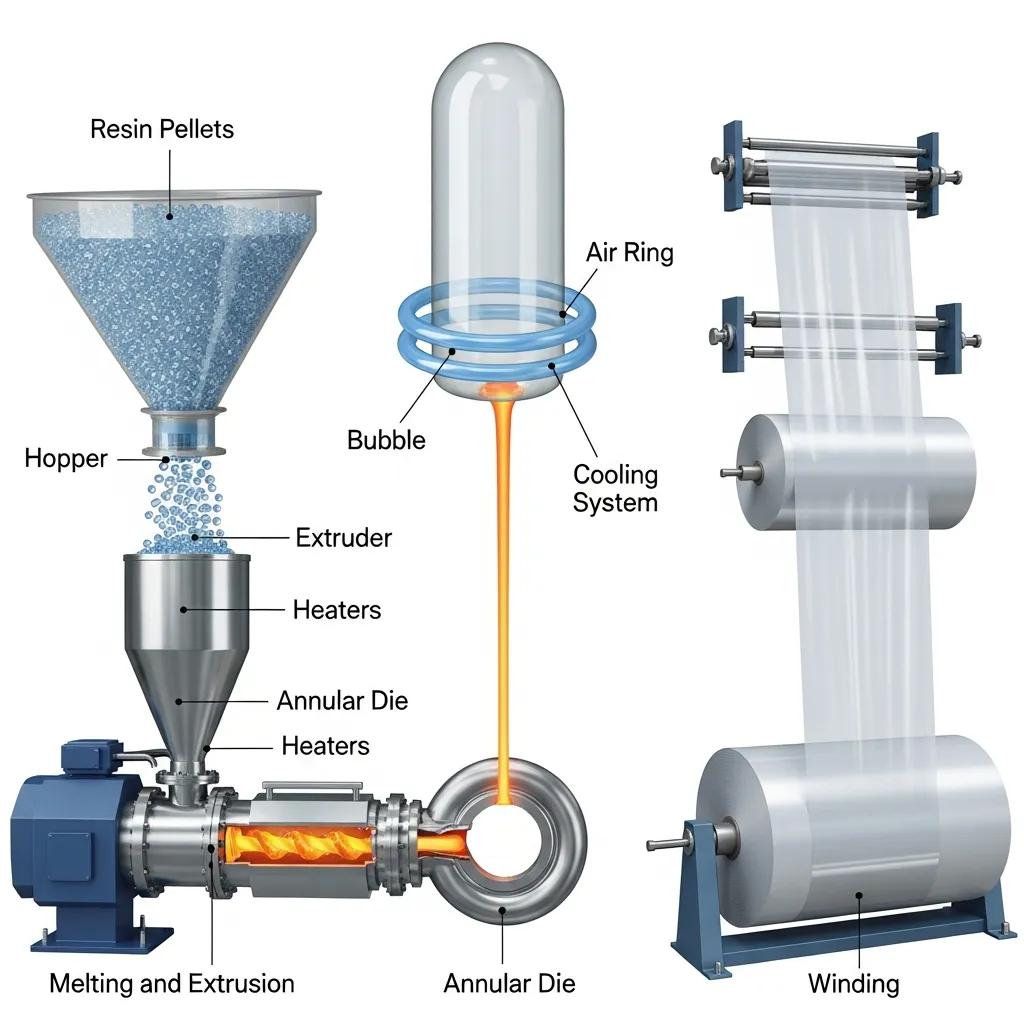
Blown film extrusion transforms resin pellets into film through four core stages: melting and homogenization in the extruder, extrusion through an annular die, bubble formation and controlled cooling, and collapsing/winding of the finished tube. Temperature control and screw design drive melt quality, while die geometry and air ring cooling determine film gauge and optical properties; precise control of bubble stability yields consistent thickness and strength. Key control points include melt pressure, frost line height, cooling air profile, and haul-off speed, all of which must be monitored to reduce gauge variability and defect rates. Understanding these process steps clarifies why certain machine features—such as a high-precision rotary die or advanced PLC control—directly improve film quality and throughput.
To clarify how individual machine parts contribute to quality and throughput, the table below breaks down major components and their functional impact on film output.
| Component | Function | Impact on Quality/Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| Extruder Screw & Barrel | Melts and pumps polymer | Controls melt homogeneity and throughput stability |
| Rotary/Annular Die | Shapes melt into tubular film | Affects bubble uniformity and gauge control |
| Air Ring / Cooling System | Cools bubble and sets film | Influences clarity, mechanical properties, and frost line |
| Haul-off & Winder | Collapses bubble and winds film | Determines layflat tension and roll quality |
| PLC / Control Panel | Automates setpoints and alarms | Reduces operator variance and improves repeatability |
This component breakdown leads naturally to operational steps and practical process tips that help operators maintain stable production and troubleshoot common issues.
The process begins with resin drying and feeding, followed by melt plastification in the extruder where the screw design sets shear and residence time to ensure homogenous melt. Melted polymer is forced through an annular die, inflated to form a bubble controlled by internal/external air and stabilized by an air ring; maintaining a stable frost line height and uniform cooling preserves gauge consistency. The bubble is collapsed by nip rollers and guided to the haul-off, which sets the final film thickness before winding onto shafts; tension control is critical to avoid telescoping or wrinkles. Operators should monitor melt pressure, die temperature profile, air ring performance, and downstream tension to reduce scrap; regular checks of filter screens and die lip condition also prevent quality issues. Mastering these steps reduces variability and supports higher first-pass yields, which saves materials and production time.
Rotary die heads enable continuous rotation of the die lip relative to the film, producing more uniform film and allowing inline adapters for multi-head production; this improves thickness uniformity and reduces oscillation marks. Auto loaders and advanced feeding systems maintain consistent pellet flow and minimize air entrainment, which protects extrusion stability when handling recycled or blended resins. Modern PLC-driven automation with recipe management, closed-loop gauge control, and remote monitoring reduces reliance on operator adjustments and shortens changeover times between product runs. Energy-efficient drives, servo haul-offs, and variable-frequency pumps further lower operating costs while improving ramp-up speed. Recognizing these features helps buyers prioritize options that deliver measurable ROI through reduced scrap, faster changeovers, and higher uptime.

Local sourcing in Pretoria and greater Gauteng should prioritize suppliers that provide end-to-end support: pre-sales technical matching, pre-delivery inspection, installation and commissioning, operator training, and timely spare parts. Evaluate suppliers based on warranty terms, inspection practices, local service capability, and lead times for spare parts and repairs to ensure production continuity. Ask suppliers for clear documentation on testing, factory acceptance procedures, and proven installations in similar applications to validate claims. The following checklist outlines the primary questions and evaluation criteria buyers should use when shortlisting suppliers for blown film extrusion equipment.
This checklist helps buyers focus supplier conversations on operational risk and supportability, which leads into a concrete example of local provider capabilities.
Plastic Bag Machine South Africa acts as the South African arm for Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., offering primary product lines that include blown film extrusion machines, plastic bag making machines, flexo printing machines, and plastic recycling machines. The company emphasizes several buyer-facing value propositions: competitive pricing, 100% final inspection, a two-year warranty, strong R&D and one-stop customized solutions, combined with high production capacity, fast delivery, and timely after-sales support. For Pretoria and Gauteng manufacturers, these service elements reduce procurement friction by aligning factory testing and warranty coverage with local installation and training needs. Prospective buyers should request demonstrations of factory inspection records and explicit warranty scope to ensure the supplier’s promises translate into on-site reliability.
This local presence overview highlights the kind of support buyers should confirm before awarding a purchase order and leads into tips for comparing suppliers across contractual terms.
When comparing suppliers, structure evaluations around transparent pricing, warranty scope, lead times, spare parts strategy, and installation support to avoid hidden costs post-delivery. Ask for a breakdown that separates machine base price, automation options, rotary die inclusion, packaging, and estimated installation charges so you can compare apples-to-apples. Insist on written service-level agreements (SLAs) that define response times for on-site support, spare-part shipping expectations, and training scope to protect production ramp-up. Use the following short checklist to compare suppliers objectively during procurement.
This comparison checklist equips buyers to negotiate meaningful contract terms and prepares them for the next major decision area: pricing and total cost evaluation.
Typical prices for blown film extrusion machines in South Africa vary by specification, automation, co-extrusion layers, and included peripherals; new entry-level monolayer lines start at lower capital levels, while fully equipped multi-layer, high-automation plants with rotary dies and advanced PLC control sit at the higher end. Used machines can offer cost savings but require careful inspection and allowance for refurbishment and re-commissioning costs; availability of used equipment in South Africa fluctuates with market cycles. Key cost drivers that materially change the purchase price include number of extruders/co-extrusion layers, inclusion of rotary die heads, level of automation and control systems, energy-efficient components, and whether installation, training, and spare parts are bundled. Below is a pricing table that summarizes approximate ranges and the attributes that typically impact movement between price tiers.
This table outlines price tiers with the features that typically govern each range.
| Machine Tier | Approximate Price Range (New) | Typical Features Included |
|---|---|---|
| Entry / Monolayer | ZAR 500,000 – 1,200,000 | Single extruder, basic PLC, manual feeding |
| Mid-spec / Multi-layer | ZAR 1,200,000 – 3,000,000 | 3-layer co-extrusion, improved PLC, auto loader |
| High-spec / Fully Automated | ZAR 3,000,000+ | 5+ layers, rotary die, advanced automation, energy-efficient drives |
This pricing overview clarifies how configuration choices affect upfront capital; the next subsection examines cost influencers and TCO.
New entry-level monolayer lines are best for low-complexity bag and film production and are priced lower because of simpler mechanics and limited automation, while mid-spec multi-layer lines add co-extruders and better control systems that justify higher investment for barrier films. High-spec lines include rotary die heads, advanced closed-loop gauge control, and higher-capacity extruders suited to large-volume production and value-added films, placing them in the top price tier. Used machines can reduce capital outlay but buyers must budget for refurbishment, spares, and potentially longer commissioning times; insist on factory inspection records and documented test runs to assess condition. Understanding these ranges helps procurement teams balance immediate capital constraints with expected savings from reduced scrap and higher throughput over time.
Cost drivers include co-extrusion complexity (more layers raise die and extruder cost), automation level (recipe management, servo drives, PLC), inclusion of a rotary die head, and energy efficiency features that lower operating expense over the machine life. Material handling features—such as robust feeding, degassing, and recycling pellet compatibility—add cost but improve uptime and reduce scrap when processing recycled content. Installation scope, training, and spare-parts strategy also influence total landed cost; including these in the purchase contract mitigates later surprises. Prioritize features that deliver measurable ROI—like closed-loop gauge control and reliable spare parts—rather than selecting options purely on headline price, because lower scrap and higher uptime typically offset higher capital expense within months to years.
Blown film extruders are the cornerstone of converting polymer pellets into films that become shopping bags, refuse sacks, industrial packaging, agricultural films, and printed retail film; downstream equipment such as flexo printers and bag-making machines convert film into final products. Typical production lines sequence blown film extrusion, film cooling and winding, optional flexo printing, and then bag making which may include slitting, gusseting, and sealing; specifying compatible line speeds and layflat widths is essential for integrated performance. Quality control for finished film targets gauge uniformity, tensile properties, seal strength, and print registration; these parameters define acceptability for end customers and recyclers. Below is a succinct description of production workflows and key control points to maintain consistent bag and film quality.
This process-to-product mapping shows how upstream film choices affect downstream conversion and product performance.
To produce bags, the blown film line must deliver consistent layflat and thickness that match the bag making machine’s web width and sealing requirements; uneven gauge causes weak seals and rejects. Printing integration requires stable web tracking and registration, so lines intended for printed film should include tension control and register-friendly winders. Typical downstream pairings combine blown film extruders with flexo printing stations and either flat-bed or continuous bag making systems depending on bag design and throughput. Operators should coordinate extrusion speed, winding tension, and printing registration to minimize makeready time and waste. Ensuring these integrations before purchase reduces conversion headaches and improves first-pass yield for finished bags.
Industrial and agricultural films often demand heavier gauge, wider layflat widths, and performance additives such as UV stabilizers, anti-fog agents, or reinforcement layers; blown film lines for these applications require higher-capacity extruders and robust cooling systems to control thicker films. Typical thickness ranges and additive requirements vary by use case: greenhouse and silage films prioritize UV resistance and clarity, while pallet wrap and heavy-duty packaging need higher tensile strength and puncture resistance. Producing these films may call for multi-layer constructions where functional inner or outer layers provide specific properties without compromising overall strength. Selecting the right machine configuration for such applications ensures long-term production reliability and product performance in the field.
Buyers should expect a full lifecycle service offering: pre-delivery inspection, site preparation guidance, supervised installation and commissioning, operator training, routine maintenance schedules, spare-part supply, and timely remote or on-site technical support. Well-documented installation and commissioning procedures reduce ramp-up time and ensure the line meets factory acceptance criteria; training packages tailored to operator skill levels improve uptime and reduce scrap. Maintenance contracts can include preventive schedules, emergency response SLA terms, and stocked critical spares to minimize downtime risk. The checklist below outlines what an effective installation and after-sales program typically includes so buyers can negotiate these into purchase agreements.
These service elements protect production continuity and lead into how local suppliers demonstrate outcomes and case studies.
Good installation includes detailed site preparation checklists, supervised commissioning runs, operator and maintenance training, and documented performance tests that confirm production rates and quality metrics. Effective maintenance programs specify preventive intervals, spare-part lead times, and on-site versus remote support options tailored to production criticality. Buyers should request written SLAs for response times and spare-part dispatch for Gauteng to reduce downtime risk. For suppliers that act as local representatives of larger manufacturers, confirm how warranty claims and technical escalation are handled across international supply chains.
If available, concise case summaries detailing installation outcomes—such as improvements in throughput, reduced scrap, or successful integration with printing and bag-making lines—provide valuable validation during procurement. Where case studies are not public, request anonymized installation summaries or references that document performance before and after equipment upgrades. Access to local case evidence helps buyers verify supplier claims about uptime, delivery, and after-sales responsiveness.
This final operational perspective naturally leads into a procurement call to action for buyers seeking quotes and technical matching.
For tailored quotations, specification assistance, and to discuss machine options for Pretoria production needs, contact Plastic Bag Machine South Africa to request a detailed quote and to review factory inspection and warranty documentation; their offering integrates local support with manufacturer-backed testing to streamline procurement and commissioning.
Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:008613088651008.
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on being a leading manufacturer of plastic bag making machines. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that our customers receive the best machinery tailored to their specific production needs. By choosing us, you are partnering with a company that has established itself as a trusted name in the industry.
Our extensive range of plastic bag machinery includes options for various applications, from shopping bags to biodegradable solutions. We understand the importance of efficiency and reliability in production, which is why our machines are designed for optimal performance, ensuring your business can meet market demands effectively.
Our plastic bag machines are engineered to provide numerous advantages, including ease of operation, low maintenance costs, and high productivity rates. These features make them ideal for businesses looking to enhance their manufacturing processes while keeping operational costs low.
Additionally, our machines are equipped with advanced technology that ensures consistent quality in production. With energy-efficient designs and robust construction, our equipment not only meets but exceeds industry standards, providing you with a competitive edge in the market.
We have had the pleasure of serving over 1000 satisfied customers across various regions, each with unique needs and challenges. Our commitment to customer satisfaction is reflected in the positive feedback we receive, showcasing the effectiveness of our machines in real-world applications.
From small start-ups to large manufacturing plants, our clients have successfully integrated our machinery into their operations, leading to increased productivity and profitability. These success stories underscore our dedication to providing tailored solutions that foster growth and innovation.
As a forward-thinking manufacturer, we continuously invest in research and development to bring the latest innovations to our plastic bag machines. This commitment allows us to offer cutting-edge technology that enhances production efficiency and reduces waste.
Our innovations include features such as automated controls, real-time monitoring systems, and environmentally friendly production processes. By adopting these advancements, our clients can not only improve their operational efficiency but also align with global sustainability goals.